Abstract
Rationale
The endocannabinoid system plays an important role in conditioned drug seeking, but the neuronal mechanisms involved in this behavior are unclear.
Objectives
Here, we evaluate the role of endogenous cannabinoids in the cortico-limbic circuitry in cue-induced nicotine-seeking behavior in rats.
Methods
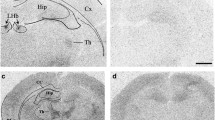
Animals were first trained to self-administer nicotine (0.03 mg/kg/injection, IV) under conditions in which responding was reinforced jointly by response-contingent nicotine injections and audiovisual stimuli. During subsequent sessions, nicotine was withdrawn and responding was reinforced by contingent presentation of the stimuli only. One month after nicotine removal, the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, rimonabant, was injected bilaterally into the shell of the nucleus accumbens (ShNAcc, 0.3, 3, or 30 ng/0.5 μl), the basolateral amygdala (BLA, 30 ng/0.5 μl), or the prelimbic cortex (PLCx, 30 ng/0.5 μl).
Results
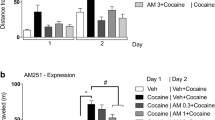
Rimonabant injected into the ShNAcc dose-dependently reduced nicotine-seeking behavior without modifying spontaneous locomotor activity. Similar results were obtained when the drug (30 ng) was injected into the BLA or the PLCx. The anatomical specificity was confirmed in a control experiment using [3H]rimonabant. Fifteen minutes after drug injection, when the behavioral effects of rimonabant were already achieved, radioactivity was detected at the site of injection and had not diffused to adjacent regions.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate that increased endocannabinoid transmission critically triggers conditioned nicotine-seeking behavior in key cortico-limbic regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot MH, Poncelet M, Soubrie P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 132:104–106
Azad SC, Monory K, Marsicano G, Cravatt BF, Lutz B, Zieglgansberger W, Rammes G (2004) Circuitry for associative plasticity in the amygdala involves endocannabinoid signaling. J Neurosci 24:9953–9961
Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL (1999) Down-regulation of cannabinoid receptor agonist-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma S binding in synaptic plasma membrane from chronic ethanol exposed mouse. Brain Res 815:89–97
Bossert JM, Gray SM, Lu L, Shaham Y (2006) Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2197–2209
Brody AL, Mandelkern MA, London ED, Childress AR, Lee GS, Bota RG, Ho ML, Saxena S, Baxter LR Jr, Madsen D, Jarvik ME (2002) Brain metabolic changes during cigarette craving. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:1162–1172
Chaperon F, Thiébot MH (1999) Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:243–281
Chaperon F, Soubrie P, Puech AJ, Thiebot MH (1998) Involvement of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors in the establishment of place conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:324–332
Childress AR, Mozley PD, McElgin W, Fitzgerald J, Reivich M, O’Brien CP (1999) Limbic activation during cue-induced cocaine craving. Am J Psychiatry 156:11–18
Ciccocioppo R, Sanna PP, Weiss F (2001) Cocaine-predictive stimulus induces drug-seeking behavior and neural activation in limbic brain regions after multiple months of abstinence: reversal by D1 antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1976–1981
Cippitelli A, Bilbao A, Hansson AC, del Arco I, Sommer W, Heilig M, Massi M, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Navarro M, Ciccocioppo R, de Fonseca FR; The European TARGALC Consortium (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonism reduces conditioned reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:2243–2251
Cohen C, Perrault G, Voltz C, Steinberg R, Soubrié P (2002) SR141716, a central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, blocks the motivational and dopamine-releasing effects of nicotine. Behav Pharmacol 13:451–463
Cohen C, Bergis OE, Galli F, Lochead AW, Jegham S, Biton B, Léonardon J, Avenet P, Sgard F, Besnard F, Graham D, Coste A, Oblin A, Curet O, Voltz C, Gardes A, Caille D, Perrault G, George P, Soubrié P, Scatton B (2003) SSR591813, (5aS,8S,10aR)-5a,6,9,10-tetrahydro,7H,11H-8,10a-methanopyrido[2′,3′:5,6]pyrano[2,3-d]azepine, a novel selective and partial α4β2 nicotinic receptor agonist with potential as an aid to smoking cessation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:407–420
Cohen C, Kodas E, Griebel G (2005a) CB1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:387–395
Cohen C, Perrault G, Griebel G, Soubrie P (2005b) Nicotine-associated cues maintain nicotine-seeking behavior in rats several weeks after nicotine withdrawal: reversal by the cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, rimonabant (SR141716). Neuropsychopharmacology 30:145–155
De Vries TJ, Schoffelmeer AN (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptors control conditioned drug seeking. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:420–426
De Vries TJ, Homberg JR, Binnekade R, Raaso H, Schoeffelmeer ANM (2003) Cannabinoid modulation of the reinforcing and motivational properties of heroin and heroin-associated cues in rats. Psychopharmacology 168:164–169
Economidou D, Mattioli L, Cifani C, Perfumi M, Massi M, Cuomo V, Trabace L, Ciccocioppo R (2006) Effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716A on ethanol self-administration and ethanol-seeking behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology 183:394–403
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci 8:1481–1489
