Abstract
Rationale
Comparison of different mouse strains can provide valuable information about the genetic control of behavioural and molecular phenotypes. Recent evidence has demonstrated the importance of GABAB receptors in anxiety and depression. Investigation of the phamacogenetics of GABAB receptor activation may aid in the understanding of mechanisms underlying the role of GABAB in affect.
Objectives
The aim of current study was to determine the relative sensitivity of different mouse strains to GABAB receptor agonism in two models of GABAB receptor function, namely hypothermia and motor incoordination.
Methods
Mice each from 11 strains (BALB/cByJIco, DBA/2JIco, OF1, FVB/NIco, CD1, C3H/HeOuJIco, 129/SvPasIco, NMRI, C57BL/6JIco, A/JOlaHsd and Swiss) were trained to walk on a rotarod for 300 s. On the following day, mice received 0, 3, 6 or 12 mg/kg of l-baclofen PO. Rectal temperature and rotarod performance were measured at 0, 1, 2 and 4 h after drug application.
Results
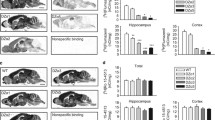
l-Baclofen produced a significant dose-dependent hypothermia and ataxia in most, but not all, mouse strains examined. The magnitude and duration of response was influenced by strain, with mice of the 129/SvPasIco strain showing largest hypothermic response to 12 mg/kg l-baclofen and C3H/HeOuJIco the lowest, whereas the BALB/cByJIco strain demonstrated greatest ataxic response on the rotarod, and NMRI the least. Interestingly, some strains (notably C3H/HeOuJIco) had marked differential hypothermic and ataxic responses, with minimal body temperature responses to l-baclofen but significant ataxia on the rotarod observed.
Conclusion
There is differential genetic control on specific GABAB receptor populations that mediate hypothermia and ataxia. Further, these studies demonstrate that background strain is an important determinant of GABAB receptor mediated responses, and that hypothermic and ataxic responses may be influenced by independent genetic loci.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler MW, Geller EB, Rosow CE, Cochin J (1988) The opioid system and temperature regulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 28:429–449
Barral J, Toro S, Galarraga E, Bargas J (2000) GABAergic presynaptic inhibition of rat neostriatal afferents is mediated by Q-type Ca(2+) channels. Neurosci Lett 283:33–36
Belknap JK, Riggan J, Cross S, Young ER, Gallaher EJ, Crabbe JC (1998) Genetic determinants of morphine activity and thermal responses in 15 inbred mouse strains. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:353–360
Benke D, Honer M, Michel C, Bettler B, Mohler H (1999) Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor splice variant proteins GBR1a and GBR1b are both associated with GBR2 in situ and display differential regional and subcellular distribution. J Biol Chem 274:27323–27330
Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Mosbacher J, Gassmann M (2004) Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABA(B) receptors. Physiol Rev 84:835–867
Bothe GW, Bolivar VJ, Vedder MJ, Geistfeld JG (2004) Genetic and behavioral differences among five inbred mouse strains commonly used in the production of transgenic and knockout mice. Genes Brain Behav 3:149–157
Boulant JA (2000) Role of the preoptic-anterior hypothalamus in thermoregulation and fever. Clin Infect Dis 31 (Suppl 5):S157–S161
Bowery NG, Hill DR, Hudson AL, Doble A, Middlemiss DN, Shaw J, Turnbull M (1980) (−)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature 283:92–94
Bowery NG, Doble A, Hill DR, Hudson AL, Shaw JS, Turnbull MJ, Warrington R (1981) Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol 71:53–70
Bowery NG, Bettler B, Froestl W, Gallagher JP, Marshall F, Raiteri M, Bonner TI, Enna SJ (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: structure and function. Pharmacol Rev 54:247–264
Brogden RN, Speight TM, Avery GS (1974) Baclofen: a preliminary report of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in spasticity. Drugs 8:1–14
Brooks SP, Pask T, Jones L, Dunnett SB (2004) Behavioural profiles of inbred mouse strains used as transgenic backgrounds. I. Motor tests. Genes Brain Behav 3:206–215
Burman KJ, Ige AO, White JH, Marshall FH, Pangalos MN, Emson PC, Minson JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ (2003) GABAB receptor subunits, R1 and R2, in brainstem catecholamine and serotonin neurons. Brain Res 970:35–46
