Abstract
Rationale
Glutamatergic dysfunction at N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors has been proposed as a neurochemical model for schizophrenia. A key feature of this disorder is impairments in cognitive function.
Objective
The present study sought to investigate the effects of ketamine, an NMDA antagonist, on the performance and neural correlates of verbal fluency, a task that engages executive function.
Methods
Ten healthy dextral male volunteers received intravenous placebo normal saline or ketamine (bolus of 0.23 mg/kg and infusion of 0.65 mg/kg), administered in a double-blind, randomized order, during two functional magnetic resonance imaging sessions. During scanning, subjects performed a verbal fluency task. Two levels of cognitive load were examined in the task, and overt responses were acquired in order to measure subject performance on-line.
Results
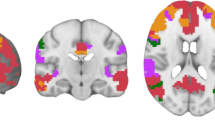
Ketamine induced symptoms in the healthy individuals comparable to an acute psychotic state. Although ketamine did not significantly impair task performance relative to placebo, an interaction of task demand with ketamine was observed in the anterior cingulate, prefrontal, and striatal regions.
Conclusions
The behavioural and functional effects of ketamine during verbal fluency in healthy individuals were comparable to those evident in patients with schizophrenia. The findings support a role for glutamatergic dysfunction in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel KM, Allin MPG, Kucharska-Pietura K et al (2003) Ketamine alters neural processing of facial emotion recognition in healthy men: an fMRI study. Neuroreport 14:387–391
Abel KM, Allin MPG, Hemsley DR, Geyer MA (2003) Low dose ketamine induces prepulse inhibition in healthy men. Neuropharmacology 44:729–737
Adler CM, Goldberg TE, Malhotra AK et al (1998) Effects of ketamine on thought disorder, working memory, and semantic memory in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry 43:811–816
Adler CM, Malhotra AK, Elman I et al (1999) Comparison of ketamine-induced thought disorder in healthy volunteers and thought disorder in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156:1646–1649
Alexander GE, Crutcher MD, DeLong MR (1990) Basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, “prefrontal” and “limbic” functions. Prog Brain Res 85:119–146
Allen HA, Liddle PF, Frith CD (1993) Negative features, retrieval processes and verbal fluency in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 163:769–775
Amaro E Jr, Williams SCR, Shergill SS et al (2002) Acoustic noise and functional magnetic resonance imaging: current strategies and future prospects. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:497–510
Ammons R, Ammons C (1962) Quick Test Missoula, MT: psychological test specialists
Angrist BM, Peselow E, Rubenstein M et al (1982) Partial improvement in negative schizophrenic symptoms after amphetamine psychosis: preliminary observations. Biol Psychiatry 2:95–107
Annett MA (1970) A classification of hand preference by association analysis. Br J Psychol 61:303–321
Arnsten AF (1998) The biology of being frazzled. Science 280:1711–1712
Artiges E, Martinot JL, Verdys M et al (2000) Altered hemispheric functional dominance during word generation in negative schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 26:709–721
Ban TA, Lohrenz JJ, Lehmann HE (1961) Observations on the action of Sernyl—a new psychotropic drug. Can Psychiatr Assoc J 6:150–156
Benton AL, Hamsher KD (1994) Multilingual aphasia examination. Oxford University Press, New York
Brammer MJ, Bullmore ET, Simmons A et al (1997) Generic brain activation mapping in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a nonparametric approach. Magn Reson Imaging 15:763–770
Breier A, Malhotra AK, Pinals DA et al (1997) Association of ketamine-induced psychosis with focal activation of the prefrontal cortex in healthy volunteers. Am J Psychiatry 154:805–811
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putnam FW et al (1991) Measurement of dissociative states with the clinician administered dissociative states scale. J Trauma Stress 11:25–136
Bullmore ET, Suckling J, Overmeyer S et al (1999) Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans Med Imag 18:32–42
Bullmore ET, Long C, Suckling J et al (2001) Colored noise and computational inference in neurophysiological (fMRI) time series analysis: resampling methods in time and wavelet domains. Hum Brain Mapp 12:61–78
