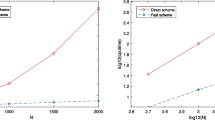
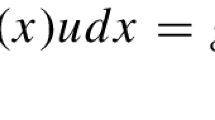Abstract
Although adaptive finite element methods for solving elliptic problems often work well in practice, they are usually not proven to converge. For Poisson like problems, an exception is given by the method of Dörfler ([8]), that was later improved by Morin, Nochetto and Siebert ([11]). In this paper we extend these methods by constructing an adaptive finite element method for a singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion equation that, in energy norm, converges uniformly in the size of the reaction term. Moreover, in this algorithm the arising Galerkin systems are solved only inexactly, so that, generally, the number of arithmetic operations is equivalent to the number of triangles in the final partition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, M., Babuška, I.: Reliable and robust a posteriori error estimation for singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36(2), 331–353 (1999)
Ainsworth, M., Oden, J.T.: A posteriori error estimation in finite element analysis. Pure and Applied Mathematics. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2000
Binev, P., Dahmen, W., DeVore, R.: Adaptive finite element methods with convergence rates. Numer. Math. 97(2), 219–268 (2004)
Binev, P., Dahmen, W., DeVore, R., Petruchev, P.: Approximation classes for adaptive methods. Serdica Math. J. 28, 1001–1026 (2002)
Binev, P., DeVore, R.: Fast computation in adaptive tree approximation. Numer. Math. 97(2), 193–217 (2004)
Bornemann, F.A.: An adaptive multilevel approach to parabolic equations III, 2D error estimates and multilevel preconditioning. IMPACT Comput. Sci. Eng. 4, 1–45 (1992)
Cohen, A., Echeverry, L.M., Sun, Q.: Finite element wavelets. Technical report, Laboratoire d’Analyse Numérique, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, 2000
Dörfler, W.: A convergent adaptive algorithm for Poisson’s equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 1106–1124 (1996)
Grisvard, P.: Elliptic Problems in Nonsmooth Domains. Pitman, Boston, 1985
Kunert, G.: Robust a posteriori error estimation for a singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion equation on anisotropic tetrahedral meshes. Adv. Comput. Math. 15, 237–259 (2001)
Morin, P., Nochetto, R., Siebert, K.: Data oscillation and convergence of adaptive FEM. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(2), 466–488 (2000)
Oswald, P.: Multilevel finite element approximation: Theory and applications. B.G. Teubner, Stuttgart, 1994
Stevenson, R.P.: An optimal adaptive finite element method. Technical Report 1271, University of Utrecht, March 2003. To appear in SIAM J. Numer. Anal.
Verfürth, R.: A Review of A Posteriori Error Estimation and Adaptive Mesh-Refinement Techniques. Wiley-Teubner, Chichester, 1996
Verfürth, R.: Robust a posteriori error estimators for a singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion equation. Numer. Math. 78, 479–493 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research and by the EU-IHP project “Breaking Complexity.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevenson, R. The uniform saturation property for a singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion equation. Numer. Math. 101, 355–379 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-005-0606-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-005-0606-5