Abstract
Rationale
The role of heroin-related stimuli in motivating the resumption of heroin use is not fully understood.
Objectives
The objective was to characterize the relative importance of drug-related contextual stimuli, discriminative stimuli (DS), or discrete conditioned stimuli (CSs) on drug seeking when rats were reintroduced into the operant context after withdrawal.
Methods
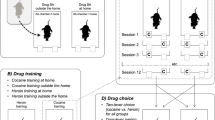
Nose-poke responding by male rats was reinforced with intravenous heroin (0.05 mg/kg per infusion, 4-h session daily) under a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement for 14 days. Each session began with the illumination of a green light in the active hole that served as DS. Each earned heroin injection was paired with a 5-s compound cue light and the sound of the infusion pump that served as the discrete CSs.
Results
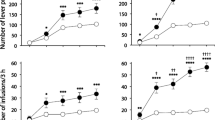
Response rates of heroin seeking induced by the contextual stimuli were comparable to the average rates of responding during self-administration training, but rates induced by either DS or CSs were greater than those induced by the contextual stimuli alone (P<0.05). The responding induced by contingent presentations of CSs was higher than that of DS after extinction of instrumental behavior. The drug seeking induced by CSs can be maintained after 3 days extinction with DS in the original context, although the responding elicited by DS cannot be recovered after 3 days of extinction with CSs.
Conclusions
The relapse to drug seeking can be elicited separately by environmental cues, heroin-predictive DS, or discrete CSs in the same rat after withdrawal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostaras SG, Schllert T, Robinson TE (2002) Memory processes governing amphetamine-induced psychomotor sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:703–715
Arroyo M, Markou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1998) Acquisition, maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration under a second-order schedule of reinforcement in rats: effects of conditioned cues and continuous access to cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 140:331–344
Bouton ME (2002) Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: source of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol Psychiatry 52:976–986
Childress AR, McLellan AT, O’Brien CP (1986) Abstinent opiate abuses exhibit conditioned craving, conditioned withdrawal and reduction in both through extinction. Br J Addict 81:655–660
Childress AR, Hole AV, Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, McLellan AT, O’Brien CP (1993) Cue reactivity and cue reactivity interventions in drug dependence. NIDA Res Monogr 137:73–95
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2004) Stimuli associated with a single cocaine experience elicit long-lasting cocaine-seeking. Nat Neurosci 7:1–2
Crombag HS, Shaham Y (2002) Renewal of drug seeking by contextual cues after prolonged extinction in rats. Behav Neurosci 116:169–173
Deroche-Gamonet V, Piat F, Le Moal M, Piazza PV (2002) Influence of cue-conditioning on acquisition, maintenance and relapse of cocaine intravenous self-administration. Eur J Neurosci 15:1363–1370
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
de Wit H, Stewart J (1981) Reinstatement of cocaine-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 75:134–143
de Wit H, Stewart J (1983) Drug reinstatement of heroin-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 79:29–31
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2001) Dissociable effect of antagonism of NMDA and AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell on cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:341–360
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2002) Reinstatement and spontaneous recovery of cocaine-seeking following extinction and different durations of withdrawal. Behav Pharmacol 13:397–405
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2003) Differential control over drug-seeking behavior by drug-associated conditioned reinforcers and discriminative stimuli predictive of drug availability. Behav Neurosci 117:952–960
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2004) Conditioned reinforcing properties of stimuli paired with self-administered cocaine, heroin or sucrose: implications for the persistence of addictive behaviour. Neuropharmacology 47:202–213
Di Ciano P, Blaha CD, Phillips AG (2001) Changes in dopamine efflux associated with extinction, CS-induced and d-amphetamine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking behavior by rats. Behav Brain Res 120:147–158
Goldberg SR (1976) Stimuli associated with drug injections as events that control behavior. Pharmacol Rev 27:325–340
Goldberg SR, Gardner ML (1981) Second-order schedules: extended sequences of behavior controlled by brief environmental stimuli associated with drug self-administration. NIDA Res Monogr 37:241–270
Gracy KN, Dankiewicz LA, Weiss F, Koob GF (2000) Heroin-specific stimuli reinstate operant heroin-seeking behavior in rats after prolonged extinction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:489–494
Grant S, London ED, Newlin DB, Villemagne VL, Liu X, Contoreggi C, Phillips RL, Kimwa AS, Margolin A (1996) Activation of memory circuits during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:4130–4146
Grimm JW, Hope BT, Wise RA, Shaham Y (2001) Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal. Nature 412:141–142
Hutcheson DM, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW, Dickinson A (2001) The role of withdrawal in heroin addiction: enhances reward or promotes avoidance? Nat Neurosci 4:943–947
Ito R, Dalley JW, Howes SR, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) Dissociation in conditioned dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in response to cocaine cues and during cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. J Neurosci 20:7489–7495
Kalivas PW, McFarland K (2003) Brain circuitry and the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:44–56
Koob GF, Weiss F, Tiffany ST, Zieglgansbenger W, Spanagel R (1999) Animal models of craving: a roundtable discussion. Alcohol Res Health 23:233–236
Kozlowski LT, Wilkinson DA (1987) Use and misuse of the concept of craving by alcohol, tobacco and drug researchers. Br J Addict 82:31–36
