Abstract
Rationale
The phenotype of genetically modified animals is thought to result from an interaction of gene manipulation with the genetic background and environmental factors.
Objectives
To test the behavioral and drug responses of Penk1−/− mice on different genetic backgrounds.
Methods
Congenic C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mouse strains with a targeted deletion of the Penk1 gene were generated. Behavior and drug effects were tested in models of pain and anxiety.
Results
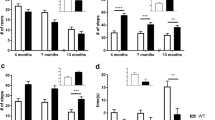
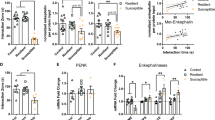
Penk1−/− mice showed exaggerated responses to painful or threatening environmental stimuli, but the expressivity of the mutant phenotype was strongly dependent on the behavioral paradigm and on the genetic background. For example, elevated levels of anxiety were readily detectable in C57BL/6J-Penk1−/− mice in the light–dark and startle response tests, but not in the social interaction test. In contrast, we found elevated levels of anxiety in DBA/2J-Penk1−/− mice only in the zero-maze and social interaction tests. In some cases, the idiosyncratic behavior masked the appearance of the knockout gene effect. The activity of the anxiogenic drug, m-chlorophenylpiperazine, but not the anxiolytic drug diazepam, was strain and genotype dependent. Mice with the Penk1 mutation on the DBA/2J, but not on other genetic backgrounds, showed an increased opioid-dependent stress-induced analgesia.
Conclusions
(1) The behavioral effects of the Penk1 gene deletion persists on different genetic backgrounds, but its detection sometimes requires the use of different behavioral paradigms. (2) The behavior of the background strain should be considered in the analysis of knockout mice to avoid floor and ceiling effects, which may mask the phenotype.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Angelis L, File SE (1979) Acute and chronic effects of three benzodiazepines in the social interaction anxiety test in mice. Psychopharmacology 64:127–129
Belknap JK, Noordewier B, Lame M (1989) Genetic dissociation of multiple morphine effects among C57BL/6J, DBA/2J and C3H/HeJ inbred mouse strains. Physiol Behav 46:69–74
Belknap JK, Lame M, Danielson PW (1990) Inbred strain differences in morphine-induced analgesia with the hot plate assay: a reassessment. Behav Genet 20:333–338
Belzung C, Le Pape G (1994) Comparison of different behavioral test situations used in psychopharmacology for measurement of anxiety. Physiol Behav 56:623–628
Bergeson SE, Helms ML, O’Toole LA, Jarvis MW, Hain HS, Mogil JS, Belknap JK (2001) Quantitative trait loci influencing morphine antinociception in four mapping populations. Mamm Genome 12:546–553
Blanchard DC, Griebel G, Blanchard RJ (2001) Mouse defensive behaviors: pharmacological and behavioral assays for anxiety and panic. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:205–218
Brady LS, Herkenham M, Rothman RB, Partilla JS, Konig M, Zimmer AM, Zimmer A (1999) Region-specific up-regulation of opioid receptor binding in enkephalin knockout mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 68:193–197
Clarke S, Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Hill RG, Kitchen I (2003) Region selective up-regulation of micro-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors but not opioid receptor-like 1 receptors in the brains of enkephalin and dynorphin knockout mice. Neuroscience 122:479–489
Clement Y, Proeschel MF, Bondoux D, Girard F, Launay JM, Chapouthier G (1997) Genetic factors regulate processes related to anxiety in mice. Brain Res 752:127–135
Costall B, Jones B, Kelly M, Naylor R, DM T (1989) Exploration of mice in a black and white test box: validation as a model of anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:777–785
Crabbe JC (2001) Use of genetic analyses to refine phenotypes related to alcohol tolerance and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:288–292
Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ, Buck KJ, Cunningham CL, Belknap JK (1999a) Identifying genes for alcohol and drug sensitivity: recent progress and future directions. Trends Neurosci 22:173–179
Crabbe JC, Wahlsten D, Dudek BC (1999b) Genetics of mouse behavior: interactions with laboratory environment. Science 284:1670–1672
Crawley JN, Belknap JK, Collins A, Crabbe JC, Frankel W, Henderson N, Hitzemann RJ, Maxson SC, Miner LL, Silva AJ, Wehner JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Paylor R (1997) Behavioral phenotypes of inbred mouse strains: implications and recommendations for molecular studies. Psychopharmacology 132:107–124
Davis M (1990) Animal models of anxiety based on classical conditioning: the conditioned emotional response (CER) and the fear-potentiated startle effect. Pharmacol Ther 47:147–165
Filliol D, Ghozland S, Chluba J, Martin M, Matthes HW, Simonin F, Befort K, Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Valverde O, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL (2000) Mice deficient for delta- and mu-opioid receptors exhibit opposing alterations of emotional responses. Nat Genet 25:195–200
Gerlai R (1996) Gene-targeting studies of mammalian behavior: is it the mutation or the background genotype? Trends Neurosci 19:177–181
