Abstract
Rationale
Females have been demonstrated repeatedly to be more sensitive to cocaine. The role of the frontal cortex (FCX) in mediating behavioral sensitization and the underlying signaling pathways are unclear.
Objective
The study was designed to characterize the role of FCX calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) activity in the behavioral supersensitization observed in female rats after prolonged cocaine exposure.
Materials and methods
Intact female rats that received cocaine for 9 days followed by 7 days of drug withdrawal constituted the model used for studying the mechanism of supersensitization.
Results
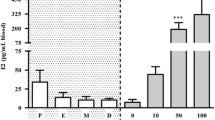
This cocaine withdrawal treatment resulted in behavioral supersensitization in intact female rats as indicated by an enhanced behavioral response to cocaine challenge assessed on day 16 (7-day withdrawal) and compared to the response on day 9 of cocaine treatment. This treatment regimen did not lead to supersensitization in male or in ovariectomized (OVX) rats. Administration of estrogen to OVX rats restored behavioral supersensitivity to repeated cocaine. FCX CaMKII activity was significantly altered by cocaine in females, and this effect was related to estrogen’s presence; cocaine-induced changes in striatal CaMKII activity were, however, less estrogen-sensitive. Furthermore, estrogen-modulated FCX CaMKII activity in cocaine-supersensitized rats was dependent on D1 dopamine receptor activation.
Conclusion
Estrogen-modulated D1 dopamine receptor activity mediates the effects of prolonged cocaine exposure on FCX CaMKII, and this, in turn, may contribute to the development of behavioral supersensitivity to repeated cocaine treatment in intact female rats.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker JB (1999) Gender differences in dopaminergic function in striatum and nucleus accumbens. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:803–812
Berhow MT, Hiroi N, Nestler EJ (1996) Regulation of ERK, part of the neurotropin signal transduction cascades, in the rat mesolimbic dopamine system by chronic exposure to morphine or cocaine. J Neurosci 16:4707–4715
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (1999) Dopamine depletion in the medial prefrontal cortex induces sensitized-like behavioral and neurochemical responses to cocaine. Brain Res 833:133–141
Beyer CE, Steketee DJ (2001) Characterization of the role of medial prefrontal cortex dopamine receptors in cocaine-induced locomotor activity. Behav Neurosci 115:1093–1100
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (2002) Cocaine sensitization: modulation by D2 receptors in the rat medial preFCX. Cerebral Cortex 12:526–535
Chin J, Sternin O, Wu HBK, Burrell S, Lu D, Jenab S, Perrotti LI, Quinones-Jenab V (2002) Endogenous gonadal hormone modulate behavioral and neurochemical response to acute and chronic cocaine administration. Brain Res 945:123–130
Cyr M, Ghribi O, Di Paolo T (2000) Regional and selective effects of estradiol and progesterone on NMDA and AMPA receptors in the rat brain. J Neuroendocrinol 12:445–452
Cyr M, Ghribi O, Thibault C, Morissette M, Landry M, Di Paolo T (2001) Ovarian steroids and selective estrogen receptor modulators activity on rat brain NMDA and AMPA receptors. Brain Res Rev 37:153–161
Di Paolo T (1994) Modulation of brain dopamine transmission by sex steroids. Rev Neurosci 5:27–41
Dunn JM, Inderwies BR, Licata SC, Pierce RC (2005) Repeated administration of AMPA or a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist into the rat ventral tegmental area augments the subsequent behavioral hyperactivity induced by cocaine. Psychopharmacology 179:172–180
Febo M, Gonzalezprodrguez LA, Capo-Ramos DE, Gonzalez-Segarra NY, Segarra AC (2003) Estrogen-dependent alteration in D2/D3-induced G protein activation in cocaine-sensitized female rats. J Neurochem 405–441
Fink G, Sumner BE, Rosie R, Grace O, Quinn JP (1996) Estrogen control of central neurotransmission: effect on mood, mental state, and memory. Cell Mol Neurobiol 16:325–344
Gazzaley AH, Weiland NG, McEwen BS, Morrison JH (1996) Differential regulation of NMDAR1 mRNA and protein by estradiol in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 16:6830–6838
Glick SD, Hinds PA (1984) Sex differences in sensitization to cocaine-induced rotation. Eur J Pharmacol 99:119–121
Goto Y, Grace AA (2005) Dopamine-dependent interactions between limbic and prefrontal cortical plasticity in the nucleus accumbens: disruption by cocaine sensitization. Neuron 47:255–266
Gu Z, Yan Z (2004) Bidirectional regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity by dopamine D4 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Mol Pharmacol 66:948–955
Haney M, Castanon N, Cador M, Moal ML, Mormede P (1994) Cocaine sensitivity in Roman high and low avoidance rats is modulated by sex and gonadal hormone status. Brain Res 645:179–185
Hu M, Becker JB (2003) Effects of sex and estrogen on behavioral sensitization to cocaine in rats. J Neurosci 23:693–699
Hummel M, Unterwald EM (2002) D1 dopamine receptor: a putative neurochemical and behavioral link to cocaine action. J Cell Physiol 191:17–27
