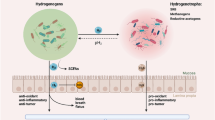
Abstract
Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) is a trending subject in recent therapy approaches despite its described toxicity. In this work, we have investigated the use of arsenic trioxide in a murine model of chemically induced inflammatory bowel disease “colitis.” Male mice were randomly separated into four different groups. Controls received vehicle, arsenic group had a daily injection of As2O3 (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.) for 2 days. Colitis was induced through intra-rectal instillation of 4% (v/v) solution of acetic acid in the second day. The treatment group (As2O3 + acetic acid) received the same treatment as the two previous groups. Twenty-four hours after colitis challenge, animals were sacrificed and organs (colons, livers, and kidneys) were taken for analysis. Disease-related macroscopic and microscopic symptoms, as well as histologic observations, showed a high index in the colitis group, which was greatly reduced by the As2O3 pretreatment. Similarly, colon length was reduced during colon inflammation, which was prevented in the presence of As2O3. Inflammatory cells and oxidative stress markers significantly increased during inflammation accompanied by a considerable reduction of antioxidants. As2O3 treatment managed to reverse these observations to normal levels. Mitochondrial implication was observed through mPTP opening phenomena and semi-quantitative cell death estimation. Low-dose As2O3 use as a mean of preventing the acute phase of colitis can be seen as an interesting approach which counts as a great addition to IBD available treatments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achitei D, Ciobica A, Balan G, Gologan E, Stanciu C, Stefanescu G (2013) Different profile of peripheral antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in active and non-active inflammatory bowel disease patients. Dig Dis Sci 58:1244–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2510-z
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Akazawa Y, Kubo M, Zhang R, Matsumoto K, Yan F, Setiawan H, Takahashi H, Fujikura Y, Ogino K (2013) Inhibition of arginase ameliorates experimental ulcerative colitis in mice. Free Radic Res 47:137–145. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2012.756980
Belzacq AS, el Hamel C, Vieira HLA, Cohen I, Haouzi D, Métivier D, Marchetti P, Brenner C, Kroemer G (2001) Adenine nucleotide translocator mediates the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization induced by lonidamine, arsenite and CD437. Oncogene 20:7579–7587. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204953
Binet F, Chiasson S, Girard D (2011) Interaction between arsenic trioxide (ATO) and human neutrophils. Hum Exp Toxicol 30:416–424. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327110372645
Birch-Machin MA, Turnbull DM (2001) Chapter 5 Assaying mitochondrial respiratory complex activity in mitochondria isolated from human cells and tissues. In: Methods in cell biology, vol 65. Academic Press, pp 97–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-679X(01)65006-4
Boyer J, Saint-Paul MC, Dadone B, Patouraux S, Vivinus MH, Ouvrier D, Michiels JF, Piche T, Tulic MK (2018) Inflammatory cell distribution in colon mucosa as a new tool for diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome: a promising pilot study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13223
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Breuille D, Obled C (2000) Cysteine and glutathione in catabolic states. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Clin Perform Programme 3:173–191 discussion 191-177
Bufill JA (1990) Colorectal cancer: evidence for distinct genetic categories based on proximal or distal tumor location. Ann Intern Med 113:779–788
Chinard FP (1952) Photometric estimation of proline and ornithine. J Biol Chem 199:91–95
Coburn LA, Gong X, Singh K, Asim M, Scull BP, Allaman MM, Williams CS, Rosen MJ, Washington MK, Barry DP, Piazuelo MB, Casero RA, Chaturvedi R, Zhao Z, Wilson KT (2012) L-arginine supplementation improves responses to injury and inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium colitis. PLoS One 7:e33546. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033546
Cuzzocrea S, Ayroldi E, di Paola R, Agostini M, Mazzon E, Bruscoli S, Genovese T, Ronchetti S, Caputi AP, Riccardi C (2005) Role of glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family gene (GITR) in collagen-induced arthritis. FASEB J 19:1253–1265. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-3556com
Di Lorenzo C et al (2013) Plant food supplements with anti-inflammatory properties: a systematic review (II). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 53:507–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2012.691916
Dulac RW, Yang TJ (1991) Differential sodium fluoride sensitivity of alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase in human, bovine, canine, and murine monocytes and lymphocytes. Exp Hematol 19:59–62
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Fedorak RN, Empey LR, Walker K (1992) Verapamil alters eicosanoid synthesis and accelerates healing during experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology 102:1229–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(92)70017-6
