Abstract
Rationale
Alcohol has been shown to impair involuntary attention studied by event-related potentials using mismatch negativity (MMN) and P3a.
Objectives
However, no studies have investigated whether alcohol affects the magnetic counterparts of N1 (N1m), MMN (MMNm) and P3a (P3am).
Methods
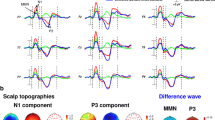
Auditory evoked potentials and magnetic fields elicited by infrequent deviant tones differing in frequency (5% and 20% change) and novel sounds were recorded with whole-head magnetoencephalography (MEG) and electroencephalography (EEG). Stimuli were presented separately to the left and right ear. Eleven right-handed subjects were studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled (0.8 g/kg ethanol or juice), cross-over design. N1m, MMNm, and P3am were calculated from the channel pair at the temporal cortex showing the strongest responses in the hemisphere contralateral to the stimulation. N1, MMN and P3a were analyzed from 12 electrodes at the midline frontocentral area.
Results
Alcohol reduced bilaterally N1, N1m, MMN and MMNm amplitudes. P3a amplitudes, but not P3am amplitudes were also significantly decreased. No effects of alcohol on the latencies of N1, MMN and P3a or their magnetic counterparts were observed.
Conclusions
Alcohol impairs the processing of tones, frequency change and novel sounds at different phases of auditory processing similarly in both hemispheres. MEG provides us with additional information unobtainable with EEG about the effects of alcohol on the neural correlates of cognition.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alho K (1995) Cerebral generators of mismatch negativity (MMN) and its magnetic counterpart (MMNm) elicited by sound changes. Ear Hear 16:38–51
Alho K, Winkler I, Escera C, Huotilainen M, Virtanen J, Jääskeläinen IP, Pekkonen E, Ilmoniemi RJ (1998) Processing of novel sounds and frequency changes in the human auditory cortex: magnetoencephalographic recordings. Psychophysiology 35:211–224
Baudena P, Halgren E, Heit G, Clarke JM (1996) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. III. Frontal cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:251–264
Boecker H, Wills AJ, Ceballos-Baumann A, Samuel M, Thompson PD, Findley LJ, Brooks DJ (1996) The effect of ethanol on alcohol-responsive essential tremor: a positron emission tomography study. Ann Neurol 39:650–658
Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (1998) Reduction in bold fMRI response to primary visual stimulation following alcohol ingestion. Psychiatry Res 82:135–146
Derogatis LR, Lipman RS, Covi L (1973) SCL-90: an outpatient psychiatric rating scale—preliminary report. Psychopharmacology 9:13–28
Escera C, Alho K, Winkler I, Näätänen R (1998) Neural mechanisms of involuntary attention to acoustic novelty and change. J Cogn Neurosci 10:590–604
Grillon C, Courchesne E, Ameli R, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1990) Increased distractibility in schizophrenic patients. Electrophysiologic and behavioral evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:171–179
Hämäläinen M, Hari R, Ilmoniemi RJ, Knuutila J, Lounasmaa OV (1993) Magnetoencephalography-theory, instrumentation, application to noninvasive studies of working brain. Rev Mod Phys 65:413–498
Huotilainen M, Winkler I, Alho K, Escera C, Virtanen J, Ilmoniemi RJ, Jääskeläinen IP, Pekkonen E, Näätänen R (1998) Combined mapping of human auditory EEG and MEG responses. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:370–379
Jääskeläinen IP, Pekkonen E, Alho K, Sinclair JD, Sillanaukee P, Näätänen R (1995a) Dose-related effect of alcohol on mismatch negativity and reaction time performance. Alcohol 12:491–495
Jääskelainen IP, Lehtokoski A, Alho K, Kujala T, Pekkonen E, Sinclair JD, Näätänen R, Sillanaukee P (1995b) Low dose of ethanol suppresses mismatch negativity of auditory event-related potentials. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:607–610
Jääskeläinen IP, Näätänen R, Sillanaukee P (1996a) Effect of acute ethanol on auditory and visual event-related potentials: a review and reinterpretation. Biol Psychiatry 40:284–291
