Abstract
Rationale
Central α1- and α2-adrenoceptors in a number of different brain regions are known to have opposing actions on gross behavioral activity, with the former stimulating and the latter inhibiting activity. Therefore, blockade of α1-receptors may induce inactivity by leading to unopposed α2 activity.
Objective
The aim of this study was to test if central blockade of α2-receptor function restores behavioral activity in α1-receptor-blocked mice.
Methods
Dose-response studies were undertaken on the effects of α1- and α2-agonists and antagonists microinjected into the dorsal pons on gross behavioral activity in a novel cage test.
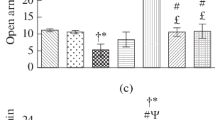
Results
The behavioral inactivity resulting from blockade of α1-receptors in the pons with the antagonist, terazosin, was reversed by either a low dose of an α2-antagonist, atipamezole, or a low dose of an α2-agonist, dexmedetomidine, but was exacerbated by a high dose of the α2-agonist.
Conclusion
The results support the hypothesis that blockade of α1-receptors in the dorsal pons of mice produces inactivity by causing unopposed activity of α2-receptors. This condition may be relevant to inactive states seen after stress or during depressive illness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler CH, Meller E, Goldstein M (1987) Receptor reserve at the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor in the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:508–515
Anden N-E, Pauksens K, Svensson K (1982) Selective blockade of brain alpha-2 autoreceptors by yohimbine: effects on motor activity and on turnover of noradrenaline and dopamine. J Neural Transm 55:111–120
Asnis GM, Sanderson WC, van Praag HM (1992) Cortisol response to intramuscular desipramine in patients with major depression and normal control subjects: a replication study. Psychiatry Res 44:237–250
Blanc G, Trovero F, Vezina P, Herve D, Godeheu A-M, Glowinski J, Tassin J-P (1994) Blockade of prefronto-cortical α1-adrenergic receptors prevents locomotor hyperactivity induced by subcortical d-amphetamine injection. Eur J Neurosci 6:293–298
Braga MF, Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Manion ST, Hough CJ, Li H (2004) Stress impairs alpha(1A) adrenoceptor-mediated noradrenergic facilitation of GABAergic transmission in the basolateral amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:45–58
Checkley S, Crammer J (1977) Hormone responses to methylamphetamine in depression. Br J Psychiatry 131:582–586
Crochet S, Sakai K (2003) Dopaminergic modulation of behavioral states in mesopontine tegmentum: a reverse microdialysis study in freely moving cats. Sleep 26:801–806
De Sarro GB, Ascioti C, Froio F, Libri V, Nistico G (1987) Evidence that locus coeruleus is the site where clonidine and drugs acting at alpha-1 and alpha-2-adrenoceptors affect sleep and arousal mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol 90:675–685
Engberg G, Eriksson E (1991) Effects of alpha-2-adrenoceptor agonists on locus coeruleus firing rate and brain noradrenaline turnover in N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline (EEDQ)-treated rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343:472–477
Escribá PV, Ozaita A, García-Sevilla JA (2004) Increased mRNA expression of α2A-adrenoceptors, serotonin receptors and μ-opioid receptors in the brains of suicide victims. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1512–1521
Flugge G (1996) Alterations in the central nervous alpha2-adrenoceptor system under chronic psychosocial stress. Neuroscience 75:187–196
Garcia-Sevilla JA, Escriba PV, Ozaita A, La Harpe R, Walzer C, Eytan A, Guimon J (1999) Up-regulation of immunolabeled alpha2A-adrenoceptors, Gi coupling proteins, and regulatory receptor kinases in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicides. J Neurochem 72:282–291
Goncalves J, Nunes JP, Paiva M, Guimaraes S (1988) Loss of selectivity of so-called selective α1-adrenoceptor agonists after phenoxybenzamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 338:234–238
Grenhoff J, North RA, Johnson SW (1995) α1-Adrenergic effects on dopamine neurons recorded intracellularly in the rat midbrain slice. Eur J Neurosci 7:1707–1713
Gross-Isseroff R, Dillon KA, Fieldust SJ, Biegon A (1990) Autoradiographic analysis of α1-noradrenergic receptors in the human brain postmortem. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:1049–1053
