Abstract
Rationale
Acute doses of Ginkgo biloba have been shown to improve attention and memory in young, healthy participants, but there has been a lack of investigation into possible effects on executive function. In addition, only one study has investigated the effects of chronic treatment in young volunteers.
Objectives
This study was conducted to compare the effects of ginkgo after acute and chronic treatment on tests of attention, memory and executive function in healthy university students.
Methods
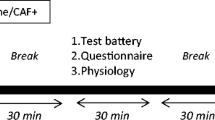
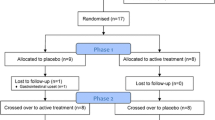
Using a placebo-controlled double-blind design, in experiment 1, 52 students were randomly allocated to receive a single dose of ginkgo (120 mg, n=26) or placebo (n=26), and were tested 4 h later. In experiment 2, 40 students were randomly allocated to receive ginkgo (120 mg/day; n=20) or placebo (n=20) for a 6-week period and were tested at baseline and after 6 weeks of treatment. In both experiments, participants underwent tests of sustained attention, episodic and working memory, mental flexibility and planning, and completed mood rating scales.
Results
The acute dose of ginkgo significantly improved performance on the sustained-attention task and pattern-recognition memory task; however, there were no effects on working memory, planning, mental flexibility or mood. After 6 weeks of treatment, there were no significant effects of ginkgo on mood or any of the cognitive tests.
Conclusions
In line with the literature, after acute administration ginkgo improved performance in tests of attention and memory. However, there were no effects after 6 weeks, suggesting that tolerance develops to the effects in young, healthy participants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Dore S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R (2000) The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by β-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci 12:1882–1890
Birks J, Grimley EV, Van Dongen M (2002) Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD003120
Bond AJ, Lader M (1974) The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47:211–218
Braquet P (1987) The Ginkgolides: potent platelet activating factor antagonists isolated from Ginkgo biloba L.: chemistry, pharmacology and clinical applications. Drugs Future 12:634–699
Bridi R, Crossetti FP, Steffen VM, Henriques AT (2001) The antioxidant activity of standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761) in rats. Phytother Res 15:449–451
Brunello N, Racagni G, Clostre F, Drieu K, Braquet P (1985) Effects of an extract of Ginkgo biloba on noradrenergic systems of rat cerebral cortex. Pharmacol Res Commun 17:1063–1072
Calapai G, Crupi A, Firenzuoli F, Marciano MC, Squadrito F, Inferrera G, Parisi A, Rizzo A, Crisafulli C, Fiore A, Caputi AP (2000) Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in brain ischemia are mediated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. Life Sci 67:2673–2683
Cieza A, Maier P, Poppel E (2003) Effects of Ginkgo biloba on mental functioning in healthy volunteers. Arch Med Res 34:373–381
DeFeudis FV (1998) Ginkgo biloba: from chemistry to clinic. Ullstein Medical, Wiesbaden, Germany
Elsabagh S, Hartley DE, File SE (2005) Limited cognitive benefits in stage +2 postmenopausal women after 6 weeks’ treatment with Ginkgo biloba. J Psychopharm 19(2)
Gessner B, Voelp A, Klasser M (1985) Study of the long-term action of a Ginkgo biloba extract on vigilance and mental performance as determined by means of quantitative pharmaco-EEG and psychometric measurements. Arzneimittelforschung 35:1459–1465
Hartley DE, Heinze L, Elsabagh S, File SE (2003) Effects on cognition and mood in postmenopausal women of 1-week treatment with Ginkgo biloba. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:711–720
Huang SH, Duke RK, Chebib M, Sasaki K, Wada K, Johnston G (2003) Bilobalide, a sesquiterpene trilactone from Ginkgo biloba is an antagonist at recombinant α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 464:1–8
Itil TM, Eralp E, Tsambis E, Itil KZ, Stein U (1996) Central nervous system effects of Ginkgo biloba, a plant extract. Am J Ther 3:63–73
Joyeux M, Lobstein A, Anton R, Mortier F (1995) Comparative antilipoperoxidant, antinecrotic and scavenging properties of terpenes and biflavones from Ginkgo, and some flavonoids. Planta Med 62:126–129
Kanowski S, Herrmann WM, Stephan K, Wierich W, Horr R (1996) Proof of efficacy of the Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb 761 in outpatients suffering from mild to moderate primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type or multi-infarct dementia. Pharmacopsychiatry 29:47–56
Kennedy DO, Scholey AB, Wesnes KA (2000) The dose-dependent cognitive effects of acute administration of Ginkgo biloba to healthy young volunteers. Psychopharmacology 151:416–423
Kennedy DO, Scholey AB, Wesnes KA (2002) Modulation of cognition and mood following administration of single doses of Ginkgo biloba, ginseng, and a ginkgo/ginseng combination to healthy young adults. Physiol Behav 75:739–751
Kennedy DO, Scholey AB, Drewery L, Marsh VR, Moore B, Ashton H (2003) Electroencephalograph effects of single doses of Ginkgo biloba and Panax ginseng in healthy young volunteers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:701–709
Krieglstein J, Beck T, Seibert A (1986) Influence of an extract of Ginkgo biloba on cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Life Sci 39:2327–2334
Le Bars PL, Katz MM, Berman N, Itil TM, Freedman AM, Schatzberg AF (1997) A placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial of an extract of Ginkgo biloba for dementia. North American EGb Study Group. JAMA 278:1327–1332
Luthringer R, d’Arbigny P, Machler JP (1995) In: Christen Y, Courtosis Y, Droy-Lefaix MT (eds) Advances in Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on aging and age-related disorders. Elsevier, Paris, pp 107–118
Mattes RD, Pawlik MK (2004) Effects of Ginkgo biloba on alertness and chemosensory function in healthy adults. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:81–90
Mix JA, Crews WD Jr (2000) An examination of the efficacy of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 on the neuropsychologic functioning of cognitively intact older adults. J Altern Complement Med 6:219–229
Mix JA, Crews WD Jr (2002) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in a sample of cognitively intact older adults: neuropsychological findings. Hum Psychopharmacol 17:267–277