Jääskeläinen IP, Pekkonen E, Hirvonen J, Sillanaukee P, Näätänen R (1996b) Mismatch negativity subcomponents and ethyl alcohol. Biol Psychol 43:13–25
Jääskelainen IP, Schroger E, Näätänen R (1999) Electrophysiological indices of acute effects of ethanol on involuntary attention shifting. Psychopharmacology 141:16–21
Kähkönen S, Ahveninen J (2002) Combination of magneto- and electroencephalography in studies of monoamine modulation on attention. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 24:27–34
Kähkönen S, Ahveninen J, Jääskeläinen IP, Kaakkola S, Näätänen R, Huttunen J, Pekkonen, E (2001) Effects of haloperidol on selective attention. A combined whole-head MEG and high-resolution EEG study. Neuropsychopharmacology 107:117–123
Kähkönen S, Ahveninen J, Pekkonen E, Kaakkola S, Huttunen J, Ilmoniemi R, Jääskeläinen IP (2002) Dopamine modulates involuntary attention shifting and reorienting: an electromagnetic study. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1894–1902
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PM, Sahgal A, Wright C (1987) Effects of alcohol on speed and accuracy in choice reaction time and visual search. Acta Psychol 65:147–163
Näätänen R (1992) Attention and brain function. Erlbaum, New Jersey
Näätänen R, Summala H (1976) Road user behaviour and traffic accidents. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Näätänen R, Ilmoniemi R, Alho K (1994) Magnetoencephalography in studies of human cognitive brain function. Trends Neurosci 17:389–395
Opitz B, Rinne T, Mecklinger A, von Cramon DY, Schröger E (2002) Differential contribution of frontal and temporal cortices to auditory change detection: fMRI and ERP results. Neuroimage 15:167–174
Parasuraman R, Beatty J (1980) Brain events underlying detection and recognition of weak sensory signals. Science 210:80–83
Porjesz B, Begleiter H (1983) Brain dysfunction and alcohol. In: Kissin B, Begleiter H (eds) The pathogenesis of alcoholism. Plenum, New York, pp 415–483
Reeves RR, Struve FA, Patrick G (1999) The effects of caffeine withdrawal on cognitive P300 auditory and visual evoked potentials. Clin Electroencephalogr 30:24–27
Rinne T, Alho K, Ilmoniemi RJ, Virtanen J, Näätänen R (2000) Separate time behaviors of the temporal and frontal MNN sources. Neuroimage 12:14–19
Sams M, Paavilainen P, Alho K, Näätänen R (1985) Auditory frequency discrimination and event-related potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 62:437–448
Tiihonen J, Kuikka J, Hakola P, Paanila J, Airaksinen J, Eronen M, Hallikainen T (1994) Acute ethanol-induced changes in cerebral blood flow. Am J Psychiatry 151:1505–1508
Virtanen J, Rinne T, Ilmoniemi RJ, Näätänen R (1996) MEG-compatible multichannel EEG electrode array. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 99:568–570
Virtanen J, Parkkonen L, Ilmoniemi RJ, Pekkonen E, Näätänen R (1997) Biopotential amplifier for simultaneous operation with biomagnetic instruments. Med Biol Eng Comput 35:402–408
Virtanen J, Ahveninen J, Ilmoniemi RJ, Näätänen R, Pekkonen E (1998) Replicability of MEG and EEG measures of the auditory N1/N1m-response. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:291–298
Volkow ND, Hitzemann R, Wolf AP, Logan J, Fowler JS, Christman D, Dewey SL, Schlyer D, Burr G, Vitkun S (1990) Acute effects of ethanol on regional brain glucose metabolism and transport. Psychiatry Res 35:39–48
Volkow ND, Mullani N, Gould L, Adler SS, Guynn RW, Overall JE, Dewey S (1998) Effects of acute alcohol intoxication on cerebral blood flow measured with PET. Psychiatry Res 24:201–209
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Franceschi D, Fowler JS, Thanos PK, Scherbaum N, Pappas N, Wong CT, Hitzemann RJ, Felder CA (2000) Regional brain metabolism during alcohol intoxication. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:822–829
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland and the research funds of the Helsinki University Central Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kähkönen, S., Marttinen Rossi, E. & Yamashita, H. Alcohol impairs auditory processing of frequency changes and novel sounds: a combined MEG and EEG study. Psychopharmacology 177, 366–372 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1960-1