Ganapathy S, Xiao S, Seo SJ, Lall R, Yang M, Xu T, Su H, Shadfan M, Ha CS, Yuan ZM (2014) Low-dose arsenic induces chemotherapy protection via p53/NF-kappaB-mediated metabolic regulation. Oncogene 33:1359–1366. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.81
Goretsky T, Dirisina R, Sinh P, Mittal N, Managlia E, Williams DB, Posca D, Ryu H, Katzman RB, Barrett TA (2012) p53 mediates TNF-induced epithelial cell apoptosis in IBD. Am J Pathol 181:1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.016
Grisham MB, Gaginella TS, von Ritter C, Tamai H, Be RM, Granger DN (1990) Effects of neutrophil-derived oxidants on intestinal permeability, electrolyte transport, and epithelial cell viability. Inflammation 14:531–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00914274
Grisham MB, Volkmer C, Tso P, Yamada T (1991) Metabolism of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid by the rat colon produces reactive oxygen species. Gastroenterology 101:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(91)90036-k
Gupta S, Yel L, Kim D, Kim C, Chiplunkar S, Gollapudi S (2003) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets by inducing oxidative stress: a role of Bcl-2. Mol Cancer Ther 2:711–719
Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Powell GE, Sandler RS (2007) Serious adverse events with infliximab: analysis of spontaneously reported adverse events. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 5:729–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2007.02.016
Higa A, Eto T, Nawa Y (1997) Evaluation of the role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acetic acid-induced colitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:564–568
Higgins PD, Skup M, Mulani PM, Lin J, Chao J (2015) Increased risk of venous thromboembolic events with corticosteroid vs biologic therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 13:316–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.07.017
Kalischuk LD, Leggett F, Inglis GD (2010) Campylobacter jejuni induces transcytosis of commensal bacteria across the intestinal epithelium through M-like cells. Gut Pathog 2:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-4749-2-14
Kandhare AD, Raygude KS, Ghosh P, Ghule AE, Gosavi TP, Badole SL, Bodhankar SL (2012) Effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Hibiscus rosa sinensis Linn. leaves in experimental colitis in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60053-7
Krawisz JE, Sharon P, Stenson WF (1984) Quantitative assay for acute intestinal inflammation based on myeloperoxidase activity. Assessment of inflammation in rat and hamster models. Gastroenterology 87:1344–1350
Kurutas EB, Cetinkaya A, Bulbuloglu E, Kantarceken B (2005) Effects of antioxidant therapy on leukocyte myeloperoxidase and Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase and plasma malondialdehyde levels in experimental colitis. Mediat Inflamm 2005:390–394. https://doi.org/10.1155/MI.2005.390
Lemarie A, Bourdonnay E, Morzadec C, Fardel O, Vernhet L (2008) Inorganic arsenic activates reduced NADPH oxidase in human primary macrophages through a Rho kinase/p38 kinase pathway. J Immunol 180:6010–6017. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.6010
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer J, Waxman S (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res 62:3893–3903
Mirallesbarrachina O et al (1999) Low levels of glutathione in endoscopic biopsies of patients with Crohn’s colitis: the role of malnutrition. Clin Nutr 18:313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0261-5614(98)80030-7
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 5:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.2000.0319
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL (1989) Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 96:795–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(89)80079-4
Moulahoum H, Boumaza BMA, Ferrat M, Djerdjouri B (2018) Arsenic trioxide exposure accelerates colon preneoplasic aberrant crypt foci induction regionally through mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicology Research 7:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tx00213k
Naranmandura H, Chen X, Tanaka M, Wang WW, Rehman K, Xu S, Chen Z, Chen SQ, Suzuki N (2012) Release of apoptotic cytochrome C from mitochondria by dimethylarsinous acid occurs through interaction with voltage-dependent anion channel in vitro. Toxicol Sci 128:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs154
Neurath MF (2014) Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:329–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3661
Neurath MF, Fuss I, Kelsall BL, Stuber E, Strober W (1995) Antibodies to interleukin 12 abrogate established experimental colitis in mice. J Exp Med 182:1281–1290. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.182.5.1281
Ogata H, Hibi T (2003) Does an elemental diet affect operation and/or recurrence rate in Crohn’s disease in Japan? J Gastroenterol 38:1019–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-003-1210-z
