Abstract
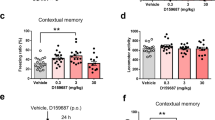
Cyclooxygenase (COX) plays a critical role in synaptic plasticity. Therefore, long-term administration of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and its main metabolite, salicylate, as a COX inhibitor may impair synaptic plasticity and subsequently memory formation. Although different studies have tried to explain the effects of ASA and sodium salicylate (SS) on learning and memory, the results are contradictory and the mechanisms are not exactly known. The present study was designed to investigate the effects of long-term low-dose (equivalent to prophylactic dose) and short-term high-dose (equivalent to analgesic dose) administration of ASA and SS respectively, on spatial learning and memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Animals were treated with a low dose of ASA (2 mg/ml solvated in drinking water, 6 weeks) or a high dose of SS, a metabolite of ASA, (300 mg/kg, 3 days, twice-daily, i.p). Spatial memory and synaptic plasticity were assessed by water maze performance and in vivo field potential recording from CA1, respectively. Animals treated with ASA but not SS showed a significant increase in escape latency and distance moved. Furthermore, in the probe test, animals treated with both drugs spent less time in the target quadrant zone. The paired-pulse ratio (PPR) at 20-ms inter-pulse intervals (IPI) as an index of short-term plasticity in both treated groups was significantly higher than of the control group. Interestingly, none of the administered drugs affected long-term potentiation (LTP). These data suggested that long-term inhibition of COX disrupted memory acquisition and retrieval. Interestingly, cognitive impairments happened along with short-term but not long-term synaptic plasticity disturbance.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Amann R, Peskar BA (2002) Anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and sodium salicylate. Eur J Pharmacol 447(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(02)01828-9
Andersen P, Morris R, Amaral D, Bliss T, O’Keefe J (2006) The hippocampus book. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195100273.001.0001
Azimi L, Pourmotabbed A, Ghadami MR, Nedaei SE, Pourmotabbed T (2012) Effects of peripheral and intra-hippocampal administration of sodium salicylate on spatial learning and memory of rats. IJBMS 15(2):709
Azimi L, Kachooeian M, Khodagholi F, Yans A, Heysieattalab S, Vakilzadeh G, Vosoughi N, Sanati M, Taghizadeh G, Sharifzadeh M (2016) Protective effects of salicylate on PKA inhibitor (H-89)-induced spatial memory deficit via lessening autophagy and apoptosis in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 150:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2016.10.008
Basta D, Ernst A (2004) Effects of salicylate on spontaneous activity in inferior colliculus brain slices. J Neurosci Res 50(2):237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2004.07.003
Berk A, Dean O, Drexhage H, McNeil JJ, Moylan S, O’Neil A, Davey CG, Sanna L, Michael Maes M (2013) Aspirin: a review of its neurobiological properties and therapeutic potential for mental illness. BMC Med 11:74
Brackmann M, Zhao C, Schmieden V, Braunewell K-H (2004) Cellular and subcellular localization of the inhibitory glycine receptor in hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324(3):1137–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.172
Bruce-Jones PN, Crome P, Kalra L (1994) Indomethacin and cognitive function in healthy elderly volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 38:45–51
Chen C, Magee JC, Bazan NG (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates prostaglandin E2 signaling in hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. J Neurophysiol 87(6):2851–2857. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.2002.87.6.2851
Choi SH, Woodlee MT, Hong JJ, Schallert T (2006) A simple modification of the water maze test to enhance daily detection of spatial memory in rats and mice. J Neurosci Methods 156(1–2):182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.03.002
Cowley T, Fahey B, O’mara S, (2008) COX-2, but not COX-1, activity is necessary for the induction of perforant path long-term potentiation and spatial learning in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 27(11):2999–3008. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06251.x
Davies C, Davies S, Collingridge G (1990) Paired-pulse depression of monosynaptic GABA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic responses in rat hippocampus. J Physiol 424(1):513–531. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018080
Dixon C, Sah P, Lynch JW, Keramidas A (2014) GABAA receptor α and γ subunits shape synaptic currents via different mechanisms. J Biol Chem 289(9):5399–5411
GholamiM MF, Semnanian S, Naghdi N, Fathollahi Y (2015) Chronic sodium salicylate administration enhances population spike long-term potentiation following a combination of theta frequency primed-burst stimulation and the transient application of pentylenetetrazol in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 767:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.10.021
Gilroy DW (2005) The role of aspirin-triggered lipoxins in the mechanism of action of aspirin. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 73(3–4):203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2005.05.007
Gong N, Zhang M, Zhang X-B, Chen L, Sun G-C, Xu T-L (2008) The aspirin metabolite salicylate enhances neuronal excitation in rat hippocampal CA1 area through reducing GABAergic inhibition. Neuropharmacology 54(2):454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.10.017
