Abstract
Astrocyte is considered to be a type of passive supportive cells that preserves neuronal activity and survival. The dysfunction of astrocytes is involved in the pathological processes of major depression. Recent studies implicate sigma-1 receptors as putative therapeutic targets for current available antidepressant drugs. However, it is absent of direct evidences whether sigma-1 receptor could promote activation of astrocyte. In the present study, we took advantage of primary astrocyte culture and a highly selective agonist of sigma-1 receptor, (+)SKF-10047 to determine the effect of sigma-1 receptor on Brdu (bromodeoxyuridine) labeling positive cells, migration as well as GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) expression of astrocyte. The results showed that (+)SKF-10047 notably increased the number of Brdu labeling positive cells, migration, and the expression of GFAP in primary astrocytes, which were blocked by antagonist of sigma-1 receptor. Moreover, we also found that (+)SKF-10047 increased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2) and GSK3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3β) (ser 9) in the primary astrocytes. In addition, pharmacological inhibition of ERK1/2 and GSK3β (ser 9) abolished sigma-1 receptor-promoted activation of astrocyte. Therefore, sigma-1 receptor could be considerate as a new pattern for modulating astrocytic function might emerge as therapeutic strategies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02180-5
Abbreviations
- MAM:
-
Mitochondrion-associated ER membranes
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2
- GSK3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
References
Allen NJ, Eroglu C (2017) Cell biology of astrocyte-synapse interactions. Neuron 96:697–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.056
Ben Haim L, Carrillo-de Sauvage MA, Ceyzeriat K, Escartin C (2015) Elusive roles for reactive astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 9:278. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00278
Boku S, Nakagawa S, Toda H, Kato A, Takamura N, Omiya Y, Inoue T, Koyama T (2013) ROCK2 regulates bFGF-induced proliferation of SH-SY5Y cells through GSK-3beta and beta-catenin pathway. Brain Res 1492:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.034
Bowley MP, Drevets WC, Ongur D, Price JL (2002) Low glial numbers in the amygdala in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 52:404–412
Burda JE, Sofroniew MV (2014) Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron. 81:229–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.034
Cheng P, Alberts I, Li X (2013) The role of ERK1/2 in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of astrocytes in developing brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 31:783–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.09.008
Clark MA, Tran H, Nguyen C (2011) Angiotensin III stimulates ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinases and astrocyte growth in cultured rat astrocytes. Neuropeptides 45:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2011.07.002
Cui W, Mizukami H, Yanagisawa M, Aida T, Nomura M, Isomura Y, Takayanagi R, Ozawa K, Tanaka K, Aizawa H (2014) Glial dysfunction in the mouse habenula causes depressive-like behaviors and sleep disturbance. J Neurosci 34:16273–16285. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1465-14.2014
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ni Z, Dong Y, Cai G, Foncelle A, Ma S, Sang K, Tang S, Li Y, Shen Y, Berry H, Wu S, Hu H (2018) Astroglial Kir4.1 in the lateral habenula drives neuronal bursts in depression. Nature 554:323–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25752
Czeh B, Di Benedetto B (2013) Antidepressants act directly on astrocytes: evidences and functional consequences. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.04.017
Ding Q, Xia W, Liu JC, Yang JY, Lee DF, Xia J, Bartholomeusz G, Li Y, Pan Y, Li Z, Bargou RC, Qin J, Lai CC, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Hung MC (2005) Erk associates with and primes GSK-3beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol Cell 19:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.009
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012) Synaptic dysfunction in depression: potential therapeutic targets. Science. 338:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222939
Gadea A, Schinelli S, Gallo V (2008) Endothelin-1 regulates astrocyte proliferation and reactive gliosis via a JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. J Neurosci 28:2394–2408. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5652-07.2008
