Abstract
Rationale
While the effects of d-amphetamine in increasing performance have been established, there is a paucity of information on the effects of methamphetamine on cognition in drug-naive subjects, and no published information on the effects of intravenous methamphetamine administration in dependent individuals. The dihydropyridine-class calcium channel antagonist, isradipine, has been posited as a putative treatment to prevent methamphetamine-associated hypertensive crisis and its sequelae. Yet, isradipine’s effects on cognitive performance in methamphetamine-dependent individuals are not known.
Objective
Since individuals whose dependence on methamphetamine is attributable to the need to enhance performance may be loath to take a cognition-impairing medication, even for the treatment of life-threatening hypertensive crisis, it would be important to determine isradipine’s effects on performance.
Methods
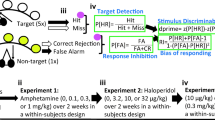
We therefore examined in a blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover design the cognitive effects of low and high doses of intravenous methamphetamine (15 mg and 30 mg, respectively) in both the presence and absence of isradipine.
Results
Intravenous d-methamphetamine produced dose-dependent increases in attention, concentration, and psychomotor performance. Isradipine, both with and without methamphetamine, had a modest effect to decrease attention.
Conclusion
Our results do not support the further testing of isradipine as a medication for improving the cognitive impairments that have been associated with chronic methamphetamine use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington D.C.
Besson JA, Palin AN, Ebmeier KP, Eagles JM (1988) Calcium antagonists and multi-infarct dementia: a trial involving sequential NMR and psychometric assessment. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 3:99–105
Birkenhager WH, de Leeuw PW, Staessen JA, Wang JG, Forette F, Seux ML (2000) Cognitive impairment and dementia in hypertension; the effect of antihypertensive medication [in Dutch]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 144:1469–1474
Brecht M-L, O’Brien A, von Mayrhauser C, Anglin MD (2004) Methamphetamine use behaviors and gender differences. Addict Behav 29:89–106
Cole BJ, Robbins TW (1987) Amphetamine impairs the discriminative performance of rats with dorsal noradrenergic bundle lesions on a 5-choice serial reaction time task: new evidence for central dopaminergic–noradrenergic interactions. Psychopharmacology 91:458–466
Cole BJ, Robbins TW (1992) Forebrain norepinephrine: role in controlled information processing in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 7:129–142
De Vries DJ, Beart PM (1984) Competitive inhibition of [3H]spiperone binding to D-2 dopamine receptors in striatal homogenates by organic calcium channel antagonists and polyvalent cations. Eur J Pharmacol 106:133–139
Denolle T, Sassano P, Allain H, Bentué-Ferrer D, Breton S, Cimarosti I, Ouatara B, Merienne M, Gandon J-M (2002) Effects of nicardipine and clonidine on cognitive functions and electroencephalography in hypertensive patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 16:527–535
Di Paolo T (1994) Modulation of brain dopamine transmission by sex steroids. Rev Neurosci 5:27–41
Drachman DA (1977) Memory and cognitive function in man: does the cholinergic system have a specific role? Neurology 27:783–790
Ernst T, Chang L, Leonido-Yee M, Speck O (2000) Evidence for long-term neurotoxicity associated with methamphetamine abuse: a 1H MRS study. Neurology 54:1344–1349
Forette F, Seux ML, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Birkenhager WH, Babarskiene MR, Babeanu S, Bossini A, Gil-Extremera B, Girerd X, Laks T, Lilov E, Moisseyev V, Tuomilehto J, Vanhanen H, Webster J, Yodfat Y, Fagard R (1998) Prevention of dementia in randomised double-blind placebo-controlled Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) trial. Lancet 352:1347–1351
Ginsberg MD, Lin B, Morikawa E, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Globus MY (1991) Calcium antagonists in the treatment of experimental cerebral ischemia. Arzneimittelforschung 41:334–337
Gunne LM (1977) Effects of amphetamine in humans. In: Martin WR (ed) Drug addiction II: amphetamine, psychotogen, and marihuana dependence. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 247–275
Harvey JA (1987) Behavioral pharmacology of central nervous system stimulants. Neuropharmacology 26:887–892
Heidrich A, Rosler M, Riederer P (1997) Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer dementia: therapy of cognitive symptoms—new results of clinical studies [German]. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 65:108–121
Hunt D (1995) Pulse check: national trends in drug abuse. Office of National Drug Control Policy, Washington D.C.