Greengard P, Allen PB, Nairn AC (1999) Beyond the dopamine receptor: the DARPP-32/protein phosphatase-1 cascade. Neuron 23(3):435–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80798-9
Hölscher C (1995) Inhibitors of cyclooxygenases produce amnesia for a passive avoidance task in the chick. Eur J Neurosci 7:1360–1365
Hosseinmardi N, Azimi L, Fathollahi Y, Javan M, Naghdi N (2011) In vivo sodium salicylate causes tolerance to acute morphine exposure and alters the ability of high frequency stimulation to induce long-term potentiation in hippocampus area CA1. Eur J Pharmacol 670(2–3):487–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.09.008
Jin Y, Luo B, Su Y-Y, Wang X-X, Chen L, Wang M, Wang W-W, Chen L (2015) Sodium salicylate suppresses GABAergic inhibitory activity in neurons of rodent dorsal raphe nucleus. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0126956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126956
Jonker C, Comijs HC, Smit JH (2003) Does aspirin or other NSAIDs reduce the risk of cognitive decline in elderly persons. Results from a population-based study. Neurobiol Aging 24:583–588
Katche C, Bekinschtein P, Slipczuk L, Goldin A, Izquierdo IA, Cammarota M, Medina JH (2010) Delayed wave of c-Fos expression in the dorsal hippocampus involved specifically in persistence of long-term memory storage. PNAS 107(1):349–354. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912931107
Kim J, Alger BE (2004) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 potentiates retrograde endocannabinoid effects in hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 7(7):697–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1262
Kozak KR, Prusakiewicz JJ, Marnett LJ (2004) Oxidative metabolism of endocannabinoids by COX-2. Curr Pharm Des 10(6):659–667
Lecomte M, Laneuville O, Ji C, DeWitt DL, Smith WL (1994) Acetylation of human prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) by aspirin. J Biol Chem 269(18):13207–13215
Lipton RB, Goldstein J, Baggish JS, Yataco AR, Sorrentino JV, Quiring JN (2005) Aspirin is efficacious for the treatment of acute migraine. J Headache Pain 45(4):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05065.x
Liu Y, Li X (2004) Effects of salicylate on transient outward and delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat inferior colliculus neurons. Neurosci Lett 369(2):115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.07.037
Liu Y, Li X, Ma C, Liu J, Lu H (2005) Salicylate blocks L-type calcium channels in rat inferior colliculus neurons. Hear Res 205(1–2):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2005.03.028
LiuY, and Li X, (2004) Effects of salicylate on voltage-gated sodium channels in rat inferior colliculus neurons. Hear Res 193(1–2):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2004.03.006
Lu Y- G, Tang Z- Q, HT Wang, YN Huang, KQ Zhou, M Zhang, TL Xu, and Chen L, (2009) Salicylate, an aspirin metabolite, specifically inhibits the current mediated by glycine receptors containing α1-subunits. Br J Pharmacol 157(8):1514–1522. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00321.x
Mitchell JA, Akarasereenont P, Thiemermann C, Flower RJ, Vane JR (1993) Selectivity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs as inhibitors of constitutive and inducible cyclooxygenase. PNAS 90(24):11693–11697. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.24.11693
Mohammed N, El-Aleem S, El-Hafiz H, McMahon R (2004) Distribution of constitutive (COX-1) and inducible (COX-2) cyclooxygenase in postviral human liver cirrhosis: a possible role for COX-2 in the pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. J Clin Pathol 57(4):350–354
Niu H, Ding S, Li H, Wei J, Ren C, Wu X, Huma T, Zhang Q (2018) Effect of long-term sodium salicylate administration on learning, memory, and neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus Biomed Res Int 2018 https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7807426
Park JY, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB (2006) Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: the role of PGE2 synthases. J Clin Immunol 119(3):229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2006.01.016
Paxinos G, Watson C (2006) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: hard, cover. Elsevier
Pernia-Andrade AJ, Tortorici V, Vanegas H (2004) Induction of opioid tolerance by lysine-acetylsalicylate in rats. Pain 111(1–2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2004.06.006
Rall JM, Mach SA, Dash PK (2003) Intrahippocampal infusion of a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor attenuates memory acquisition in rats. Brain Res 968:273–276
Rao SK, Andrade C, Reddy K, Madappa KN, Thyagarajan S, Chandra S (2002) Memory protective effect of indomethacin against electroconvulsive shock-induced retrograde amnesia in rats. Biol Psychiatry 51:770–773
Roth G, Majerus PW (1975) The mechanism of the effect of aspirin on human platelets. I. Acetylation of a particulate fraction protein. J Clin Invest 56(3):624–632
Roth GJ, Stanford N, Majerus PW (1975) Acetylation of prostaglandin synthase by aspirin. PNAS 72(8):3073–3076. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.72.8.3073
Sadegh M, Fathollahi Y, Semnanian S (2013) The chronic treatment in vivo of salicylate or morphine alters excitatory effects of subsequent salicylate or morphine tests in vitro in hippocampus area CA1. Eur J Pharmacol 721(1–3):103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.048
