Abstract.
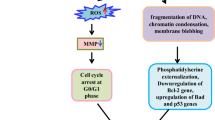
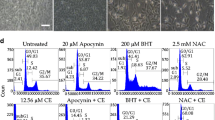
The cytotoxic effects of ginkgetin, a natural biflavone isolated from Selaginella moellendorffii Hieron, were evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in three different human cell lines: ovarian adenocarcinoma (OVCAR-3), cervical carcinoma (HeLa) and foreskin fibroblast (FS-5). The concentrations of ginkgetin required to induce 50% death (EC50) in OVCAR-3, HeLa, and FS-5 were 3.0, 5.2, and 8.3 µg/ml, respectively. Morphological changes in cells and their nuclei, DNA fragmentation with a characteristic pattern of inter-nucleosomal ladder, and double-stranded DNA breaks were detected following treatment with 3 µg/ml of this biflavone for 24 h. Incubation with 5 µg/ml ginkgetin led to increased intracellular levels of hydrogen peroxide as early as 30 min. The cytotoxicity of ginkgetin was partially inhibited by pretreating cells with vitamin C, vitamin E or catalase. Catalase not only afforded the best protective effect among three antioxidants, but also reduced both the DNA fragmentation and double-stranded DNA breakage induced by ginkgetin. Moreover, the involvement of caspase(s) in ginkgetin-induced apoptosis was demonstrated by the activation of caspase 3 after drug treatment and the suppression of cell death by a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor, benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethylketone (z-VAD-fmk). However, the protective effects of z-VAD-fmk and catalase were not additive. Taken together, our results indicated that the apoptosis induced by ginkgetin (especially at 5 µg/ml) is mediated mainly through the activation of caspase(s) by the hydrogen peroxide generated possibly through autooxidation of this biflavone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Sun, CM., Chuang, HH. et al. Studies on the cytotoxic mechanisms of ginkgetin in a human ovarian adenocarcinoma cell line. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 362, 82–90 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000240
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000240