Callicott JH, Bertolino A, Mattay VS et al (2000) Physiological dysfunction of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia revisited. Cereb Cortex 10:1078–1092
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1990) Interactions between glutamatergic and monoaminergic systems within the basal ganglia–implications for schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci 13:272–276
Carter CS, Barch D, Cohen JD et al (1997) CNS catecholamines and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 24:211
Cleghorn JM, Franco S, Szechtman B et al (1992) Towards a brain map of auditory hallucinations. Am J Psychiatry 149:1062–1069
Collins VJ, Gorospe CA, Rovenstine EA (1960) Intravenous nonbarbiturate, nonnarcotic analgesics: preliminary studies. I. cyclohexylamines. Anesth Analg 39:303–306
Corssen G, Domino EF (1966) Dissociative anesthesia: further pharmacologic studies and first clinical experience with the phencyclidine derivative CI-581. Anesth Analg 45:29–40
Cotman CW, Monaghan DT (1987) Anatomical organization of excitatory amino acid receptors and their properties. Adv Exp Med Biol 203:237–252
Coyle JT, Leski M, Morrison J (2001) Diverse role of l-glutamate acid in brain signal transduction. In: Neuropsychopharmacology: fifth generation of progress. Lippincott, New York
Crespo-Facorro B, Paradiso S, Andreasen NC et al (1999) Recalling word lists reveals “cognitive dysmetria” in schizophrenia: a positron emission tomography study. Am J Psychiatry 156:386–392
Curtis VA, Bullmore ET, Brammer MJ et al (1998) Attenuated frontal activation during a verbal fluency task in patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 155:1056–1063
Curtis VA, Bullmore ET, Morris RG et al (1999) Attenuated frontal activation in schizophrenia may be task dependent. Schizophr Res 37:35–44
Desmond JE, Fiez JA (1998) Neuroimaging studies of the cerebellum: language, learning and memory. Trends Cogn Neurosci 2:355–362
Duncan J, Owen AM (2000) Common regions of the human frontal lobe recruited by diverse cognitive demands. Trends Neurosci 23:475–483
Dye SM, Spence SA, Bench CJ et al (1999) No evidence for left superior temporal dysfunction in asymptomatic schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. PET study of verbal fluency. Br J Psychiatry 175:367–374
Ebmeier KP, Blackwood DH, Murray C et al (1993) Single-photon emission computed tomography with 99mTc-exametazime in unmedicated schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 33:487–495
Fletcher PC, Frith CD, Grasby PM et al (1996) Local and distributed effects of apomorphine on fronto-temporal function in acute unmedicated schizophrenia. J Neurosci 16:7055–7062
Frith CD, Friston KJ, Herold S et al (1995) Regional brain activity in chronic schizophrenic patients during the performance of a verbal fluency task. Br J Psychiatry 167:343–349
Fu CHY, McGuire PK (1999) Functional neuroimaging in psychiatry. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 354:1359–1370
Fu CHY, Morgan K, Suckling J et al (2002) An fMRI study of overt letter verbal fluency using a clustered acquisition sequence: greater anterior cingulate activation with increased task demand. Neuroimage 17:871–879
Fu CHY, Suckling J, Williams SCR et al (2005) Effects of psychotic state and task demand on prefrontal function in schizophrenia: an fMRI study of overt verbal fluency. Am J Psychiatry 162:485–494
Ghoneim MM, Hinrichs JV, Mewaldt SP et al (1985) Ketamine: behavioral effects of subanesthetic doses. J Clin Psychopharmacol 5:70–77
Goldman-Rakic PS, Selemon LD (1997) Function and anatomical aspects of prefrontal pathology in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 23:437–458
Halligan PW, David AS (2001) Cognitive neuropsychiatry: towards a scientific psychopathology. Nat Neurosci Rev 2:209–215
Hetem LA, Danion JM, Diemunsch P et al (2000) Effect of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on memory and conscious awareness in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:283–288
Holcomb HH, Lahti AC, Medoff DR et al (2001) Sequential regional cerebral blood flow brain scans using PET with H2(15)O demonstrate ketamine actions in CNS dynamically. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:165–172
Honey RAE, Honey GD, O'Loughlin C et al (2004) Acute ketamine administration alters the brain responses to executive demands in a verbal working memory task: an fMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1203–1214
Honey GD, Honey RAE, O'Loughlin C et al (2005) Ketamine disrupts frontal and hippocampal contribution to encoding and retrieval of episodic memory: an fMRI study. Cereb Cortex 15:749–759