Carlsson A, Biswas B, Lindqvist M (1977) Influence of GABA and GABA-like drugs on monoaminergic mechanisms. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 16:471–475
Chan PK, Leung CK, Yung WH (1998) Differential expression of pre- and postsynaptic GABA(B) receptors in rat substantia nigra pars reticulata neurones. Eur J Pharmacol 349:187–197
Chen L, Boyes J, Yung WH, Bolam JP (2004) Subcellular localization of GABAB receptor subunits in rat globus pallidus. J Comp Neurol 474:340–352
Crabbe JC, Gallaher ES, Phillips TJ, Belknap JK (1994) Genetic determinants of sensitivity to ethanol in inbred mice. Behav Neurosci 108:186–195
Crabbe JC, Gallaher EJ, Cross SJ, Belknap JK (1998) Genetic determinants of sensitivity to diazepam in inbred mice. Behav Neurosci 112:668–677
Crabbe JC, Metten P, Gallaher EJ, Belknap JK (2002) Genetic determinants of sensitivity to pentobarbital in inbred mice. Psychopharmacology 161:408–416
Crawley JN (2000) Whats wrong with my mouse? Behavioral phenotyping of transgenic and knockout mice. Wiley, New York
Crawley JN, Belknap JK, Collins A, Crabbe JC, Frankel W, Henderson N, Hitzemann RJ, Maxson SC, Miner LL, Silva AJ, Wehner JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Paylor R (1997) Behavioral phenotypes of inbred mouse strains: implications and recommendations for molecular studies. Psychopharmacology 132:107–124
Cryan JF, Kaupmann K (2005) Don’t worry “B” happy: a role for GABAB receptors in anxiety and depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:36–43
Cryan JF, Kelliher P, Kelly JP, Leonard BE (1999) Comparative effects of serotonergic agonists with varying efficacy at the 5-HT(1A) receptor on core body temperature: modification by the selective 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY 100635. J Psychopharmacol 13:278–283
Cryan JF, Harkin A, Naughton M, Kelly JP, Leonard BE (2000) Characterization of d-fenfluramine-induced hypothermia: evidence for multiple sites of action. Eur J Pharmacol 390:275–285
Cryan JF, Kelly PH, Chaperon F, Gentsch C, Mombereau C, Lingenhoehl K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Spooren WP (2004) Behavioral characterization of the novel GABAB receptor-positive modulator GS39783 (N,N′-dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine): anxiolytic-like activity without side effects associated with baclofen or benzodiazepines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:952–963
Dar MS (1996) Mouse cerebellar GABAB participation in the expression of acute ethanol-induced ataxia and in its modulation by the cerebellar adenosinergic A1 system. Brain Res Bull 41:53–59
Daszuta A, Barrit MC (1982) Endogenous serotonin (5-HT) and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) levels in large regions and in discrete brain areas of C57BL and BALBc mice at three times of the day. Brain Res Bull 8:477–482
Daszuta A, Barrit MC, Faudon M (1982a) Developmental variations of brain serotonin, tryptophan, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid, and noradrenaline and dopamine content in two inbred strains of mice. Dev Neurosci 5:130–142
Daszuta A, Faudon M, Ternaux JP (1982b) Uptake of [3H]serotonin and [3H]noradrenaline in the raphe nuclei and the locus coeruleus of C57BL/6 Rholco and BALB/c Cenlco mice at three times of the day. Neurosci Lett 29:141–146
Dunham NW, Miya TS (1957) A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J Am Pharm Assoc (Baltim) 46:208–209
Festing MF, Simpson EM, Davisson MT, Mobraaten LE (1999) Revised nomenclature for strain 129 mice. Mamm Genome 10:836
Francis DD, Szegda K, Campbell G, Martin WD, Insel TR (2003) Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice. Nat Neurosci 6:445–446
Fritschy JM, Sidler C, Parpan F, Gassmann M, Kaupmann K, Bettler B, Benke D (2004) Independent maturation of the GABA(B) receptor subunits GABA(B1) and GABA(B2) during postnatal development in rodent brain. J Comp Neurol 477:235–252
Froestl W, Bettler B, Bittiger H, Heid J, Kaupmann K, Mickel SJ, Strub D (2003) Ligands for expression cloning and isolation of GABA(B) receptors. Farmaco 58:173–183
Frosini M, Valoti M, Sgaragli G (2004) Changes in rectal temperature and ECoG spectral power of sensorimotor cortex elicited in conscious rabbits by i.c.v. injection of GABA, GABA(A) and GABA(B) agonists and antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 141:152–162