Sairanen T, Kanerva M, Valanne L, Lyytinen J, Pekkonen E (2011) Churg-Strauss syndrome as an unusual aetiology of stroke with haemorrhagic transformation in a patient with no cardiovascular risk factors. Case reports in neurology 3(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323214
Sang N, Zhang J, Marcheselli V, Bazan NG, Chen C (2005) Postsynaptically synthesized prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) modulates hippocampal synaptic transmission via a presynaptic PGE2 EP2 receptor. J Neurosci 25(43):9858–9870
Santschi LA, Stanton PK (2003) A paired-pulse facilitation analysis of long-term synaptic depression at excitatory synapses in rat hippocampal CA1 and CA3 regions. Brain Res 962(1–2):78–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03846-5
Sharifzadeh M, Naghdi N, Khosrovani S, Ostad SN, Sharifzadeh K, Roghani A (2005) Post-training intrahippocampal infusion of the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib impaired spatial memory retention in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 511(2–3):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.01.041
Simmons DL, Botting RM, Hla T (2004) Cyclooxygenase isozymes: the biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol Rev 56(3):387–437. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.56.3.3
Slanina KA, Roberto M, Schweitzer P (2005) Endocannabinoids restrict hippocampal long-term potentiation via CB1. Neuropharmacology 49(5):660–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.04.021
Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM (2000) Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem 69(1):145–182. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.145
Smith JW, Al-Khamees O, Costall B, Naylor RJ, Smythe JW (2002) Chronic aspirin ingestion improves spatial learning in adult and aged rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71(1–2):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(01)00675-
Swinney DC, Mak AY, Barnett J, Ramesha CS (1997) Differential allosteric regulation of prostaglandin H synthase 1 and 2 by arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem 272(19):12393–12398. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.19.12393
Sztriha LK, Sas K, Vecsei L (2005) Aspirin resistance in stroke: 2004. J Neurol Sci 229:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2004.11.023
Vane JR and Botting RM (1992) Aspirin and other salicylates. Chapman & Hall Medical, London
Wagner JJ, Etemad LR, Thompson AM (2001) Opioid-mediated facilitation of long-term depression in rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296(3):776–781
Wang H-T, Luo B, Zhou K-Q, Xu T-L, Chen L (2006) Sodium salicylate reduces inhibitory postsynaptic currents in neurons of rat auditory cortex. Hear Res 215(1–2):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2006.03.004
Woo NH, Abel T, Nguyen PV (2002) Genetic and pharmacological demonstration of a role for cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-mediated suppression of protein phosphatases in gating the expression of late LTP. Eur J Neurosci 16(10):1871–1876. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02260.x
Xu T-L, Gong N (2010) Glycine and glycine receptor signaling in hippocampal neurons: diversity, function and regulation. Prog Neurobiol 91(4):349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.04.008
Yamagata K, Andreasson KI, Kaufmann WE, Barnes CA, Worley PF (1993) Expression of a mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in brain neurons: regulation by synaptic activity and glucocorticoids. Neuron 11(2):371–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(93)90192-t
Yang H, Chen C (2008) Cyclooxygenase-2 in synaptic signaling. Curr Pharm Des 14(14):1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161208784480144
Yang H, Zhang J, Andreasson K, Chen C (2008) COX-2 oxidative metabolism of endocannabinoids augments hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci 37(4):682–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2007.12.019
Yermakova AV, O’Banion MK (2001) Down regulation of neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in end stage Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:823–836
Zhang L-H, Gong N, Fei D, Xu L, Xu T-L (2008) Glycine uptake regulates hippocampal network activity via glycine receptor-mediated tonic inhibition. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(3):701–711. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301449
Zugaib J, Leão RM (2018) Enhancement of endocannabinoid-dependent depolarization-induced suppression of excitation in glycinergic neurons by prolonged exposure to high doses of salicylate. Neuroscience 376:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.02.016
Funding
The authors would like to thank Dr. Fereshteh Motamedi for her technical support. We also would like to thank the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for its support (grant number: 91000228). We also gratefully acknowledge support from Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NH and MJ designed and supervised the study and SH wrote the manuscript. MG, NS, and MD revised the manuscript. JD and SC conducted and analyzed experiments. All authors read and approved the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heysieattalab, S., Doostmohammadi, J., Darvishmolla, M. et al. Non-selective COX inhibitors impair memory formation and short-term but not long-term synaptic plasticity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 1879–1891 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02092-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02092-4