Lee SH, Mouradian MM (1999) Upregulation of D1A receptor gene transcription by estrogen. Mol Cell Endocrinol 156:151–157
Li Y, Hu XT, Berney TG, Vartanian AJ, Stine CD, Wolf ME, White FJ (1999) Both glutamate receptor antagonists and preFCX lesions prevent induction of cocaine sensitization and associated neuroadaptations. Synapse 34:169–180
Licata SC, Pierce RC (2003) The roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the development of psychostimulant-induced behavioral sensitization. J Neurochem 85:14–22
Licata SC, Schmidt HD, Pierce RC (2004) Suppressing calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in the ventral tegmental area enhances the acute behavioural response to cocaine but attenuates the initiation of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats. Eur J Neurosci 19:405–414
Lu L, Hope BT, Dempsey J, Liu SY, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2005) Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat Neurosci 8:212–219
Lukas SE, Sholar M, Lundahl LH, Lamas X, Kouri E, Wines JD, Kragie L, Mendelson JH (1996) Sex differences in plasma cocaine levels and subjective effects after acute cocaine administration in human volunteers. Psychopharmacology 125:346–354
Lynch WJ, Carroll ME (1999) Sex differences in the acquisition of intravenously self-administered cocaine and heroin in rats. Psychopharmacology 144:77–82
Miller CA, Marshall JF (2004) Altered prelimbic cortex output during cue-elicited drug seeking. J Neurosci 24:6889–6897
Nausieda PA, Koller WC, Weiner WJ, Klawans HL (1979) Modifications of postsynaptic dopaminergic sensitivity by female sex hormones. Life Sci 25:521–526
Pierce RC, Quick EA, Reeder DC, Morgan ZR, Kalivas PW (1998) Calcium-mediated second messengers modulate the expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:1171–1176
Peris J, Decambre N, Coleman-Hardee ML, Simpkins JW (1991) Estradiol enhances behavioral sensitization to cocaine and amphetamine-stimulated striatal [3H] dopamine release. Brain Res 566:255–264
Robinson TE, Kolb B (1999) Alterations in the morphology of dendrites and dendritic spines in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex following repeated treatment with amphetamine cocaine. Eur J Neurosci 11:1598–1604
Sawai T, Bernier F, Fukushima T, Hashimoto T, Ogura H, Nishizawa Y (2002) Estrogen induces a rapid increase of calcium–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in the hippocampus. Brain Res 950:308–311
Sell SL, Thomas ML, Cunningham KA (2002) Influence of estrous cycle and estradiol on behavioral sensitization to cocaine in female rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 67:281–290
Sircar R, Kim D (1999) Female gonadal hormones differentially modulate cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in Fischer, Lewis, and Sprague-Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:54–65
Steketee JD (2003) Neurotrasmitter system of the medial prefrontal cortex: potential role in sensitization to psychostimulants. Brain Res Rev 41:203–228
Szumlinski KK, Maisonneuve IM, Glick SD (2000) Differential effects of ibogaine on behavioural and dopamine sensitization to cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 398:259–262
Van Haaren F, Meyer ME (1998) Sex differences in locomotor activity after acute and chronic cocaine administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:923–927
Vezina P, Glowinski J, Tassin J (1991) Opposed behavioral outputs of increased dopamine transmission in prefrontal cortical and subcortical areas: a role for the cortical D1 dopamine receptor. Eur J Neurosci 3:1001–1007
Xu M, Hu X, Cooper DC, Moratalla R, Graybiel AM, White FJ, Tonegawa S (1994) Elimination of cocaine-induced hyperactivity and dopamine-mediated neurophysiological effects in dopamine D1 receptor mutant mice. Cell 79:945–955
Zhang L, Lou D, Jiao H, Zhang D, Wang X, Xia Y, Zhang J, Xu M (2004) Cocaine-induced intracellular signaling and gene expression are oppositely regulated by the dopamine D1 and D3 receptors. J Neurosci 24:3344–3354
Zhou W, Cunningham KA, Thomas ML (2002) Estrogen regulation of gene expression in the brain: a possible mechanism altering the response to psychostimulants in female rats. Mol Brain Res 100:75–83
Zhen XC, Torres C, Cai C, Friedman E (2002) Inhibition of protein tyrosine/mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase activity is associated with D2 dopamine receptor supersensitivity in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Pharmacol 62:1356–1362
Zhen XC, Goswami S, Abdali SA, Gil M, Bakshi K, Friedman E (2004) Regulation of cdk5 and CaMK II by PI-linked dopamine receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 66:1500–1507
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NIH grant DA 18055.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhen, X., Goswami, S., Abdali, S.A. et al. Estrogen-modulated frontal cortical CaMKII activity and behavioral supersensitization induced by prolonged cocaine treatment in female rats. Psychopharmacology 191, 323–331 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0648-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0648-0