Everitt BJ, Cardinal RN, Parkinson JA, Robbins TW (2003) Appetitive behavior: impact of amygdala-dependent mechanisms of emotional learning. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:233–250
Floresco SB, Yang CR, Phillips AG, Blaha CD (1998) Basolateral amygdala stimulation evokes glutamate receptor-dependent dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens of the anaesthetized rat. Eur J Neurosci 10:1241–1251
Forget B, Hamon M, Thiebot MH (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptors are involved in motivational effects of nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology 181:722–734
Fuchs RA, See RE (2002) Basolateral amygdala inactivation abolishes conditioned stimulus- and heroin-induced reinstatement of extinguished heroin-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 160:425–433
Fuchs RA, Feltenstein MW, See RE (2006) The role of the basolateral amygdala in stimulus-reward memory and extinction memory consolidation and in subsequent conditioned cued reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Eur J Neurosci 23:2809–2813
Gessa GL, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai MA, Colombo G (2005) Suppressing effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR147778, on alcohol intake and motivational properties of alcohol in alcohol-preferring sP rats. Alcohol Alcohol 40:46–53
Ghitza UE, Fabbricatore AT, Prokopenko V, Pawlak AP, West MO (2003) Persistent cue-evoked activity of accumbens neurons after prolonged abstinence from self-administered cocaine. J Neurosci 23:7239–7245
Gonzalez S, Cascio MG, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Fezza F, Di Marzo V, Ramos JA (2002) Changes in endocannabinoid contents in the brain of rats chronically exposed to nicotine, ethanol or cocaine. Brain Res 954:73–81
Grusser SM, Wrase J, Klein S, Hermann D, Smolka MN, Ruf M, Weber-Fahr W, Flor H, Mann K, Braus DF, Heinz A (2004) Cue-induced activation of the striatum and medial prefrontal cortex is associated with subsequent relapse in abstinent alcoholics. Psychopharmacology 175:296–302
Hansson AC, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Malinen H, Hyytia P, Sanchez-Vera I, Rimondini R, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Kunos G, Sommer WH, Heilig M (2006) Genetic impairment of frontocortical endocannabinoid degradation and high alcohol preference. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(1):117–126
Hayes RJ, Vorel SR, Spector J, Liu X, Gardner EL (2003) Electrical and chemical stimulation of the basolateral complex of the amygdala reinstates cocaine-seeking behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology 168:75–83
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1991) Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci 11:563–583
Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C (2003) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 84:698–704
Ito R, Dalley JW, Howes SR, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) Dissociation in conditioned dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in response to cocaine cues and during cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. J Neurosci 20:7489–7495
Jacobs EH, Spijker S, Verhoog CW, Kamprath K, de Vries TJ, Smit AB, Schoffelmeer AN (2002) Active heroin administration induces specific genomic responses in the nucleus accumbens shell. FASEB J 16:1961–1963
Kalivas PW, Volkow ND (2005) The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry 162:1403–1413
Katona I, Rancz EA, Acsady L, Ledent C, Mackie K, Hajos N, Freund TF (2001) Distribution of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the amygdala and their role in the control of GABAergic transmission. J Neurosci 21:9506–9518
Kruzich PJ, See RE (2001) Differential contributions of the basolateral and central amygdala in the acquisition and expression of conditioned relapse to cocaine-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 21:RC155
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR (2004) Rimonabant, a CB1 antagonist, blocks nicotine-conditioned place preferences. Neuroreport 15:2139–2143
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists as promising new medications for drug dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:875–883
Lecca D, Cacciapaglia F, Valentini V, Gronli J, Spiga S, Di Chiara G (2006) Preferential increase of extracellular dopamine in the rat nucleus accumbens shell as compared to that in the core during acquisition and maintenance of intravenous nicotine self-administration. Psychopharmacology 184:435–446
Lupica CR, Riegel AC (2005) Endocannabinoid release from midbrain dopamine neurons: a potential substrate for cannabinoid receptor antagonist treatment of addiction. Neuropharmacology 48:1105–1116
Mailleux P, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1992) Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult rat brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 48:655–668
Mato S, Robbe D, Puente N, Grandes P, Manzoni OJ (2005) Presynaptic homeostatic plasticity rescues long-term depression after chronic Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol exposure. J Neurosci 25:11619–11627
McGregor A, Baker G, Roberts DC (1996) Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex on intravenous cocaine self-administration under a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:5–9
McLaughlin J, See RE (2003) Selective inactivation of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and the basolateral amygdala attenuates conditioned–cued reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 168:57–65
