Abstract
Rationale
Despite the increasing use of cannabis among adolescents, there is scarce information about the long-term effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists in appropriate animal models.
Objectives
We aimed to investigate the behavioural features of adult male and female Wistar rats that had been exposed to a chronic treatment with the cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 (CP) during the juvenile period.
Methods
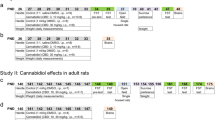
CP (0.4 mg/kg i.p.) or its corresponding vehicle was administered once daily, from day 35 to day 45. In adulthood, the animals were tested in the holeboard, the open field and the elevated plus-maze, under different stress (illumination) conditions. After a resting period, the serum corticosterone levels (radioimmunoassay) of the animals were measured. The effects of CP on food intake and somatic growth were monitored throughout the experimental period.
Results
The CP treatment induced significant sex-dependent effects on holeboard activity, as well as a decrease in the level of emotionality/anxiety in the open field and in the plus-maze. The animals receiving CP also showed diminished food intake and body weights during the treatment period, but both parameters recovered normal values during the period after treatment. No significant effect of the CP treatment on corticosterone levels was found.
Conclusions
The results demonstrate that chronic administration of CP during the peri-adolescent period resulted in marked behavioural effects in adulthood. The nature of these effects depended on the sex of the animals and on the specific behavioural test. The possible neurobiological substrates underlying the effects of CP are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrendero F, Maldonado R (2002) Involvement of the opioid system in the anxiolytic-like effects induced by delta (9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacology 163:111–117
Chaperon F, Thiébot M-H (1999) Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:243–281
De Cabo C, Viveros MP (1997) Effects of neonatal naltrexone on neurological and somatic development in rats of both genders. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19:499–509
De Cabo de la Vega C, Pujol A, Viveros MP (1995) Neonatally administered naltrexone affects several behavioral responses in adult rats of both genders. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:277–286
Fernández B, Antelo MT, Guaza C, Alberti I, Pinillos ML, Viveros MP (1999) Naltrindole administration during the preweanling period and manipulation affect adrenocortical reactivity in young rats. Dev Brain Res 112:135–137
Fernández-Ruiz J, Berrendero F, Hernández ML, Romero J, Ramos JA (1999) Role of endocannabinoids in brain development. Life Sci 65:725–736
File SE (1992) Behavioral detection of anxiolytic action. In: Elliot JM, Heal DJ, Marsden CA (eds) Experimental approaches to anxiety and depression. Wiley, New York, pp 25–44
Fuentes JA, Ruiz-Gallo M, Manzanares J, Vela G, Reche I, Corchero J (1999) Cannabinoids as potential new analgesics. Life Sci 65:675–685
Gray JA (1987) The psychology of fear and stress. Problems in the behavioural sciences, vol 5. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gruber AJ, Pope HG Jr (2002) Marijuana use among adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 49:389–413
Johnston AL, File SE (1991) Sex differences in animal tests of anxiety. Physiol Behav 49:245–250
König M, Zimmer AM, Steiner H, Holmes PV, Crawley JN, Brownstein MJ, Zimmer A (1996) Pain responses, anxiety and aggression in mice deficient in pre-proenkephalin. Nature 383:535–538
Kshama D, Hrishikeshavan HJ, Shanbhogue R, Munonyedi US (1990) Modulation of baseline behavior in rats by putative serotonergic agents in three ethoexperimental paradigms. Behav Neural Biol 54:234–253
Kumar AM, Haney M, Becker T, Thompson ML, Kream RM, Miczek KA (1990) Effect of early exposure to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the levels of opioid peptides, gonadotropin-releasing hormone and substance P in adult male rat brain. Brain Res 525:78–83
Lynskey MT, Heath AC, Bucholz KK, Slutske WS, Madden PAF, Nelson EC, Statham DJ, Martin NG (2003) Escalation of drug use in early-onset cannabis users vs co-twin controls. JAMA 289:427–433
Manning FJ, McDonough JH, Elsmore TF, Saller C, Sodetz FJ (1971) Inhibition of normal growth by chronic administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Science 174:424–426
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Romero J, Fernández-Ruiz J, Ramos JA, Fuentes JA (1998) Chronic administration of cannabinoids regulates proenkephalin mRNA levels in selected regions of the rat brain. Mol Brain Res 55:126–132