Gittins RA, Harrison PJ (2011) A morphometric study of glia and neurons in the anterior cingulate cortex in mood disorder. J Affect Disord 133:328–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.03.042
Hanner M, Moebius FF, Flandorfer A, Knaus HG, Striessnig J, Kempner E, Glossmann H (1996) Purification, molecular cloning, and expression of the mammalian sigma1-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:8072–8077
Harrison PJ, Geddes JR, Tunbridge EM (2018) The emerging neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Trends Neurosci 41:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.10.006
Hashimoto K (2015) Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication. J Pharmacol Sci 127:6–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2014.11.010
Hayashi T, Su TP (2007) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate ca(2+) signaling and cell survival. Cell 131:596–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036
Hertz L, Rothman DL, Li B, Peng L (2015) Chronic SSRI stimulation of astrocytic 5-HT2B receptors change multiple gene expressions/editings and metabolism of glutamate, glucose and glycogen: a potential paradigm shift. Front Behav Neurosci 9:25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00025
Hu Z, Feng J, Bo W, Wu R, Dong Z, Liu Y, Qiang L, Liu M (2017) Fidgetin regulates cultured astrocyte migration by severing tyrosinated microtubules at the leading edge. Mol Biol Cell 28:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-09-0628
Imbe H, Kimura A, Donishi T, Kaneoke Y (2013) Effects of restraint stress on glial activity in the rostral ventromedial medulla. Neuroscience. 241:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.008
Jiang H, Guo W, Liang X, Rao Y (2005) Both the establishment and the maintenance of neuronal polarity require active mechanisms: critical roles of GSK-3beta and its upstream regulators. Cell. 120:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.033
Jung EM, Ka M, Kim WY (2016) Loss of GSK-3 causes abnormal Astrogenesis and behavior in mice. Mol Neurobiol 53:3954–3966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9326-8
Kim WY, Zhou FQ, Zhou J, Yokota Y, Wang YM, Yoshimura T, Kaibuchi K, Woodgett JR, Anton ES, Snider WD (2006) Essential roles for GSK-3s and GSK-3-primed substrates in neurotrophin-induced and hippocampal axon growth. Neuron. 52:981–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.031
Kimura Y, Fujita Y, Shibata K, Mori M, Yamashita T (2013) Sigma-1 receptor enhances neurite elongation of cerebellar granule neurons via TrkB signaling. PLoS One 8:e75760. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075760
Kourrich S, Su TP, Fujimoto M, Bonci A (2012) The sigma-1 receptor: roles in neuronal plasticity and disease. Trends Neurosci 35:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.09.007
Koyama Y (2015) Functional alterations of astrocytes in mental disorders: pharmacological significance as a drug target. Front Cell Neurosci 9:261. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00261
Maurer MH, Bromme JO, Feldmann RE Jr, Jarve A, Sabouri F, Burgers HF et al (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) regulates differentiation and proliferation in neural stem cells from the rat subventricular zone. J Proteome Res 6:1198–1208. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr0605825
Mebratu Y, Tesfaigzi Y (2009) How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle 8:1168–1175
Moon JY, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Choi SR, Kwon SG, Choi HS, Kang SY, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Oh SB, Lee JH (2014) sigma1 receptors activate astrocytes via p38 MAPK phosphorylation leading to the development of mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol 171:5881–5897. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12893
Nagy C, Suderman M, Yang J, Szyf M, Mechawar N, Ernst C, Turecki G (2015) Astrocytic abnormalities and global DNA methylation patterns in depression and suicide. Mol Psychiatry 20:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.21
Navarro G, Moreno E, Bonaventura J, Brugarolas M, Farre D, Aguinaga D et al (2013) Cocaine inhibits dopamine D2 receptor signaling via sigma-1-D2 receptor heteromers. PLoS One 8:e61245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061245
Nguyen L, Lucke-Wold BP, Mookerjee SA, Cavendish JZ, Robson MJ, Scandinaro AL, Matsumoto RR (2015) Role of sigma-1 receptors in neurodegenerative diseases. J Pharmacol Sci 127:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2014.12.005
