Abstract.
The roles of sarcolemmal ATP-sensitive K+ (sarcKATP) and mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ (mitoKATP) channels in the cardioprotection induced by KATP channel openers remain unclear, though the mitoKATP channel has been proposed to be involved as a subcellular mediator in cardioprotection afforded by ischemic preconditioning (PC). In the present study, selective inhibitors of the sarcKATP and mitoKATP channels were used to examine the role of each channel subtype in infarct size limitation by KATP channel openers.
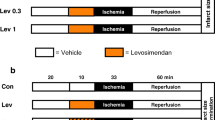
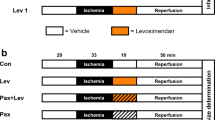
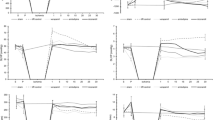
Isolated rabbit hearts were perfused in the Langendorff mode with monitoring of the activation recovery interval (ARI) and subjected to 30-min global ischemia/2-h reperfusion to induce infarction. Before ischemia, hearts received 10 µM pinacidil, 100 µM diazoxide, or PC with or without preceding infusion of a sarcKATP channel-selective blocker (5 µM HMR1098) or a mitoKATP channel-selective blocker (100 µM 5-hydroxydecanoate, 5-HD). ARI, an index of action potential duration, was shortened from 118±3 ms to 77±5 ms after 10 min of ischemia in untreated control hearts. Pinacidil shortened ARI before ischemia from 113±2 ms to 78±5 ms and enhanced the ARI shortening during ischemia. Diazoxide did not affect ARI before ischemia but accelerated ischemia-induced shortening of ARI. Infarct size as a percentage of the left ventricle (%IS/LV) was reduced by pinacidil and diazoxide from the control value of 47.2±4.0% to 4.5±1.5% and 5.2±1.2%, respectively. HMR1098 significantly inhibited the shortening of ARI by ischemia, pinacidil and diazoxide and partially blocked infarct size limitation by these KATP channel openers (%IS/LV=32.6±4.2% and 23.4±5.3%, respectively). Infusion of 5-HD did not modify the change in ARI caused by the KATP channel openers but completely abolished cardioprotection (%IS/LV=46.0±6.2% with pinacidil and 57.2±7.0% with diazoxide). PC with two episodes of 5-min ischemia limited %IS/LV to 21.6±4.0%, and this protection was not inhibited by HMR1098. Neither HMR1098 nor 5-HD alone modified infarct size.
In conclusion, both sarcKATP and mitoKATP channels may contribute to the anti-infarct tolerance afforded by pinacidil and diazoxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanno, M., Miura, T., Tsuchida, A. et al. Contribution of both the sarcolemmal KATP and mitochondrial KATP channels to infarct size limitation by KATP channel openers: differences from preconditioning in the role of sarcolemmal KATP channels. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 364, 226–232 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100100448
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100100448