Abstract.
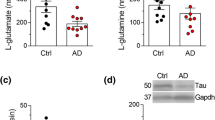
Down syndrome (DS) is a genetic disease with developmental brain abnormalities resulting in early mental retardation and precocious, age-dependent Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration. Furthermore, non-cognitive symptoms may be a cardinal feature of functional decline in adults with DS. A number of amino acids [glutamate, aspartate, γ-aminobutyrate (GABA), glycine, taurine, glutamine, serine, arginine] were investigated in post-mortem tissue samples from temporal, occipital cortex, thalamus, caudate nucleus, and cerebellum of adult patients with Down syndrome (DS) exhibiting Alzheimer-like neuropatholgy, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and from controls by use of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In DS, no significant differences from control values could be observed in any of the brain regions. In AD, significant loss of GABA content was found in the temporal cortex (0.5±0.2 µmol/g vs. 1.3±0.8 µmol/g wet weight tissue, P<0.01), occipital cortex (0.8±0.2 µmol/g vs. 1.4±0.6 µmol/g, P<0.05) and cerebellum (1.1±0.3 µmol/g vs. 1.8±0.5 µmol/g, P<0.05). Glutamate and aspartate concentrations were significantly reduced in the caudate nucleus of AD subjects (glutamate: 6.1±3.4 µmol/g vs. 14.7±1.8 µmol/g; aspartate: 1.5±0.3 µmol/g vs. 3.3±0.4 µmol/g, P<0.05). The results of this study confirm previous findings in late stage AD and provide further information with respect to DS which may be relevant to understanding different pathogenesis of cognitive and non-cognitive (behavioral) features in DS and AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidl, R., Cairns, N., Singewald, N. et al. Differences between GABA levels in Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome with Alzheimer-like neuropathology. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 363, 139–145 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000346
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000346