Peng L, Gu L, Li B, Hertz L (2014) Fluoxetine and all other SSRIs are 5-HT2B agonists - importance for their therapeutic effects. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:365–379. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X12666140828221720
Roh DH, Yoon SY (2014) Sigma-1 receptor antagonist, BD1047 reduces nociceptive responses and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in mice orofacial formalin model. Biol Pharm Bull 37:145–151
Romero L, Zamanillo D, Nadal X, Sanchez-Arroyos R, Rivera-Arconada I, Dordal A et al (2012) Pharmacological properties of S1RA, a new sigma-1 receptor antagonist that inhibits neuropathic pain and activity-induced spinal sensitization. Br J Pharmacol 166:2289–2306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01942.x
Saijo K, Winner B, Carson CT, Collier JG, Boyer L, Rosenfeld MG, Gage FH, Glass CK (2009) A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death. Cell. 137:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.038
Son JS, Kwon YB (2010) Sigma-1 receptor antagonist BD1047 reduces allodynia and spinal ERK phosphorylation following chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 14:359–364. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359
Tan F, Guio-Aguilar PL, Downes C, Zhang M, O'Donovan L, Callaway JK et al (2010) The sigma 1 receptor agonist 4-PPBP elicits ERK1/2 phosphorylation in primary neurons: a possible mechanism of neuroprotective action. Neuropharmacology 59:416–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.05.014
Tsai SY, Hayashi T, Harvey BK, Wang Y, Wu WW, Shen RF, Zhang Y, Becker KG, Hoffer BJ, Su TP (2009) Sigma-1 receptors regulate hippocampal dendritic spine formation via a free radical-sensitive mechanism involving Rac1xGTP pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22468–22473. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909089106
Wang W, Wang W, Mei X, Huang J, Wei Y, Wang Y, Wu S, Li Y (2009) Crosstalk between spinal astrocytes and neurons in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. PLoS One 4:e6973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006973
Wang Y, Guo L, Jiang HF, Zheng LT, Zhang A, Zhen XC (2016) Allosteric modulation of Sigma-1 receptors elicits rapid antidepressant activity. CNS Neurosci Ther 22:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12502
Wang Q, Jie W, Liu JH, Yang JM, Gao TM (2017) An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview. Glia. 65:1227–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23143
Wang Y, Xie L, Gao C, Zhai L, Zhang N, Guo L (2018) Astrocytes activation contributes to the antidepressant-like effect of ketamine but not scopolamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 170:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2018.05.001
Yuskaitis CJ, Jope RS (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates microglial migration, inflammation, and inflammation-induced neurotoxicity. Cell Signal 21:264–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.10.014
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Wang Z (2015) Chronic corticosterone exposure reduces hippocampal astrocyte structural plasticity and induces hippocampal atrophy in mice. Neurosci Lett 592:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.03.006
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81603086), the project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M601894), the Postgraduate Scientific Research and Innovation Project of Jiangsu Province (1701052A), Science and Technology Planning Project of Xuzhou (KC18047), and Fund of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacy (ZR-XY201504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LG designed and wrote the manuscript. YW, JN, and FHJ performed the experiments and analyzed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the National Institutes of Health (USA) and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Xuzhou Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S
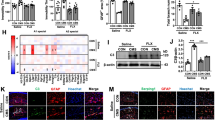
Effect of sigma-1 receptor activation on phosphorylation of AKT (ser 473) in the primary astrocytes. (+)SKF-10047 rapidly increased the phosphorylation of AKT (ser 437, 40 min), which was blocked by LY293004 (50 μM, 30 min) pretreatment (two-way ANOVA). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, each experiment was replicated three times. (PNG 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jiang, Hf., Ni, J. et al. Pharmacological stimulation of sigma-1 receptor promotes activation of astrocyte via ERK1/2 and GSK3β signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 801–812 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01632-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01632-3