Abstract
Rationale
Possible effects of reinforcer type on the results of drug discrimination studies have not been examined systematically, but different deprivation operations and differentially effective reinforcers might well influence outcomes.
Objective
Therefore, this study examined the influence of reinforcer (food or water) as well as route of administration (IP or IG) on gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) discrimination.
Methods
Four separate groups of six rats were trained under a resetting fixed-ratio schedule to discriminate between 300 mg/kg GHB and vehicle under these conditions, then generalization tests were conducted with gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD), ethanol, and ethanol plus 150 mg/kg GHB.
Results
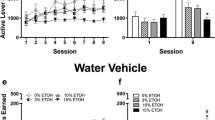
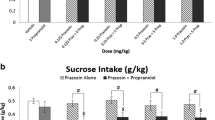
Food maintained significantly higher response rates than water, but there were no significant differences among the four training groups in response accuracy or sessions required to meet the discrimination criterion. Training conditions significantly affected the results of stimulus generalization tests. The IG-Water group was most sensitive to a lower dose of GHB, and only the IP-Water group failed to generalize to orally-administered GHB. Gamma-butyrolactone and 1,4-butanediol fully substituted in all except the IP-Food group. Ethanol did not fully substitute for GHB in any group, and the combination of GHB (150 mg/kg) and ethanol did not have additive effects.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that methodological variables during drug discrimination training can certainly influence the results of stimulus generalization. Future investigations into the behavioral and/or physiological mechanisms that account for these effects are warranted.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker LE, Taylor MM (1997) Assessment of the MDA and MDMA optical isomers in a stimulant-hallucinogen discrimination. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:737–748
Carter LP, Flores LR, Wu H, Chen W, Unzeitig AW, Coop A, France, CP (2003) The role of GABAB receptors in the discriminative stimulus effects of γ-hydroxybutyrate in rats: time course and antagonism studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:668–674
Colombo G, Agabio R, Bourguignon J, Fadda F, Lobina C, Maitre M, Reali R, Schmitt M, Gessa GL (1995a) Blockade of the discriminative stimulus effects of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) by the GHB receptor antagonist NCS-382. Physiol Behav 58:587–590
Colombo G, Agabio R, Lobina C, Reali R, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1995b) Symmetrical generalization between the discriminative stimulus effects of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and ethanol: occurrence within narrow dose ranges. Physiol Behav 57:105–111
Colombo G, Agabio R, Lobina C, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998) Involvement of GABAA and GABAB receptors in the mediation of discriminative stimulus effects of γ-hydroxybutyric acid. Physiol Behav 64:293–302
Goodwin AK, Baker LE (2000) A three-choice drug discrimination procedure dissociates the discriminative stimulus effects of MDMA and d-amphetamine. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:415–423
Goodwin AK, Pynnonen D, Baker LE (2003) Serotonergic-dopaminergic mediation of MDMA’s discriminative stimulus effects in a three-choice discrimination. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:987–995
Extance K, Goudie AJ (1981) Inter-animal olfactory cues in operant drug discrimination procedure in rats. Psychopharmacology 91:67–73
Lobina C, Agabio R, Reali R, Gessa GL, Colombo G (1999) Contribution of GABAA and GABAB receptors to the discriminative stimulus produced by gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Pharmacol Biochem Behavior 64:363–365
Makhay M, Young A, Poling A (1998) Establishing morphine and U-50,488H as discriminative stimuli in a three-choice assay with pigeons. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 6:3–9
Metcalf BR, Stahl JM, Allen JD, Woolfolk DR, Soto PL (2001) Discrimination of gamma-hydroxybutyrate and ethanol administered separately and as a mixture in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 70:31–41
National Research Council, Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, Commission on Life Sciences (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington D.C.
Nicholson KL, Balster RL (2001) GHB: a new and novel drug of abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend 63:1–22
Stolerman IP (1993) Drug discrimination. In: van Haaren F (ed), Methods in behavioral pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 217–244
Stolerman IP, D’Mello GD (1981) Role of training conditions in discrimination of central nervous system stimulants Psychopharmacology 73:295–302
White FJ, Appel JB (1982) Training dose as a factor in LSD-saline discrimination. Psychopharmacology 76:20–25
Whitton L (2001) Conference highlights increasing GHB abuse. NIDA Notes 16 (2), http://www.drugabuse.gov/NIDA_Notes/NNVol16N2/Conference.html
Winter JC (1981) The stimulus properties of γ-hydroxybutyrate. Psychopharmacology 73:372–375
Wu H, Zink N, Carter LP (2003) A tertiary alcohol analog of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid as a specific gamma-hydroxybutyric acid receptor ligand. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:639–675
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (1 R01 DA14904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, L.E., Pynnonen, D. & Poling, A. Influence of reinforcer type and route of administration on gamma-hydroxybutyrate discrimination in rats. Psychopharmacology 174, 220–227 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1744-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1744-z