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Fuentes JA (1999a) Opioid and cannabinoid receptor-mediated regulation of the increase in adrenocorticotropin hormone and corticosterone plasma concentrations induced by central administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Brain Res 839:73–179
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Romero J, Fernández-Ruiz JJ, Ramos JA, Fuentes JA (1999b) Pharmacological and biochemical interactions between opioids and cannabinoids. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:287–294
Marín S, Marco E, Biscaia M, Fernández B, Rubio M, Guaza C, Schmidhammer H, Viveros MP (2003) Involvement of the κ-opioid receptor in the anxiogenic-like effect of CP 55,940 in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:649–656
McGregor IS, Issakidis CN, Prior G (1996) Aversive effects of the synthetic cannabinoid CP 55,940 in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:657–664
Miczek KA, Dixit BN (1980) Behavioral and biochemical effects of chronic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Psychopharmacology 67:195–202
Mokler DJ, Robinson SE, Johnson JH, Hong JS, Rosencrans JA (1986) Effects of postweaning administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on adult behavioral and neuroendocrine function in Sprague-Dawley and Fischer-344 rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 8:407–413
Navarro M, Rubio P, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (1994) Sex-dimorphic psychomotor activation after perinatal exposure to (−)-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. An ontogenic study in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 116:414–422
Navarro M, Rubio P, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (1995) Behavioural consequences of maternal exposure to natural cannabinoids in rats. Psychopharmacology 122:1–14
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arms entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Robbins TW (1977) A critique of the methods available for the measurement of spontaneous motor activity. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 7. Plenum, New York, pp 37–82
Rodriguez De Fonseca F, Ramos JA, Bonin A, Fernández-Ruiz JJ (1993) Presence of cannabinoid binding sites in the brain from early postnatal ages. Neuroreport 4:135–138
Romero EM, Fernández B, Sagredo O, Gomez N, Urigüen L, Guaza C, De Miguel R, Ramos JA, Viveros MP (2002) Antinociceptive, behavioural and neuroendocrine effects of CP 55,940 in young rats. Dev Brain Res 136:85–92
Rubino T, Massi P, Patrini G, Venier I, Giagnoni G, Parolaro D (1994) Chronic CP-55,940 alters cannabinoid receptor mRNA in the rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. Neuroreport 5:2493–2496
Sañudo-Peña MC, Romero J, Seale GE, Fernández-Ruiz JJ, Walker JM (2000) Activational role of cannabinoids on movement. Eur J Pharmacol 391:269–274
Vela G, Martín S, García-Gil L, Crespo JA, Ruiz-Gayo M, Fernández-Ruiz JJ, García-Lecumberri C, Pélaprat D, Fuentes JA, Ramos JA, Ambrosio E (1998) Maternal exposure to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol facilitates morphine self-administration behavior and changes regional binding to central μ opioid receptors in adult offspring female rats. Brain Res 807:101–109
Viveros MP, Hernández R, Martinez I, González P (1988) Effects of social isolation and crowding upon adrenocortical reactivity and behavior in the rat. Rev Esp Fisiol 44:315–322
Viveros MP, Martín S, Ormazabal MJ, Alfaro MJ, Martín MI (1996) Effects of nimodipine and nifedipine upon behavior and regional brain monoamines in the rat. Psychopharmacology 127:123–132
Viveros MP, Fernández B, Guayerbas N, De la Fuente M (2001) Behavioral characterization of a mouse model of premature immunosenescence. J Neuroimmunol 114:80–88
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (BFI2000–0611) and Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid (CAM 08.8–004.97–02). The authors wish to thank Dr. A Gallego for assistance in the statistical analysis. Beatriz Fernández and Miguel Biscaia have a postdoctoral and a predoctoral grant, respectively, from the Ministerio de Educación y Cultura.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biscaia, M., Marín, S., Fernández, B. et al. Chronic treatment with CP 55,940 during the peri-adolescent period differentially affects the behavioural responses of male and female rats in adulthood. Psychopharmacology 170, 301–308 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1550-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1550-7