Abstract
Rationale
The selective CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716, has been demonstrated to reduce food consumption in a range of animal species.
Objective
To assess the effect of chronic administration of SR 141716 on body weight and ingestive behaviour of lean and obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats.
Methods
Lean and obese Zucker rats were orally dosed with SR 141716 (3, 10, 30 mg/kg PO), sibutramine (5 mg/kg PO) or vehicle for one week. Pair-fed controls provided insight as to whether the effect of SR 141716 on body weight was attributable to drug-induced hypophagia. Subsequently, the effect of chronic oral administration of SR 141716 (1, 3, 10 mg/kg) was assessed for 28 days. At the end of this period, all animals were given vehicle for 14 days. The incidence of wet-dog shakes, yawning, scratching, and grooming behaviours, was assessed after acute administration and at weekly intervals thereafter for 4 weeks.
Results
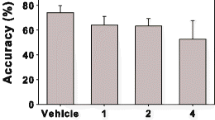
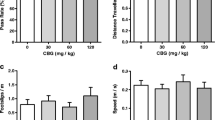
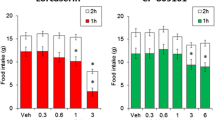
SR 141716 dose-dependently decreased food intake and body weight gain in both lean and obese animals. The inhibition of food intake and body weight gain was greater in obese Zuckers than in lean Zucker controls. Changes in the body weights of pair-fed controls closely paralleled those of their drug-treated counterparts. Chronic 28-day treatment led to a maintained reduction of body weight gain. Withdrawal of SR 141716 on day 28 resulted in rebound hyperphagia and a significant weight gain. On acute administration, SR 141716 dose-dependently induced motor behaviours that showed tolerance upon repeated administration.
Conclusion
These data indicate that chronic oral treatment with SR 141716 significantly reduces the food intake and body weight gain of obese and lean Zucker rats, an effect that is greater in obese animals and reversible upon drug withdrawal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceto MD, Scates SM, Lowe JA, Martin BR (1996) Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: studies on precipitated and abrupt withdrawal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1290–1295
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot MH, Poncelet M, Soubrie P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 132:104–106
Black SC, Hildebrandt AL, Kelly-Sullivan DM (2002) Determination of CB1 receptor antagonist anorectic efficacy vs adipose tissue mass reduction. Symposium on the cannabinoids, Burlington, Vt., International Cannabinoid Research Society
Colombo G, Agabio R, Diaz G, Lobina C, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998) Appetite suppression and weight loss after the cannabinoid antagonist SR141716. Life Sci 63:PL113–117
Darmani NA, Pandya DK (2000) Involvement of other neurotransmitters in behaviours induced by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716A in naive mice. J Neural Transm 107:931–945
Devane WA, Dysfarz FA, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, Howlett AC (1988) Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 34:605–613
Devane WA, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, tevenson LA, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R (1992) Isolation of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 258:1946–1949
Di Marzo V, Goparaju SK, Wang L, Liu J, Batkai S, Jaral Z, Fezza F, Miura GI, Palmiter RD, Sugiura T, Kunos G (2001) Leptin-regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature 410:822–825
Foltin RW, Fischmann MW, Byme MF (1988) Effects of smoked marijuana on food intake and body weight of humans living in a residential laboratory. Appetite 11:1–14
Gomez R, Navarro M, Ferrer B, Trigo JM, Bilbao A, Del Arco I, Cippitelli A, Nava F, Piomelli D, Rodriguez de Fonseca (2002) A peripheral mechanism for CB1 cannabinoid receptor-dependent modulation of feeding. J Neurosci 22:9612–9617
Hanus L, Abu-Lafi S, Fride E, Breuer A, Vogel Z, Shalev DE, Kustanovich I, Mechoulam R (2001) 2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether, an endogenous agonist of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3662–3665
Heshmati HM, Caplain H, Bellisle F, Mosse M, Fauveau C, Le Fur G (2001) SR141716, a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, reduces hunger, caloric intake, and body weight in overweight or obese men. Obesity Res 9:O69
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, Felder CC, Herkenham M, Mackie K, Martin BR, Mechoulam R, Pertwee RG (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:161–202
Janoyan JJ, Crim JL, Darmani NA (2002) Reversal of SR 141716A-induced head-twitch and ear-scratch responses in mice by Δ9-THC and other cannabinoids. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:155–162
Jamshidi N, Taylor DA (2001) Anandamide administration into the ventromedial hypothalamus stimulates appetite in rats. Br J Pharmacol 134:1151–1154
Kirkham TC, Williams CM (2001) Endogenous cannabinoids and appetite. Nutr Res Rev 14:65–86
Kirkham TC, Williams CM, Fezza F, Di Marzo V (2002) Endocannabinoid levels in rat limbic forebrain and hypothalamus in relation to fasting, feeding and satiation: stimulation of eating by 2-arachidonoyl glycerol. Br J Pharmacol 136:550–557
Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (1990) Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346:561–564
Mechoulam R, Ben-Shabat S, Hanus L, Ligumsky M, Kaminski NE, Schatz AR, Gopher A, Almog S, Martin BR, Compton DR, Pertwee RG, Griffin G, Bayewitch M, Barg J, Vogel Z (1995) Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 50:83–90
Navarro M, Hernandez E, Munoz RM, del Arco I, Villanua MA, Carrera MRA, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (1997) Acute administration of the CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716A induces anxiety-like responses in the rat. NeuroReport 8:491–496
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Heaulme M, Shire D, Calandra B, Congy C, Martinez S, Maruani J, Neliat G, Caput D, Ferrara P, Soubrie P (1994) SR141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the brain cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett 350:240–244
Rowland NE, Mukherjee M, Robertson K (2001) Effects of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR 141716, alone and in combination with dexfenfluramine or naloxone, on food intake in rats. Psychopharmacology 159:111–116
Ryan DH, Kaiser P, Bray GA (1995) Sibutramine: a novel new agent for obesity treatment. Obesity Res 3:553S–559S
Simiand J, Keane M, Keane PE, Soubrie P (1998) SR 141716, a cannabinoid receptor antagonist, selectively reduces sweet food intake in marmoset. Behav Pharmacol 9:179–181
Vickers SP, Benwell KR, Porter RH, Bickerdike MJ, Kennett GA, Dourish CT (2000) Comparative effects of continuous infusion of mCPP, Ro 60-0175 and d-fenfluramine on food intake, water intake, body weight and locomotor activity in rats. Br J Pharmacol 130:1305–1314
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (1999) Anandamide induces overeating: mediation by central cannabinoid receptors. Psychopharmacology 143:315–317
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2002) Reversal of Δ9-THC hyperphagia by SR141716 and naloxone but not dexfenfluramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:341–348
Williams CM, Rogers PJ, Kirkham TC (1998) Hyperphagia in pre-fed rats following oral Δ9-THC. Physiol Behav 65:343–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vickers, S.P., Webster, L.J., Wyatt, A. et al. Preferential effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716, on food intake and body weight gain of obese (fa/fa) compared to lean Zucker rats. Psychopharmacology 167, 103–111 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1384-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1384-8