Abstract
Rationale
Since baclofen, the prototypical GABAB receptor agonist, is known to reduce the activity of dopaminergic mesolimbic neurons, a putative antipsychotic property of this compound has been suggested, but the evidence for this is still controversial.
Objectives
The aim of the present study was to elucidate the effects of baclofen on the prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR), a behavioral paradigm considered to be one of the most powerful tools for the evaluation of sensorimotor gating and for the screening of antipsychotics.
Methods
We tested the effects of baclofen (1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/kg IP) in rats, per se and in co-treatment with some of the substances known to induce a robust reduction of PPI, such as apomorphine (0.25 mg/kg SC) and dizocilpine (0.1 mg/kg SC). Finally, in order to ascertain whether the effects of baclofen could be ascribed to its activity on GABAB receptors, we analyzed whether its action could be prevented by pretreatment with SCH 50911, a selective GABAB receptor antagonist (20 mg/kg IP). All the experiments were carried out using standard procedures for the assessment of PPI of the ASR.
Results
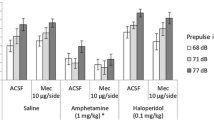
Baclofen per se produced no significant change in PPI parameters. Moreover, while no effect on apomorphine-mediated alterations in PPI parameters was observed, baclofen proved able to reverse dizocilpine-induced PPI disruption, and this effect was significantly prevented by SCH 50911. On the other hand, this last compound exhibited no effects per se at the same dose.
Conclusions
These results indicate that GABAB receptors are implicated in the neurobiological circuitry accounting for glutamatergic action in sensorimotor gating, and therefore can be proposed as putative new targets in the pharmacological therapy of psychotic disorders. Further studies should be addressed to evaluate more closely the clinical efficacy of baclofen in this respect.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese G (2002) The medical management of spasticity. Eur J Neurol 9:30–34
Angrist B (1994) Clinical variations of amphetamine psychosis. In: Cho AK, Segal DS (eds) Amphetamine and its analogs: psychopharmacology, toxicology, and abuse. Academic Press, New York, pp 387–414
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1998) Multiple limbic regions mediate the disruption of prepulse inhibition produced in rats by the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist dizocilpine. J Neurosci 18:8394–8401
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1994) Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:787–794
Bartholini G (1985) GABA receptor agonists: pharmacological spectrum and therapeutic action. Med Res Rev 5:55–75
Bast T, Zhang W, Feldon J, White IM (2000) Effects of MK801 and neuroleptics on prepulse inhibition: re-examination in two strains of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:647–658
Beckmann H, Frische M, Ruther E, Zimmer R (1977) Baclofen (para-chlorphenyl-GABA) in schizophrenia. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol 10:26–31
Benes FM, Berretta S (2001) GABAergic interneurons: implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:1–27
Beskid M, Rozycka Z, Taraszewska A (1999) Quinolinic acid and GABA-B receptor ligand: effect on pyramidal neurons of the CA1 sector of rat's dorsal hippocampus following peripheral administration. Folia Neuropathol 37:99–106
Bigelow LB (1977) Baclofen in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull 13:4–5
Braff DL, Geyer MA, Light GA, Sprock J, Perry W, Cadenhead KS, Swerdlow NR (2001) Impact of prepulse characteristics on the detection of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 49:171–178
Bubser M, Keseberg U, Notz PK, Schmidt WJ (1992) Differential behavioural and neurochemical effects of competitive and non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 229:75–82
Caine SB, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1992) Hippocampal modulation of acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1201–1208
Charles KJ, Evans ML, Robbins MJ, Calver AR, Leslie RA, Pangalos MN (2001) Comparative immunohistochemical localisation of GABA(B1a), GABA(B1b) and GABA(B2) subunits in rat brain, spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion. Neuroscience 106:447–467
Cott J, Carlsson A, Engel J, Lindqvist M (1976) Suppression of ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation by GABA-like drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 295:203–209
Cousins MS, Roberts DC, De Wit H (2002) GABA(B) receptor agonists for the treatment of drug addiction: a review of recent findings. Drug Alcohol Depend 65:209–220
Danober L, Heinbockel T, Driesang RB, Pape HC (2000) Synaptic mechanisms of NMDA-mediated hyperpolarization in lateral amygdaloid projection neurons. Neuroreport 11:2501–2506
Decker MW, Curzon P, Brioni JD (1995) Influence of separate and combined septal and amygdala lesions on memory, acoustic startle, anxiety, and locomotor activity in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 64:156–168
Durkin MM, Gunwaldsen CA, Borowsky B, Jones KA, Branchek TA (1999) An in situ hybridization study of the distribution of the GABA(B2) protein mRNA in the rat CNS. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 71:185–200
Engberg G, Kling-Petersen T, Nissbrandt H (1993) GABAB-receptor activation alters the firing pattern of dopamine neurons in the rat substantia nigra. Synapse 15:229–238
Erhardt S, Mathe JM, Chergui K, Engberg G, Svensson TH (2002) GABA(B) receptor-mediated modulation of the firing pattern of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 365:173–180
Frederiksen PK (1975) Baclofen in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lancet 1:702
Furuya Y, Kagaya T, Ogura H, Nishizawa Y (1999) Competitive NMDA receptor antagonists disrupt prepulse inhibition without reduction of startle amplitude in a dopamine receptor-independent manner in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 364:133–140
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1998) Measurement of startle response, prepulse inhibition, and habituation. In: Crawley JN, Skolnick P (eds) Current protocols in neuroscience. Wiley, New York, pp 1–15
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull 25:485–498
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Graham FK (1975) The more or less startling effects of weak prestimulation. Psychophysiology 1:238–248