Gassmann M, Shaban H, Vigot R, Sansig G, Haller C, Barbieri S, Humeau Y, Schuler V, Muller M, Kinzel B, Klebs K, Schmutz M, Froestl W, Heid J, Kelly PH, Gentry C, Jaton AL, Van der Putten H, Mombereau C, Lecourtier L, Mosbacher J, Cryan JF, Fritschy JM, Luthi A, Kaupmann K, Bettler B (2004) Redistribution of GABAB(1) protein and atypical GABAB responses in GABAB(2)-deficient mice. J Neurosci 24:6086–6097
Gray JA, Goodwin GM, Heal DJ, Green AR (1987) Hypothermia induced by baclofen, a possible index of GABAB receptor function in mice, is enhanced by antidepressant drugs and ECS. Br J Pharmacol 92:863–870
Griebel G, Belzung C, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (2000) Differences in anxiety-related behaviours and in sensitivity to diazepam in inbred and outbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 148:164–170
Hedlund PB, Kelly L, Mazur C, Lovenberg T, Sutcliffe JG, Bonaventure P (2004) 8-OH-DPAT acts on both 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors to induce hypothermia in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 487:125–132
Hegmann JP, Possidente B (1981) Estimating genetic correlations from inbred strains. Behav Genet 11:103–114
Humeniuk RE, Ong J, Kerr DI, White JM (1995) Characterization of GABAB ligands in vivo. Gen Pharmacol 26:417–424
Jackson HC, Nutt DJ (1991) Inhibition of baclofen-induced hypothermia in mice by the novel GABAB antagonist CGP 35348. Neuropharmacology 30:535–538
Jha SK, Islam F, Mallick BN (2001) GABA exerts opposite influence on warm and cold sensitive neurons in medial preoptic area in rats. J Neurobiol 48:291–300
Judge SJ, Ingram CD, Gartside SE (2004) GABA receptor modulation of 5-HT neuronal firing: characterization and effect of moderate in vivo variations in glucocorticoid levels. Neurochem Int 45:1057–1065
Kasture SB, Mandhane SN, Chopde CT (1996) Baclofen-induced catatonia: modification by serotonergic agents. Neuropharmacology 35:595–598
Kaupmann K, Cryan JF, Wellendorph P, Mombereau C, Sansig G, Klebs K, Schmutz M, Froestl W, van der Putten H, Mosbacher J, Brauner-Osborne H, Waldmeier P, Bettler B (2003) Specific gamma-hydroxybutyrate-binding sites but loss of pharmacological effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in GABA(B)(1)-deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 18:2722–2730
Lehmann A, Mattsson JP, Edlund A, Johansson T, Ekstrand AJ (2003) Effects of repeated administration of baclofen to rats on GABAB receptor binding sites and subunit expression in the brain. Neurochem Res 28:387–393
Liang F, Hatanaka Y, Saito H, Yamamori T, Hashikawa T (2000) Differential expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor-1a and -1b mRNA variants in GABA and non-GABAergic neurons of the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 416:475–495
Lucki I, Dalvi A, Mayorga AJ (2001) Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 155:315–322
Luscher C, Jan LY, Stoffel M, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA (1997) G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs) mediate postsynaptic but not presynaptic transmitter actions in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 19:687–695
Mannoury la Cour C, Hanoun N, Melfort M, Hen R, Lesch KP, Hamon M, Lanfumey L (2004) GABA(B) receptors in 5-HT transporter- and 5-HT1A receptor-knock-out mice: further evidence of a transduction pathway shared with 5-HT1A receptors. J Neurochem 89:886–896
McFadyen MP, Kusek G, Bolivar VJ, Flaherty L (2003) Differences among eight inbred strains of mice in motor ability and motor learning on a rotorod. Genes Brain Behav 2:214–219
Mineur YS, Crusio WE (2002) Behavioral and neuroanatomical characterization of FVB/N inbred mice. Brain Res Bull 57:41–47
Mombereau C, Kaupmann K, Froestl W, Sansig G, van der Putten H, Cryan JF (2004) Genetic and pharmacological evidence of a role for GABA(B) receptors in the modulation of anxiety- and antidepressant-like behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1050–1062
Myers RD, Beleslin DB, Rezvani AH (1987) Hypothermia: role of alpha 1- and alpha 2-noradrenergic receptors in the hypothalamus of the cat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:373–379
Perry HE, Wright RO, Shannon MW, Woolf AD (1998) Baclofen overdose: drug experimentation in a group of adolescents. Pediatrics 101:1045–1048
Pierau FK, Yakimova KS, Sann H, Schmid HA (1997) Specific action of GABAB ligands on the temperature sensitivity of hypothalamic neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 813:146–155