Johnson BA, Oldman D, Goodall EM, Chen YR, Cowen PJ (1996) Effects of GR 68755 on d-amphetamine-induced changes in mood, cognitive performance, appetite, food preference, and caloric and macronutrient intake in humans. Behav Pharmacol 7:216–227
Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Wells LT (2000) Effects of isradipine, a dihydropyridine-class calcium channel antagonist, on d-methamphetamine-induced cognitive and physiological changes in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:504–512
King TS, Steger RW, Morgan WW (1986) Effect of ovarian steroids to stimulate region-specific hypothalamic 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis in ovariectomized rats. Neuroendocrinology 42:344–350
Lee EHY, Lin WR (1991) Nifedipine and verapamil block the memory-facilitating effect of corticotropin-releasing factor in rats. Life Sci 48:1333–1340
Lepakhin VK, Ivleva AI, Romashova MF, Udotova SA, Zubovskii LG (1992) The effect of isradipine on the central and cerebral hemodynamics of patients with circulatory encephalopathy and hypertension [in Russian]. Eksp Klin Farmakol 55:24–26
LeVere SD, LeVere TE (1994) Old age and cognition: evaluation of a human short-term memory test with nonhuman primates and the memory-enhancing effects of nimodipine. Psychobiology 22:106–111
Levy A, Kong RM, Stillman MJ, Shukitt-Hale B, Kadar T, Rauch TM, Lieberman HR (1991) Nimodipine improves spatial working memory and elevates hippocampal acetylcholine in young rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:781–786
von Mayrhauser C, Brecht M-L, Anglin MD (2002) Use ecology and drug use motivations of methamphetamine users admitted to substance abuse treatment facilities in Los Angeles: an emerging profile. J Addict Dis 21:45–60
McLeod DR, Griffiths RR, Bigelow GE, Yingling J (1982) An automated version of the digit symbol substitution test (DSST). Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 14:463–466
McTavish SF, McPherson MH, Harmer CJ, Clark L, Sharp T, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2001) Antidopaminergic effects of dietary tyrosine depletion in healthy subjects and patients with manic illness. Br J Psychiatry 179:356–360
Mintzer MZ, Guarino J, Kirk T, Roache JD, Griffiths RR (1997) Ethanol and pentobarbital: comparison of behavioral and subjective effects in sedative drug abusers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 5:203–215
Nakane H, Ooboshi H, Ibayashi S, Yao H, Sadoshima S, Fujishima M (1995) Isradipine, a calcium channel blocker, attenuates the ischemia-induced release of dopamine but not glutamate in rats. Neurosci Lett 188:151–154
Quevedo J, Vianna M, Daroit D, Born AG, Kuyven CR, Roesler R, Quillfeldt JA (1998) L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel blocker nifedipine enhances memory retention when infused into the hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 69:320–325
Rawson RA, McCann MJ, Hasson AJ, Ling W (2000) Addiction pharmacotherapy 2000: new options, new challenges. J Psychoact Drugs 32:371–378
Roache JD, Cherek DR, Bennett RH, Schenkler JC, Cowan KA (1993) Differential effects of triazolam and ethanol on awareness, memory, and psychomotor performance. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:3–15
Rudin M, Sauter A, Wiederhold KH (1987) Application of NMR imaging and spectroscopy to the pharmacology of cerebro-vascular disorders. Therapie 42:477–481
Salo R, Nordahl TE, Possin K, Leamon M, Gibson DR, Galloway GP, Flynn NM, Henik A, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV (2002) Preliminary evidence of reduced cognitive inhibition in methamphetamine-dependent individuals. Psychiatry Res 111:65–74
SAS Institute, Inc. (2002) SAS user’s guide: statistics, version 9.00. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC
Sauter A, Rudin M (1986) Calcium antagonists reduce the extent of infarction in rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model as determined by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 17:1228–1234
Sauter A, Rudin M, Wiederhold KH (1988) Reduction of neural damage in irreversible cerebral ischemia by calcium antagonists. Neurochem Pathol 9:211–236
Schwartz BL, Fay-McCarthy M, Kendrick K, Rosse RB, Deutsch SI (1997) Effects of nifedipine, a calcium channel antagonist, on cognitive function in schizophrenic patients with tardive dyskinesia. Clin Neuropharmacol 20:364–370
Silverstone PH, Oldman D, Johnson B, Cowen PJ (1992) Ondansetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, partially attenuates the effects of amphetamine: a pilot study in healthy volunteers. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 7:37–43
Spiegel R (1979) Effects of amphetamines on performance and on polygraphic sleep parameters in man. In: Passouant P, Oswald I (eds) Pharmacology of the states of alertness. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 189–201
Taya K, Watanabe Y, Kobayashi H, Fujiwara M (2000) Nimodipine improves the disruption of spatial cognition induced by cerebral ischemia. Physiol Behav 70:19–25
Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, Simon SL, Geaga JA, Hong MS, Sui Y, Le JY, Toga AW, Ling W, London ED (2004) Structural abnormalities in the brains of human subjects who use methamphetamine. J Neurosci 24:6028–6036
US Department of Health and Human Services (2001) The DAWN report. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN), Washington D.C.
Vetulani J, Battaglia M, Sansone M (1997) Nimodipine on shuttle-box avoidance learning in mice: no impairment but slight improvement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:577–581
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D, Sedler MJ, Gatley SJ, Hitzemann R, Ding YS, Logan J, Wong C, Miller EN (2001) Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am J Psychiatry 158:377–382
Weiss B, Laties VG (1962) Enhancement of human performance by caffeine and the amphetamines. Pharmacol Rev 14:1–36
Yamada S, Uchida S, Ohkura T, Kimura R, Yamaguchi M, Suzuki M, Yamamoto M (1996) Alterations in calcium antagonist receptors and calcium content in senescent brain and attenuation by nimodipine and nicardipine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:721–727
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the National Institute on Drug Abuse for its support through Grant R01 DA 12969-04. We would like to thank Robert H. Cormier, Jr, for his technical assistance with preparation of the manuscript. We also appreciate the staff of the University Clinical Psychopharmacology Laboratory and the South Texas Addiction Research and Technology Center for their skilled work and dedication to this project. The experiment described in this article complies with the current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, B.A., Roache, J.D., Ait-Daoud, N. et al. Effects of isradipine on methamphetamine-induced changes in attentional and perceptual-motor skills of cognition. Psychopharmacology 178, 296–302 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1998-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1998-0