Happe HK, Coulter CL, Gerety ME, Sanders JD, O'Rourke M, Bylund DB, Murrin LC (2004) Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor development in rat CNS: an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 123:167–178
Izumi J, Washizuka M, Hayashi-Kuwabara Y, Yoshinaga K, Tanaka Y, Ikeda Y, Kiuchi Y, Oguchi K (1996) An attenuated α1-potentiation of β-adrenoceptor-stimulated cyclic AMP formation after repeated saline injections in Fischer 344 strain rats. Life Sci 59:33–42
Miyahara S, Komori T, Fujiwara R, Shizuya K, Yamamoto M, Ohmori M, Okazaki Y (1999) Effects of restraint stress on α1 adrenoceptor mRNA expression in the hypothalamus and midbrain of the rat. Brain Res 843:130–135
Nicoll RA, Malenka RC, Kauer JA (1990) Functional comparison of neurotransmitter receptor subtypes in mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev 70:513–565
Shebuski RJ, Fujita T, Ruffolo RR Jr (1987) Interaction of dopamine, (+/−)-dobutamine and the (−)-enantiomer of dobutamine with alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the pulmonary circulation of the dog. Pharmacology 34:201–212
Stolk J, Vantini G, Perry B, Guchhait R, U'Prichard D (1984) Assessment of the functional role of brain adrenergic neurons: chronic effects of PNMT inhibitors and alpha adrenergic receptor antagonists on brain norepinephrine metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:577–586
Stone E, Quartermain D (2004) Rate dependent behavioral effects of stimulation of central motoric α1-adrenoceptors: hypothesized relation to depolarization blockade. Psychopharmacology 178:109–114
Stone E, Quartermain D (2005) Brain epinephrine-stimulated α1-adrenoceptor system in behavioral activation and depression. Curr Psychiatry Rev 1:33–43
Stone EA, Platt JE, Herrera AS, Kirk KL (1986) The effect of repeated restraint stress, desmethylimipramine or adrenocorticotropin on the α and β adrenergic components of the cyclic AMP response to norepinephrine in rat brain slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:702–707
Stone E, Zhang Y, Rosengarten H, Yeretsian J, Quartermain D (1999) Brain α1-adrenergic neurotransmission is necessary for behavioral activation to environmental change in mice. Neuroscience 94:1245–1252
Stone E, Lin Y, Itteera A, Quartermain D (2001a) Pharmacological evidence for the role of brain alpha 1B-adrenergic receptors in the motor activity and spontaneous movement of mice. Neuropharmacology 40:254–261
Stone E, Rosengarten H, Lin Y, Quartermain D (2001b) Pharmacological blockade of brain alpha 1-adrenoceptors as measured by ex vivo [3H]prazosin binding is correlated with behavioral immobility. Eur J Pharmacol 420:97–102
Stone E, Grunewald G, Lin Y, Ahsan R, Rosengarten H, Kramer K, Quartermain D (2003a) Role of epinephrine stimulation of CNS α1-adrenoceptors in motor activity in mice. Synapse 49:67–76
Stone E, Lin Y, Rosengarten H, Kramer H, Quartermain D (2003b) Emerging evidence for a central epinephrine-innervated α1-adrenergic system that regulates behavioral activation and is impaired in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1387–1399
Stone E, Lin Y, Ahsan R, Quartermain D (2004a) Gross mapping of α1-adrenoceptors that regulate behavioral activation in the mouse brain. Behav Brain Res 152:167–175
Stone E, Lin Y, Ahsan R, Quartermain D (2004b) Role of locus coeruleus α1-adrenoceptors in motor activity in rats. Synapse 54:164–172
Underwood MD, Mann JJ, Arango V (2004) Serotonergic and noradrenergic neurobiology of alcoholic suicide. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:57S–69S
Unnerstall JR, Kopajtic TA, Kuhar MJ (1984) Distribution of alpha 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human central nervous system: analysis of some functional, anatomic correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related adrenergic agents. Brain Res 319:69–101
Wisor JP, Eriksson KS (2005) Dopaminergic-adrenergic interactions in the wake promoting mechanism of modafinil. Neuroscience 132:1027–1034
Zhang WP, Ming OY, Thomas SA (2004) Potency of catecholamines and other l-tyrosine derivatives at the cloned mouse adrenergic receptors. Neuropharmacology 47:438–449
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by MH45265 (E.A.S.) and NIDA T32 DA07254 (M.R.A.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stone, E.A., Lin, Y., Ahsan, M.R. et al. α1-Adrenergic and α2-adrenergic balance in the dorsal pons and gross behavioral activity of mice in a novel environment. Psychopharmacology 183, 127–132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0171-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0171-8