Abstract
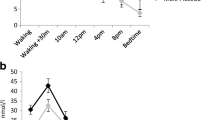
Rationale. Intravenous administration of the selective serotonin (5-HT) re-uptake inhibitor, citalopram, increases plasma cortisol. This would be expected to produce a parallel increase in salivary cortisol concentration.
Objective. To find out whether IV citalopram produces correlated increases in plasma and salivary cortisol levels.
Methods. Twelve healthy volunteers were tested on two occasions receiving either citalopram (10 mg IV) or saline in a double-blind, randomised, cross-over design. Plasma and salivary cortisol levels were measured before and for150 min after each infusion.
Results. Relative to placebo, citalopram significantly increased cortisol levels in both plasma and saliva. The size of the increases in plasma and saliva cortisol correlated significantly with each other.
Conclusions. Monitoring changes in salivary cortisol might be a valid and acceptable means of measuring 5-HT-mediated cortisol release.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhagwagar, Z., Hafizi, S. & Cowen, P. Acute citalopram administration produces correlated increases in plasma and salivary cortisol. Psychopharmacology 163, 118–120 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1149-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1149-4