Gulmann NC, Bahr B, Andersen B, Eliassen HM (1976) A double-blind trial of baclofen against placebo in the treatment of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 54:287–293
Hide TM, Casanova MF, Kleinman JE (1991) Neuroanatomical and neurochemical pathology in schizophrenia. In: Tasman A, Goldfinger SM (eds) American Psychiatric Press review of psychiatry, vol 10. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, pp 7–23
Hoffman DC, Donovan H, Cassella JV (1993) The effects of haloperidol and clozapine on the disruption of sensorimotor gating induced by the noncompetitive glutamate antagonist MK-801. Psychopharmacology 116:437–442
Kato K, Goto M, Fukuda H (1982) Baclofen: inhibition of the release of l-[3H]glutamate and l-[3H]aspartate from rat whole brain synaptosomes. Gen Pharmacol 13:445–447
Keith VA, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Failure of haloperidol to block the effects of phencyclidine and dizocilpine on prepulse inhibition of startle. Biol Psychiatry 30:557–566
Knable MB, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR (1998) Neurobiology of schizophrenia. In: Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB (eds) American Psychiatric Press textbook of psychopharmacology, 2nd edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, pp 589–607
Koch M, Fendt M, Kretschmer BD (2000) Role of the substantia nigra pars reticulata in sensorimotor gating, measured by prepulse inhibition of startle in rats. Behav Brain Res 117:153–162
Lehmann-Masten VD, Geyer MA (1991) Spatial and temporal patterning distinguishes the locomotor activating effects of dizocilpine and phencyclidine in rats. Neuropharmacology 30:629–636
Lewis DA (2000) GABAergic local circuit neurons and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:270–276
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
McGhie A, Chapman J (1961) Disorders of attention and perception in early schizophrenia. Br J Pharmacol 34:102–116
Menon MK, Clark WG, Vivonia C (1980) Interaction between phencyclidine (PCP) and GABA-ergic drugs: clinical implications. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:113–117
Mizukami K, Sasaki M, Ishikawa M, Iwakiri M, Hidaka S, Shiraishi H, Iritani S (2000) Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptor in the hippocampus of subjects with schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 283:101–104
Mizukami K, Ishikawa M, Hidaka S, Iwakiri M, Sasaki M, Iritani S (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of GABAB receptor in the entorhinal cortex and inferior temporal cortex of schizophrenic brain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26:393–396
Moghaddam B, Adams B, Verma A, Daly D (1997) Activation of glutamatergic neurotransmission by ketamine: a novel step in the pathway from NMDA receptor blockade to dopaminergic and cognitive disruptions associated with the prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 17:2921–2927
Nevins ME, Nash SA, Beardsley PM (1993) Quantitative grip strength assessment as a means of evaluating muscle relaxation in mice. Psychopharmacology 110:92–96
Prosser HM, Gill CH, Hirst WD, Grau E, Robbins M, Calver A, Soffin EM, Farmer CE, Lanneau C, Gray J, Schenck E, Warmerdam BS, Clapham C, Reavill C, Rogers DC, Stean T, Upton N, Humphreys K, Randall A, Geppert M, Davies CH, Pangalos MN (2001) Epileptogenesis and enhanced prepulse inhibition in GABA(B1)-deficient mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 17:1059–1070
Ralph-Williams RJ, Lehmann-Masten V, Otero-Corchon V, Low MJ, Geyer MA (2002) Differential effects of direct and indirect dopamine agonists on prepulse inhibition: a study in D1 and D2 receptor knock-out mice. J Neurosci 22:9604–9611
Reijmers LG, Vanderheyden PM, Peeters BW (1995) Changes in prepulse inhibition after local administration of NMDA receptor ligands in the core region of the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 272:131–138
Reynolds GP, Beasley CL, Zhang ZJ (2002) Understanding the neurotransmitter pathology of schizophrenia: selective deficits of subtypes of cortical GABAergic neurons. J Neural Transm 109:881–889
Schopf J, Hucker H (1977) Baclofen in the treatment of schizophrenia: a pilot study. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol 10:89–91
Sharkey J, Ritchie IM, Butcher SP, Kelly JS (1996) Comparison of the patterns of altered cerebral glucose utilisation produced by competitive and non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists. Brain Res 735:67–82
Steinpresis RE (1996) The behavioral and neurochemical effects of phencyclidine in humans and animals: some implications for modeling psychosis. Behav Brain Res 74:45–55
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1991) Effects of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:530–536
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Geyer MA (1992) Regionally selective effects of intracerebral dopamine infusion on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 108:189–195
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (2000) Animal models of sensorimotor gating: what we know, what we think we know, and what we hope we know soon. Behav Pharmacol 11:185–204
Yamada J, Saitow F, Satake S, Kiyohara T, Konishi S (1999) GABA(B) receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission in the basolateral amygdala. Neuropharmacology 38:1743–1753
Zhang J, Chiodo LA, Freeman AS (1992) Electrophysiological effects of MK-801 on rat nigrostriatal and mesoaccumbal dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 590:153–163
Zhang J, Engel JA, Ericson M, Svensson L (1999) Involvement of the medial geniculate body in prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Psychopharmacology 141:189–196
Zhang WN, Bast T, Feldon J (2000) Microinfusion of the non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801 (dizocilpine) into the dorsal hippocampus of Wistar rats does not affect latent inhibition and prepulse inhibition, but increases startle reaction and locomotor activity. Neuroscience 101:589–599
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Pierfranco Spano, Department of Pharmacology, University of Brescia, for his precious suggestions as well as Mr. Grant C. Luckey, for his assistance with manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bortolato, M., Frau, R., Aru, G.N. et al. Baclofen reverses the reduction in prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response induced by dizocilpine, but not by apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 171, 322–330 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1589-5