Abstract
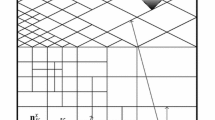
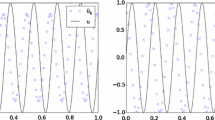
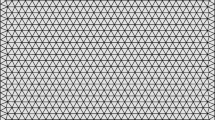
The convergence of a discontinuous Galerkin method for the linear Schrödinger equation in non-cylindrical domains of \({\mathbb{R}^m}\), m ≥ 1, is analyzed in this paper. We show the existence of the resulting approximations and prove stability and error estimates in finite element spaces of general type. When m = 1 the resulting problem is related to the standard narrow angle ‘parabolic’ approximation of the Helmholtz equation, as it appears in underwater acoustics. In this case we investigate theoretically and numerically the order of convergence using finite element spaces of piecewise polynomial functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsson L., Kreiss H.-O.: Boundary conditions for the parabolic equation in range-dependent duct. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(6), 2438–2441 (1990)
Akrivis G., Dougalis V.A., Zouraris G.E.: Finite difference schemes for the ‘Parabolic’ Equation in a variable depth environment with a rigid bottom boundary condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39, 539–565 (2001)
Akrivis G., Makridakis C.: Galerkin time-stepping methods for nonlinear parabolic equations. ESAIM: Math. Mod. Num. Anal. 38, 261–289 (2004)
Antonopoulou, D.C.: Theory and numerical analysis of parabolic approximations. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Mathematics, University of Athens, 2006
Aziz A.K., Monk P.: Continuous finite elements in space and time for the heat equation. Math. Comput. 52, 255–274 (1989)
Brenner, S.C., Scott, L.R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (1994)
Brocéhn, A.: Galerkin methods for approximation of solutions of second order partial differential equations of Schrödinger type. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Mathematics-Natural Science, University of Göteborg, Sweden (1980)
Castillo P., Cockburn B., Perugia I., Schötzau D.: An a priori error analysis of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(5), 1676–1706 (2000)
Cazenave, T.: An Introduction to Nonlinear Schrödinger Equations, Instituto de Mathemática-UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro (1996)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Cockburn B., Shu C.W.: The local discontinuous Galerkin method for time-dependent convection-diffusion systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35(6), 2440–2463 (1998)
Jamet P.: Estimation d’erreur pour des éleménts finis droits presque dégénérés. Rev. Francaise Automat. Informat. Recherche Opérationelle Sér. Rouge Anal. Numér. 10, 43–61 (1976)
Jamet P.: Galerkin-type approximations which are discontinuous in time for parabolic equations in a variable domain. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 15, 913–928 (1978)
Jensen F.B., Ferla C.M.: Numerical solutions of range-dependent benchmark problems in ocean acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 1499–1510 (1990)
Jensen, F.B., Kuperman, W.A., Porter, M.B., Schmidt, H.: Computational Ocean Acoustics. AIP Series in Modern Acoustics and Signal Processing, American Institute of Physics, New York (1994)
Karakashian O., Makridakis C.: A space–time finite element method for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation: the discontinuous Galerkin method. Math. Comput. 67, 479–499 (1998)
Lee D., McDaniel S.T.: Ocean acoustic propagation by finite difference methods. Comput. Math. Appl. 14, 305–423 (1987)
Lesaint, P., Raviart, P.A.: On a finite element method for solving the neutron transport equation. In: deBoor, C., (ed.) Mathematical Aspects of Finite Elements in Partial Differential Equations. Academic Press, New York (1974)
Lions, J.-L., Magenes, E.: Problèmes aux Limites Non Homogènes et Applications, vol. 1. Travaux et Recherches Mathématiques, No. 17, Dunod, Paris (1968)
Pozzi G.A.: Problemi di Cauchy e problemi ai limiti per equazioni di evoluzione del tipo di Schroedinger lineari e non lineari, Parte Prima, L’Equazione Lineare Astratta. Ann. Mat. Pur. Appl. 78, 197–258 (1968)
Reed, W.H., Hill, T.R.: Triangular mesh methods for the neutron transport equation. Tech. Report LA-UR-73-479, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory (1973)
Sulem, C., Sulem, P-L.: The Nonlinear Scrödinger Equation. Self-Focusing and Wave Collapse. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 139. Springer, New York (1999)
Tappert, F.D.: The parabolic approximation method, Wave Propagation and Underwater Acoustics. In: Keller, J.B., Papadakis, J.S. (eds.) Lecture Notes in Phys., vol. 70, pp. 224–287. Springer, Berlin (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonopoulou, D.C., Plexousakis, M. Discontinuous Galerkin methods for the linear Schrödinger equation in non-cylindrical domains. Numer. Math. 115, 585–608 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-010-0296-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-010-0296-5