Miller CA, Marshall JF (2005) Altered Fos expression in neural pathways underlying cue-elicited drug seeking in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 21:1385–1393
Muramoto K, Ono T, Nishijo H, Fukuda M (1993) Rat amygdaloid neuron responses during auditory discrimination. Neuroscience 52:621–636
Neisewander JL, Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Tran-Nguyen LT, Palmer A, Marshall JF (2000) Fos protein expression and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats after exposure to a cocaine self-administration environment. J Neurosci 20:798–805
Parkinson JA, Crofts HS, McGuigan M, Tomic DL, Everitt BJ, Roberts AC (2001) The role of the primate amygdala in conditioned reinforcement. J Neurosci 21:7770–7780
Paxinos G, Watson W (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, London
Perra S, Pillolla G, Melis M, Muntoni AL, Gessa GL, Pistis M (2005) Involvement of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the effects of alcohol in the mesolimbic reward circuit: electrophysiological evidence in vivo. Psychopharmacology 183:368–377
Phillips AG, Ahn S, Howland JG (2003a) Amygdalar control of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system: parallel pathways to motivated behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:543–554
Phillips PEM, Stuber GD, Heien MLAV, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2003b). Subsecond dopamine release promotes cocaine seeking. Nature 422:614–618
Piazza PV, Rouge-Pont F, Deminiere JM, Kharoubi M, Le Moal M, Simon H (1991) Dopaminergic activity is reduced in the prefrontal cortex and increased in the nucleus accumbens of rats predisposed to develop amphetamine self-administration. Brain Res 567:169–174
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Congy C, Martinez S, Oustric D, Perio A, Poncelet M, Maruani J, Arnone M, Finance O, Soubrie P, Le Fur G (2004) SR147778 [5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-ethyl-N-(1-piperidinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide], a new potent and selective antagonist of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor: biochemical and pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:905–914
Robbe D, Alonso G, Duchamp F, Bockaert J, Manzoni OJ (2001) Localization and mechanisms of action of cannabinoid receptors at the glutamatergic synapses of the mouse nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 21:109–116
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Schlicker E, Kathmann M (2001) Modulation of transmitter release via presynaptic cannabinoid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:565–572
Schroeder BE, Binzak JM, Kelley AE (2001) A common profile of prefrontal cortical activation following exposure to nicotine- or chocolate-associated contextual cues. Neuroscience 105:535–545
Sokolowski JD, Salamone JD (1994) Effects of dopamine depletions in the medial prefrontal cortex on DRL performance and motor activity in the rat. Brain Res 642:20–28
Thomas KL, Everitt BJ (2001) Limbic–cortical–ventral striatal activation during retrieval of a discrete cocaine-associated stimulus: a cellular imaging study with gamma protein kinase C expression. J Neurosci 21:2526–2535
Tzavara ET, Davis RJ, Perry KW, Li X, Salhoff C, Bymaster FP, Witkin JM, Nomikos GG (2003) The CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A selectively increases monoaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex: implications for therapeutic actions. Br J Pharmacol 138:544–553
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Logan J, Childress AR, Jayne M, Ma Y, Wong C (2006) Cocaine cues and dopamine in dorsal striatum: mechanism of craving in cocaine addiction. J Neurosci 26:6583–6588
Weiss F, Maldonado-Vlaar CS, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O (2000) Control of cocaine-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats: effects on recovery of extinguished operant-responding and extracellular dopamine levels in amygdala and nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4321–4326
Weissenborn R, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1997) Effects of medial prefrontal or anterior cingulate cortex lesions on responding for cocaine under fixed-ratio and second-order schedules of reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 134:242–257
Wong DF, Kuwabara H, Schretlen DJ, Bonson KR, Zhou Y, Nandi A, Brasic JR, Kimes AS, Maris MA, Kumar A, Contoreggi C, Links J, Ernst M, Rousset O, Zukin S, Grace AA, Lee JS, Rohde C, Jasinski DR, Gjedde A, London ED (2006) Increased occupancy of dopamine receptors in human striatum during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2716–2727
Zangen A, Solinas M, Ikemoto S, Goldberg SR, Wise RA (2006) Two brain sites for cannabinoid reward. J Neurosci 26:4901–4907
Zarrindast MR, Rezayof A, Sahraei H, Haeri-Rohani A, Rassouli Y (2003) Involvement of dopamine D1 receptors of the central amygdala on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference in rat. Brain Res 965:212–221
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Stéphanie Hamon for her technical assistance with self-administration and Carolle Voltz for measuring brain radioactivity.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodas, E., Cohen, C., Louis, C. et al. Cortico-limbic circuitry for conditioned nicotine-seeking behavior in rats involves endocannabinoid signaling. Psychopharmacology 194, 161–171 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0813-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0813-0