Abstract
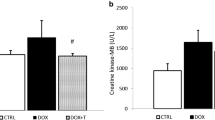
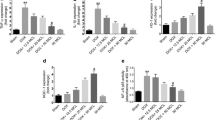
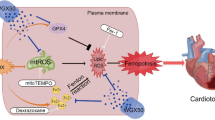
Because of limitation of doxorubicin (DOX) clinical application in chemotherapy due to its cardiotoxicity, finding new strategies to reduce DOX challenge and improve patients’ outcomes is crucial. Due to positive cardiovascular impacts of troxerutin (TXR), here we have investigated the effect of TXR on DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by evaluating the myocardial oxidative stress and expression of genes regulating mitochondrial biogenesis. Male Wistar rats (250–300 g) were randomly allocated into four groups: control, TXR, DOX, and TXR + DOX. Troxerutin (150 mg/kg) was orally administrated once a day through a gavage tube for 4 weeks before DOX challenge. The TXR-treated and time-matched control rats received intraperitoneal injection of DOX (20 mg/kg). Three days after DOX challenge, the left ventricular samples were obtained to determine the expression of genes regulating mitochondrial biogenesis via real-time PCR. Myocardial creatine kinase (CK-mB), oxidative stress markers, and mitochondrial function (generation of reactive oxygen species or ROS and ATP levels) were also evaluated using commercial kits and spectrophotometric and fluorometric methods. DOX administration significantly increased the levels of CK-mB, malondialdehyde (MDA), and mitochondrial ROS levels, while reduced the cellular ATP production and expression levels of SIRT-1, PGC-1α, and NRF-2 as well as superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase activity in comparison to control group (P < 0.05 to P < 0.01). Pretreatment of DOX-received rats with TXR significantly upregulated the expression of all biogenesis genes and antioxidant enzymes with non-significant effect on catalase activity, and significantly reduced CK-mB and MDA levels toward control values (P < 0.05 to P < 0.01). Mitochondrial ROS and ATP levels were also restored significantly by pretreatment with TXR (P < 0.05). The data suggested that preconditioning of rats with TXR had protective effect on DOX-induced cardiotoxicity through inducing antioxidative properties and restoring the mitochondrial function and the expression profiles of myocardial SIRT-1/PGC-1α/NRF-2 network.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas NAT, Kabil SL (2017) Liraglutide ameliorates cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in rats through the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390(11):1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1414-z
Badalzadeh R, Layeghzadeh N, Alihemmati A, Mohammadi M (2015) Beneficial effect of troxerutin on diabetes-induced vascular damages in rat aorta: histopathological alterations and antioxidation mechanism. Int J Endocrinol Metab 13(2):e25969. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.25969
Badalzadeh R, Baradaran B, Alihemmati A, Yousefi B, Abbaszadeh A (2016) Troxerutin preconditioning and ischemic postconditioning modulate inflammatory response after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat model. Inflammation 40(1):136–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0462-8
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Abramov AY (2015) The emerging role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med 88:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.036
Fan SH, Zhang ZF, Zheng YL, Lu J, Wu DM, Shan Q, Hu B, Wang YY (2009) Troxerutin protects the mouse kidney from d-galactose-caused injury through anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation. Int Immunopharmacol 9(1):91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2008.10.008
Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Auwerx J (2011) Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr 93(4):884S–890S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.110.001917
Geetha R, Yogalakshmi B, Sreeja S, Bhavani K, Anuradha CV (2014) Troxerutin suppresses lipid abnormalities in the heart of high-fat-high-fructose diet-fed mice. Mol Cell Biochem 387(1–2):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1877-2
Gorini S, De Angelis A, Berrino L, Malara N, Rosano G, Ferraro E (2018) Chemotherapeutic drugs and mitochondrial dysfunction: focus on doxorubicin, trastuzumab, and sunitinib. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:7582730. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/75827303
Guo Q, Guo J, Yang R, Peng H, Zhao J, Li L, Peng S (2015) Cyclovirobuxine D attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by suppression of oxidative damage and mitochondrial biogenesis impairment. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:151972. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/151972
Holmström KM, Kostov RV, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2016) The multifaceted role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Curr Opin Toxicol 1:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2016.10.002
Hosseini L, Vafaee MS, Mahmoudi J, Badalzadeh R (2019) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide emerges as a therapeutic target in aging and ischemic conditions. Biogerontology 20(4):381–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-019-09805-6
Huang L, Zhang K, Guo Y, Huang F, Yang K, Chen L, Huang K, Zhang F, Long Q, Yang Q (2017a) Honokiol protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via improving mitochondrial function in mouse hearts. Sci Rep 7:11989. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12095-y