Kruzich PJ, Congleton KM, See RE (2001) Conditioned reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior with a discrete compound stimulus classically conditioned with intravenous cocaine. Behav Neurosci 115:1086–1092
Leri F, Stewart J (2002) Consequences of different “lapses” on relapse to heroin seeking in rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 10:339–349
Lu L, Grimm JW, Hope B, Shaham Y (2004) Incubation of cocaine seeking after withdrawal in rats: a review. Neuropharmacology 47:214–226
Markou A, Weiss F, Gold LH, Caine SB, Schulteis G, Koob GF (1993) Animal models of drug craving. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:163–182
McFarland K, Ettenberg A (1997) Reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior produced by heroin-predictive environmental stimuli. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131:86–92
Neisewander JL, O’Dell LE, Tran-Nguyen LT, Castaneda E, Fuchs RA (1996) Dopamine overflow in the nucleus accumbens during extinction and reinstatement of cocaine self-administration behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:506–514
O’Brien CP (1997) A range of research-based pharmacotherapies for addiction. Science 278:66–70
Panlilio LV, Weiss SJ, Schindler CW (1998) Motivational effects of compounding discriminative stimuli associated with food and cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 136:70–74
Powell J, Gray JA, Bradley BP, Kasvikis Y, Strang J, Barratt L, Marks I (1990) Effects of exposure to drug-related cues in detoxified opiate addicts: a theoretical review and some new data. Addict Behav 15:339–354
Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1999) Drug addiction: bad habits add up. Nature 398:567–570
Robinson TE (2004) Addicted rats. Science 305:951–953
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Schindler CW, Panlilio LV, Goldberg SR (2002) Second-order schedules of drug-administration in animals. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:327–344
Schmajuk NA, Lamoureux JA, Holland PC (1998) Occasion setting: a neural network approach. Psychol Rev 105:3–32
See RE (2002) Neural substrates of conditioned-cued relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:517–529
See RE, Grimm JW, Kruzich PJ, Rustay N (1999) The importance of a compound stimulus in conditioned drug-seeking behavior following one week of extinction from self-administered cocaine in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 57:41–49
Shaham Y, Shalev U, Lu L, de Wit H, Stewart J (2003) The reinstatement model of drug relapse: history, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:3–20
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–37
Sherman JE, Zinser MC, Sideroff SI, Baker TB (1989) Subjective dimensions of heroin urges: influence of heroin-related and affectively negative stimuli. Addict Behav 14:611–623
Stafford D, LeSage MG, Glowa JR (1998) Progressive-ratio schedules of drug delivery in the analysis of drug self-administration: a review. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 139:169–184
Stewart J, Wise RA (1992) Reinstatement of heroin self-administration habits: morphine prompts and naltrexone discourages renewed responding after extinction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 108:79–84
Sutton MA, Karanian DA, Self DW (2000) Factors that determine a propensity for cocaine-seeking behavior during abstinence in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:626–641
Sutton MA, Schmidt EF, Chol K, Schad CA, Whisler K, Simmons D, Karanian DA, Menteggia LM, Neve RL, Self DW (2003) Extinction-induced upregulation in AMPA receptors reduces cocaine-seeking behaviour. Nature 421:70–75
Tiffany ST, Carter BL (1998) Is craving the source of compulsive drug use? J Psychopharmacol 12:23–30
Tran-Nguyen LT, Fuchs RA, Coffey GP, Baker DA, O’Dell LE, Neisewander JL (1998) Time-dependent changes in cocaine-seeking behavior and extracellular dopamine levels in the amygdala during cocaine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:48–59
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Everitt BJ (2004) Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305:1017–1019
Weiss F (2005) Neurobiology of craving, conditioned reward and relapse. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:9–19
Weiss F, Maldonado-Vlaar CS, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O (2000) Control of cocaine-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats: effects on recovery of extinguished operant-responding and extracellular dopamine levels in amygdala and nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4321–4326
Weiss F, Martin-Fardon R, Ciccocioppo R, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O (2001) Enduring resistance to extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior induced by drug-related cues. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:361–372
Yun IA, Nicola SM, Fields HL (2004) Contrasting effects of dopamine and glutamate receptor antagonist injection in the nucleus accumbens suggest a neural mechanism underlying cue-evoked goal-directed behavior. Eur J Neurosci 20:249–263
Zhang F, Zhou W, Tang S, Liu H, Lai M, Zhu H, Yang G (2004) Motivation of heroin-seeking elicited by drug-associated cues is related to total amount of heroin exposure during self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:291–298
Zhou W, Zhang F, Tang S, Liu H, Lai M, Yang G (2004) Low dose of heroin inhibits drug-seeking elicited by cues after prolonged withdrawal from heroin self-administration in rats. NeuroReport 15:727–730
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Charles Schindler and Dr. Tatia Lee for comments on the manuscript. The valuable comments and suggestions of the reviewers are kindly acknowledged. This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2003CB515404) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30100051, No. 30470554).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Zhang, F., Tang, S. et al. The dissociation of heroin-seeking patterns induced by contextual, discriminative, or discrete conditioned cues in a model of relapse to heroin in rats. Psychopharmacology 181, 197–206 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2262-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2262-y