Indefrey P, Levelt WJM (2000) The neural correlates of language production. In: Gazzaniga MS (ed) The new cognitive neurosciences, 2nd edn. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 845–865
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148:1301–1308
Jentsch JD, Roth RH (1999) The neuropsychopharmacology of phencyclidine: from NMDA receptor hypofunction to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:201–225
Kegeles LS, Abi-Dargham A, Zea-Ponce Y et al (2000) Modulation of amphetamine-induced striatal dopamine release by ketamine in humans: implications for schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 48:627–640
Kravariti E, Dixon T, Frith C et al (2005) Association of symptoms and executive function in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 74:221–231
Krystal JK, Karper LP, Seibyl JP et al (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, ketamine, in humans: psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:199–214
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Bennett A et al (1998) Interactive effects of subanesthetic ketamine and subhypnotic lorazepam in humans. Psychopharmacology 135:213–229
Lahti AC, Holcomb HH, Medoff DR et al (1995) Ketamine activates psychosis and alters limbic blood flow in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 6:869–872
Lewis SW, Ford RA, Syed GM et al (1992) A controlled study of 99mTc-HMPAO single-photon emission imaging in chronic schizophrenia. Psychol Med 22:27–35
Lezak MD (1995) Neuropsychological assessment, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 544–546
Liddle PF (1987) The symptoms of chronic schizophrenia. A re-examination of the positive–negative dichotomy. Br J Psychiatry 151:145–151
Luby ED, Cohen BD, Rosenbaum F et al (1959) Study of a new schizophrenomimetic drug, Sernyl. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81:363–369
Malhotra AK, Pinals DA, Weingartner H et al (1996) NMDA receptor function and human cognition: the effect of ketamine in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 14:301–307
Malhotra AK, Pinals DA, Adler CM et al (1997) Ketamine-induced exacerbation of psychotic symptoms and cognitive impairment in neuroleptic-free schizophrenics. Neuropsychopharmacolgy 17:141–150
Manoach DS, Press DZ, Thangaraj V et al (1999) Schizophrenic subjects activate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during a working memory task, as measured by fMRI. Biol Psychiatry 45:1128–1137
Mattay VS, Callicott JH, Bertolino A et al (2000) Efects of dextroamphetamine on cognitive performance and cortical activation. Neuroimage 12:268–275
McGuire PK, Shah GMS, Murray RM (1993) Increased blood flow in Broca's area during auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia. Lancet 342:703–706
Meyer JS, Greifenstein F, DeVault M (1959) A new drug causing symptoms of sensory deprivation. J Nerv Ment Dis 129:54–61
Monaghan DT, Cotman CW (1985) Distribution of N-methyl-d-aspartate-sensitive l-[3H]glutamate-binding sites in rat brain. J Neurosci 5:2909–2919
Murphy BL, Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS et al (1996) Increased dopamine turnover in the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in rats and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:1325–1329
Newcomer JW, Krystal JH (2001) NMDA receptor regulation of memory and behavior in humans. Hippocampus 11:529–542
Newcomer JW, Farber NB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V et al (1999) Ketamine-induced NMDA receptor hypofunction as a model of memory impairment and psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:106–118
Northoff G, Richter A, Bermpohl F et al (2005) NMDA hypofunction in the posterior cingulate as a model for schizophrenia: an exploratory ketamine administration study in fMRI. Schizophr Res 72:235–248
Olney JW, Labruyere J, Price MT (1989) Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phenylcyclidine and related drugs. Science 244:1360–1362
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Perlstein WM, Carter CS, Noll DC et al (2001) Relation of prefrontal cortex dysfunction to working memory and symptoms in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158:1105–1113
Petersen SE, Fox PT, Posner MI et al (1988) Positron emission tomographic studies of the cortical anatomy of single-word processing. Nature 331:585–589
Rainey JM Jr, Crowder MK (1975) Prolonged psychosis attributed to phencyclidine: report of three cases. Am J Psychiatry 132:1076–1078