Moulton PL, Boyko LN, Fitzpatrick JL, Petros TV (2001) The effect of Ginkgo biloba on memory in healthy male volunteers. Physiol Behav 73:659–665
Nathan PJ, Ricketts E, Wesnes K, Mrazek L, Greville W, Stough C (2002) The acute nootropic effects of Ginkgo biloba in healthy older human subjects: a preliminary investigation. Hum Psychopharmacol 17:45–49
Nelson HE, Willison JR (1991) Restandardisation of the NART against the WAIS-R. NFER-Nelson, Windsor
Oken BS, Storzbach DM, Kaye JA (1998) The efficacy of Ginkgo biloba on cognitive function in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 55:1409–1415
Owen AM, Downes JJ, Sahakian BJ, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1990) Planning and spatial working memory following frontal lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 28:1021–1034
Owen AM, Roberts AC, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1991) Extra-dimensional versus intra-dimensional set shifting performance following frontal lobe excisions, temporal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 29:993–1006
Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Semple J, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995) Visuo-spatial short-term recognition memory and learning after temporal lobe excisions, frontal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 33:1–24
Owen AM, Doyon J, Petrides M, Evans AC (1996) Planning and spatial working memory: a positron emission tomography study in humans. Eur J Neurosci 8:353–364
Oyama Y, Chikahisa L, Ueha T, Kanemaru K, Noda K (1996) Ginkgo biloba extract protects brain neurons against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Brain Res 712:349–352
Persson J, Bringlov E, Nilsson LG, Nyberg L (2004) The memory-enhancing effects of ginseng and Ginkgo biloba in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 172:430–434
Rapin JR, Franchet S, Drieu K (1991) In: DeFeudis FV (ed) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761): pharmacological activities and clinical applications. Elsevier, Paris, pp 80–82
Rigney U, Kimber S, Hindmarch I (1999) The effects of acute doses of standardized Ginkgo biloba extract on memory and psychomotor performance in volunteers. Phytother Res 13:408–415
Robbins TW, James M, Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Lawrence AD, McInnes L, Rabbitt PM (1998) A study of performance on tests from the CANTAB battery sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction in a large sample of normal volunteers: implications for theories of executive functioning and cognitive aging. Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 4:474–490
Rogers RD, Andrews TC, Grasby PM, Brooks DJ, Robbins TW (2000) Contrasting cortical and subcortical activations produced by attentional-set shifting and reversal learning in humans. J Cogn Neurosci 12:142–162
Sastre J, Millan A, Garcia de la Asuncion J, Pla R, Juan G, Pallardo, O’Connor E, Martin JA, Droy-Lefaix MT, Vina J (1998) A Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) prevents mitochondrial aging by protecting against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 24:298–304
Scholey AB, Kennedy DO (2002) Acute, dose-dependent cognitive effects of Ginkgo biloba, Panax ginseng and their combination in healthy young volunteers: differential interactions with cognitive demand. Hum Psychopharmacol 17:35–44
Snodgrass JG, Vanderwart M (1980) A standardized set of 260 pictures: norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. J Exp Psychol Hum Learn Mem 6:174–215
Snyder FR, Henningfield JE (1989) Effects of nicotine administration following 12 h of tobacco deprivation: assessment on computerized performance tasks. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 97:17–22
Solomon PR, Adams F, Silver A, Zimmer J, DeVeaux R (2002) Ginkgo for memory enhancement: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288:835–840
Spreen O, Strauss E (1991) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration norms and commentary. Oxford University Press, New York
Stough C, Clarke J, Lloyd J, Nathan PJ (2001) Neuropsychological changes after 30-day Ginkgo biloba administration in healthy participants. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 4:131–134
Subhan Z, Hindmarch I (1984) The psychopharmacological effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in normal healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 4:89–93
Svenningsson P, Nomikos GG, Fredholm BB (1999) The stimulatory action and the development of tolerance to caffeine is associated with alterations in gene expression in specific brain regions. J Neurosci 19:4011–4022
Taylor (1991) Effect of EGb 761 on brain muscarinic receptors. In: DeFeudis (ed) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761): pharmacological activities and clinical applications. Elsevier, Paris, p 80
Upton R (2003) Ginkgo leaf and ginkgo leaf extract: Ginkgo biloba L. Standards of analysis, quality control, and therapeutics. American Herbal Pharmacopoeia, p 24
Wagner H (1999) New targets in the phytopharmacology of plants. In: Herbal medicine, a concise overview for health care professionals. Butterworth-Heinemann, pp 34–42
Weingartner HJ, Joyce EM, Sirocco KY, Adams CM, Eckardt MJ, George T, Lister RG (1993) Specific memory and sedative effects of the benzodiazepine triazolam. J Psychopharm 7:305–315
Williamson EM (2000) Synergy and other interactions in phytomedicines. Phytomedicine 8:401–409
Zhou L-J, Zhu X-Z (2000) Reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and protective effect of bilobalide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:982–988
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP (1983) The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatric Scand 67:361–370
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a grant from the Dunhill Medical Trust. We would like to thank Dr. R. Middleton of Lichtwer Pharma UK for the generous gift of Ginkyo and matched placebo tablets, and Yasser Khan for his assistance with testing some of the participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsabagh, S., Hartley, D.E., Ali, O. et al. Differential cognitive effects of Ginkgo biloba after acute and chronic treatment in healthy young volunteers. Psychopharmacology 179, 437–446 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2206-6