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Paul MK, Rajinder K, Mukhopadhyay AK (2008) Characterization of rat liver mitochondrial permeability transition pore by using mitochondrial swelling assay. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2:014–021
Qin HY, Wu JC, Tong XD, Sung JJ, Xu HX, Bian ZX (2011) Systematic review of animal models of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol 46:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0321-6
Ramasamy S, Nguyen DD, Eston MA, Nasrin Alam S, Moss AK, Ebrahimi F, Biswas B, Mostafa G, Chen KT, Kaliannan K, Yammine H, Narisawa S, Millán JL, Warren SH, Hohmann EL, Mizoguchi E, Reinecker HC, Bhan AK, Snapper SB, Malo MS, Hodin RA (2011) Intestinal alkaline phosphatase has beneficial effects in mouse models of chronic colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17:532–542. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21377
Sands BE (2007) Inflammatory bowel disease: past, present, and future. J Gastroenterol 42:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-006-1995-7
Sengupta M, Bishayi B (2002) Effect of lead and arsenic on murine macrophage response. Drug Chem Toxicol 25:459–472. https://doi.org/10.1081/DCT-120014796
Sharma A, Sharma MK, Kumar M (2007) Protective effect of Mentha piperita against arsenic-induced toxicity in liver of Swiss albino mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00030.x
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, Fang ZW, Wang YT, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Chen SJ, Chen Z, Wang ZY (1997) Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood 89:3354–3360
Sido B, Hack V, Hochlehnert A, Lipps H, Herfarth C, Droge W (1998) Impairment of intestinal glutathione synthesis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 42:485–492. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.42.4.485
Singer M, Trugnan G, Chelbi-Alix MK (2011) Arsenic trioxide reduces 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced murine colitis via nuclear factor-kappaB down-regulation and caspase-3 activation. Innate Immun 17:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425910371668
Sunkara S, Swanson G, Forsyth CB, Keshavarzian A (2011) Chronic inflammation and malignancy in ulcerative colitis. Ulcers 2011:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/714046
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Etzrodt M, Wildgruber M, Cortez-Retamozo V, Panizzi P, Figueiredo JL, Kohler RH, Chudnovskiy A, Waterman P, Aikawa E, Mempel TR, Libby P, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2009) Identification of splenic reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites. Science 325:612–616. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1175202
Takhshid MA, Mehrabani D, Ai J, Zarepoor M (2011) The healing effect of licorice extract in acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rat model. Comp Clin Pathol 21:1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1249-9
Wong R, Steenbergen C, Murphy E (2012) Mitochondrial permeability transition pore and calcium handling. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 810:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-382-0_15
Yang X, Meng S, Jiang H, Chen T, Wu W (2010) Exosomes derived from interleukin-10-treated dendritic cells can inhibit trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced rat colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 45:1168–1177. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2010.490596
Yeh JY, Cheng LC, Ou BR, Whanger PD, Chang LW (2002) Differential influences of various arsenic compounds on glutathione redox status and antioxidative enzymes in porcine endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:1972–1982. https://doi.org/10.1007/Pl00012519
Zhou XG, Scharf ME, Sarath G, Meinke LJ, Chandler LD, Siegfried BD (2004) Partial purification and characterization of a methyl-parathion resistance-associated general esterase in Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (Coleoptera : Chrysomelidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 78:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2003.10.003
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the DGRSDT (Direction Générale de la Recherche Scientifique et du Développement Technologique), Algiers, Algeria (PNR project, ATRSS/PNR 08/N°305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM, BMAB, AB, and BD conceived and designed the research plan. HM, BMAB, and MF conducted experiments. HM, BMAB, and MF analyzed the data. HM wrote the manuscript. AB and BD supervised the work. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were performed according to the “Ethics Committee for handling laboratory animals” guidelines at the “University of Sciences and Technology Houari Boumediene, Algiers, Algeria.”
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moulahoum, H., Boumaza, B.M.A., Ferrat, M. et al. Arsenic trioxide ameliorates murine colon inflammation through inflammatory cell enzymatic modulation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 259–270 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1578-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1578-1