Huang K, Gao X, Wei W (2017b) The crosstalk between Sirt1 and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE anti-oxidative pathway forms a positive feedback loop to inhibit FN and TGF-β1 expressions in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Cell Res 361(1):63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.042
Khafaga AF, El-Sayed YS (2018) All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: in vivo potential involvement of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via caspase-3 and p53 down-expression. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391(1):59–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1437-5
Liu CM, Ma JQ, Lou Y (2010) Chronic administration of troxerutin protects mouse kidney against D-galactose-induced oxidative DNA damage. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2809–2817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.011
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Cheng W, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF, Ye Q, Fan SH, Shan Q, Wang YJ (2010) Chronic administration of troxerutin protects mouse brain against D-galactose-induced impairment of cholinergic system. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93(2):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2009.09.006
Meredith AM, Dass CR (2016) Increasing role of the cancer chemotherapeutic doxorubicin in cellular metabolism. J Pharm Pharmacol 68(6):729–741. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12539
Mohamed JS, Hajira A, Pardo PS, Boriek AM (2014) MicroRNA-149 inhibits PARP-2 and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis via SIRT-1/PGC-1α network in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 63(5):1546–1559. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1364
Najafi M, Noroozi E, Javadi A, Badalzadeh R (2018) Anti-arrhythmogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of troxerutin in ischemia/reperfusion injury of diabetic myocardium. Biomed Pharmacother 102:385–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.047
Nebigil CG, Désaubry L (2018) Updates in anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity. Front Pharmacol 9:1262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01262
Pugazhendhi A, Edison TNJI, Velmurugan BK, Jacob JA, Karuppusamy I (2018) Toxicity of doxorubicin (Dox) to different experimental organ systems. Life Sci 200:26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.023
Wang S, Konorev EA, Kotamraju S, Joseph J, Kalivendi S, Kalyanaraman B (2004) Doxorubicin induces apoptosis in normal and tumor cells via distinctly different mechanisms. Intermediacy of H(2)O(2)- and p53-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 11 279(24):25535–25543
Yousefi B, Azimi A, Majidinia M, Shafiei-Irannejad V, Badalzadeh R, Baradaran B, Zarghami N, Samadi N (2017) Balaglitazone reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance via upregulation of PTEN in a PPARγ-dependent manner in leukemia cells. Tumour Biol 39(10):1010428317716501. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317716501
Yu Y, Zheng G (2017) Troxerutin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy through NF-κB/AKT/IRS1 in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Mol Med Rep 15(6):3473–3478. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6456
Zare P, Moghadaszadeh M, Asadi M, Ebadi F, Badalzadeh R (2019) Effect of high-intensity interval training on expression of microRNA-149 and genes regulating mitochondrial biogenesis in doxorubicin-cardiotoxicity in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 2019:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03077-9
Zhang ZF, Fan SH, Zheng YL, Lu J, Wu DM, Shan Q, Hu B (2009) Troxerutin protects the mouse liver against oxidative stress-mediated injury induced by D-galactose. J Agric Food Chem 57(17):7731–7736. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9012357
Zhào H, Liu Y, Zeng J, Li D, Zhang W, Huang Y (2018) Troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection protects neurovascular units from oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced injury in vitro. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:9859672. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9859672
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff of the Biotechnology and Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. This study was the PhD thesis of Sara Babaei Kouchaki and granted by Sciences and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran-Iran, and Clinical Development Research Unit of Shohada Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz-Iran.
Author contribution statement
SB, VB, and RB conceived and designed research. SB and RB conducted experiments. NP contributed new reagents. VB, NP, and RB analyzed data. SB and RB wrote the manuscript. All authors read, edited, and approved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All steps of this study were performed under the control of local animal research committee according to the standard guidelines with ethical approval number of 97-61754.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babaei-Kouchaki, S., Babapour, V., Panahi, N. et al. Effect of troxerutin on oxidative stress and expression of genes regulating mitochondrial biogenesis in doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 1187–1195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01818-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01818-0