Griebel G, Belzung C, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (2000) Differences in anxiety-related behaviours and in sensitivity to diazepam in inbred and outbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 148:164–170
Harris RB, Zhou J, Shi M, Redmann S, Mynatt RL, Ryan DH (2001) Overexpression of agouti protein and stress responsiveness in mice. Physiol Behav 73:599–608
Holmes A, Lit Q, Murphy DL, Gold E, Crawley JN (2003) Abnormal anxiety-related behavior in serotonin transporter null mutant mice: the influence of genetic background. Genes Brain Behav 2:365–380
Hood HM, Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Buck KJ (2001) Genomewide search for epistasis in a complex trait: pentobarbital withdrawal convulsions in mice. Behav Genet 31:93–100
Jenck F, Broekkamp CL, Van Delft AM (1989) Effects of serotonin receptor antagonists on PAG stimulation induced aversion: different contributions of 5HT1, 5HT2 and 5HT3 receptors. Psychopharmacology 97:489–495
Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C (2002) Exploring the opioid system by gene knockout. Prog Neurobiol 66:285–306
Konig M, Zimmer AM, Steiner H, Holmes PV, Crawley JN, Brownstein MJ, Zimmer A (1996) Pain responses, anxiety and aggression in mice deficient in pre-proenkephalin. Nature 383:535–538
Magara F, Muller U, Li ZW, Lipp HP, Weissmann C, Stagljar M, Wolfer DP (1999) Genetic background changes the pattern of forebrain commissure defects in transgenic mice underexpressing the beta-amyloid-precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4656–4661
Mogil JS, Marek P, O’Toole LA, Helms ML, Sadowski B, Liebeskind JC, Belknap JK (1994) Mu-opiate receptor binding is up-regulated in mice selectively bred for high stress-induced analgesia. Brain Res 653:16–22
Mogil JS, Sternberg WF, Balian H, Liebeskind JC, Sadowski B (1996) Opioid and nonopioid swim stress-induced analgesia: a parametric analysis in mice. Physiol Behav 59:123–132
Mogil JS, Wilson SG, Bon K, Lee SE, Chung K, Raber P, Pieper JO, Hain HS, Belknap JK, Hubert L, Elmer GI, Chung JM, Devor M (1999a) Heritability of nociception. I. Responses of 11 inbred mouse strains on 12 measures of nociception. Pain 80:67–82
Mogil JS, Wilson SG, Bon K, Lee SE, Chung K, Raber P, Pieper JO, Hain HS, Belknap JK, Hubert L, Elmer GI, Chung JM, Devor M (1999b) Heritability of nociception. II. ‘Types’ of nociception revealed by genetic correlation analysis. Pain 80:83–93
Ng GY, O’Dowd BF, George SR (1996) Genotypic differences in mesolimbic enkephalin gene expression in DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mice. Eur J Pharmacol 311:45–52
Nic Dhonnchadha BA, Bourin M, Hascoet M (2003) Anxiolytic-like effects of 5-HT2 ligands on three mouse models of anxiety. Behav Brain Res 140:203–214
O’Connor P, Chipkin RE (1984) Comparisons between warm and cold water swim stress in mice. Life Sci 35:631–639
Paylor R, Crawley JN (1997) Inbred strain differences in prepulse inhibition of the mouse startle response. Psychopharmacology 132:169–180
Pelleymounter MA, Joppa M, Ling N, Foster AC (2002) Pharmacological evidence supporting a role for central corticotropin-releasing factor (2) receptors in behavioral, but not endocrine, response to environmental stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:145–152
Petruzzi R, Ferraro TN, Kurschner VC, Golden GT, Berrettini WH (1997) The effects of repeated morphine exposure on mu opioid receptor number and affinity in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Life Sci 61:2057–2064
Przewlocka B, Vetulani J, Lason W, Dziedzicka M, Silberring J, Castellano C, Przewlocki R (1988) The difference in stress-induced analgesia in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice: a search for biochemical correlates. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 40:497–506
Raber J, Akana SF, Bhatnagar S, Dallman MF, Wong D, Mucke L (2000) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal dysfunction in Apoe(−/−) mice: possible role in behavioral and metabolic alterations. J Neurosci 20:2064–2071
Ragnauth A, Schuller A, Morgan M, Chan J, Ogawa S, Pintar J, Bodnar RJ, Pfaff DW (2001) Female preproenkephalin-knockout mice display altered emotional responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1958–1963
Shepherd JK, Grewal SS, Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Dourish CT (1994) Behavioural and pharmacological characterisation of the elevated “zero-maze” as an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology 116:56–64
Trullas R, Skolnick P (1993) Differences in fear motivated behaviors among inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 111:323–331
Wahlsten D (2001) Standardizing tests of mouse behavior: reasons, recommendations, and reality. Physiol Behav 73:695–704
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the lab for suggestions on the experiments and the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Land Nordrhein Westphalen (Innovationsprogramm Forschung) and the BONFOR Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilkei-Gorzo, A., Racz, I., Michel, K. et al. Behavioral phenotype of pre-proenkephalin-deficient mice on diverse congenic backgrounds. Psychopharmacology 176, 343–352 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1904-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1904-9