Rice CD, Done DJ, Manly T et al (2002) Schizophrenic patients with symptoms show more impairment than those without symptoms on an ecologically valid test of executive function. Schizophr Res 53:133
Schorn TO, Witwam JG (1980) Are there long-term effects of ketamine on the central nervous system? Br J Anaesth 52:967–968
Seamans JK, Floresco SB, Phillips AG (1998) D1 receptor modulation of hippocampal–prefrontal cortical circuits integrating spatial memory with executive functions in the rat. J Neurosci 18:1613–1621
Shergill SS, Brammer MJ, Williams SC et al (2000) Mapping auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:1033–1088
Smith EE, Jonides J (1999) Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science 283:1657–1661
Smith GS, Schloesser R, Brodie JD et al (1998) Glutamate modulation of dopamine measured in vivo with positron emission tomography (PET) and 11C-raclopride in normal human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:18–25
Sommer IEC, Ramsey NF, Kahn RS (2001) Language lateralisation in schizophrenia, an fMRI study. Schizophr Res 52:57–67
Spence SA, Hirsch SR, Brooks DJ et al (1998) Prefrontal cortex activity in people with schizophrenia and control subjects: evidence from positron emission tomography for remission of “hypofrontality” with recovery from acute schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 172:316–323
Spence SA, Liddle PF, Stefan MD et al (2000) Functional anatomy of verbal fluency in people with schizophrenia and those at genetic risk. Br J Psychiatry 176:52–60
Stevens AA, Goldman-Rakic PS, Gore JC et al (1998) Cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia during auditory word and tone working memory demonstrated by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:1097–1103
Svensson TH, Mathe JM, Andersson JL et al (1995) Mode of action of atypical neuroleptics in relation to the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia: role of 5-HT2 receptor and alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism. J Clin Psychopharmacol 11–18S
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Thieme, New York
Tamminga C (1999) Glutamatergic aspects of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 37:12–15
Tsai G, Coyle JT (2002) Glutamatergic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:165–179
Tso IF, Chan RCK, Chen EYH et al (2002) Longitudinal profiles of neurocognitive function in first-episode psychosis. Schizophr Res 53:121
Verma A, Moghaddam B (1996) NMDA receptor antagonists impair prefrontal cortex function as assessed via spatial delayed alternation performance in rats: modulation by dopamine. J Neurosci 16:373–379
Vincent JP, Kartalovski B, Geneste P et al (1979) Interaction of phencyclidine (“angel dust”) with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:4678–4682
Volkow ND, Brodie JD, Wolf AP et al (1986) Brain metabolism in patients with schizophrenia before and after acute neuroleptics administration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1199–1202
Vollenweider FX, Leenders KL, Scharfetter C et al (1997) Metabolic hyperfrontality and psychopathology in the ketamine model of psychosis using positron emission tomography (PET) and [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 7:9–24
Vollenweider FX, Vontobel P, Oye I et al (2000) Effects of (S)-ketamine on striatal dopamine: a [11C]raclopride PET study of a model psychosis in humans. J Psychiatr Res 34:35–43
Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Modulation of memory fields by dopamine D1 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Nature 6:572–575
Yurgelun-Todd D, Waternaux C, Cohen B et al (1996) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of schizophrenic patients during word production. Am J Psychiatry 153:200–205
Zukin SR, Zukin RS (1979) Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:5372–5376
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Wellcome Trust Fellowship to CF and from the Mason Medical Foundation to KMA. We would also like to thank the radiographers at the MRI Center, Maudsley and South London NHS Trust, for their expert assistance. The experiments in the present study comply with the current laws of the UK, in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, C.H.Y., Abel, K.M., Allin, M.P.G. et al. Effects of ketamine on prefrontal and striatal regions in an overt verbal fluency task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychopharmacology 183, 92–102 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0154-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0154-9