Pugh PL, Ahmed SF, Smith MI, Upton N, Hunter AJ (2004) A behavioural characterisation of the FVB/N mouse strain. Behav Brain Res 155:283–289
Queva C, Bremner-Danielsen M, Edlund A, Ekstrand AJ, Elg S, Erickson S, Johansson T, Lehmann A, Mattsson JP (2003) Effects of GABA agonists on body temperature regulation in GABA(B(1))−/− mice. Br J Pharmacol 140:315–322
Rustay NR, Wahlsten D, Crabbe JC (2003a) Assessment of genetic susceptibility to ethanol intoxication in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2917–2922
Rustay NR, Wahlsten D, Crabbe JC (2003b) Influence of task parameters on rotarod performance and sensitivity to ethanol in mice. Behav Brain Res 141:237–249
Sawynok J, Reid A (1986) Clonidine reverses baclofen-induced increases in noradrenaline turnover in rat brain. Neurochem Res 11:723–731
Schuler V, Luscher C, Blanchet C, Klix N, Sansig G, Klebs K, Schmutz M, Heid J, Gentry C, Urban L, Fox A, Spooren W, Jaton AL, Vigouret J, Pozza M, Kelly PH, Mosbacher J, Froestl W, Kaslin E, Korn R, Bischoff S, Kaupmann K, van der Putten H, Bettler B (2001) Epilepsy, hyperalgesia, impaired memory, and loss of pre- and postsynaptic GABA(B) responses in mice lacking GABA(B(1)). Neuron 31:47–58
Serrano JS, Minano FJ, Sancibrian M, Duran JA (1985) Involvement of bicuculline-insensitive receptors in the hypothermic effect of GABA and its agonists. Gen Pharmacol 16:505–508
Simpson EM, Linder CC, Sargent EE, Davisson MT, Mobraaten LE, Sharp JJ (1997) Genetic variation among 129 substrains and its importance for targeted mutagenesis in mice. Nat Genet 16:19–27
Smith DF, Vestergaard P (1979) The role of monoamines for the central effects of baclofen on behavior of rats. J Neural Transm 46:215–223
Smith MA, Yancey DL, Morgan D, Liu Y, Froestl W, Roberts DC (2004) Effects of positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor on cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 173:105–111
Svensson A, Carlsson ML, Carlsson A (1995) Crucial role of the accumbens nucleus in the neurotransmitter interactions regulating motor control in mice. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 101:127–148
Tarantino LM, Gould TJ, Druhan JP, Bucan M (2000) Behavior and mutagenesis screens: the importance of baseline analysis of inbred strains. Mamm Genome 11:555–564
Threadgill DW, Yee D, Matin A, Nadeau JH, Magnuson T (1997) Genealogy of the 129 inbred strains: 129/SvJ is a contaminated inbred strain. Mamm Genome 8:390–393
Turski L, Klockgether T, Schwarz M, Turski WA, Sontag KH (1990) Substantia nigra: a site of action of muscle relaxant drugs. Ann Neurol 28:341–348
Unal CB, Demiral Y, Ulus IH (1998) The effects of choline on body temperature in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 363:121–126
Urwyler S, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Mosbacher J, Lampert C, Froestl W, Koller M, Kaupmann K (2003) N,N′-Dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine (GS39783) and structurally related compounds: novel allosteric enhancers of gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:322–330
Waldvogel HJ, Billinton A, White JH, Emson PC, Faull RL (2004) Comparative cellular distribution of GABAA and GABAB receptors in the human basal ganglia: immunohistochemical colocalization of the alpha 1 subunit of the GABAA receptor, and the GABABR1 and GABABR2 receptor subunits. J Comp Neurol 470:339–356
Yakimova K, Sann H, Schmid HA, Pierau FK (1996) Effects of GABA agonists and antagonists on temperature-sensitive neurones in the rat hypothalamus. J Physiol 494(Pt 1):217–230
Zarrindast MR, Oveissi Y (1988) GABAA and GABAB receptor sites involvement in rat thermoregulation. Gen Pharmacol 19:223–226
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Cedric Mombereau for initiating inter-strain temperature studies and Christine Hunn and Hugo Buerki for excellent technical support. The authors would like to thank Dr. David Slattery for critical reading of the manuscript. This work is supported by National Institutes of Mental Health/National Institute on Drug Abuse grant U01 MH69062 to J.F.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobson, L.H., Cryan, J.F. Differential sensitivity to the motor and hypothermic effects of the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen in various mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 179, 688–699 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2086-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2086-1