Abstract
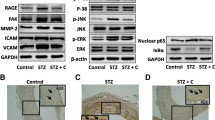
Endothelial dysfunction is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of vascular disease in diabetes mellitus and RhoA/Rho-kinase (ROCK) system appears to play a crucial role in this setting. The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of the selective ROCK inhibitor, fasudil, on diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction and elucidated its underlying mechanism(s). Diabetes was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 50 mg/kg), and fasudil (5 mg/kg per day) was orally administered for 8 weeks. Our results showed that fasudil administration attenuated the increased activity/expression of ROCK (627.5 ± 27 vs. 247.8 ± 19.1) and the NADPH oxidase subunits, NOX2 and p47phox, in diabetic rat aorta. Fasudil could reduce the elevated tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (70.2 ± 14.1 vs. 25.3 ± 5.2) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β) levels and restored the deficit in antioxidant level of the diabetic aorta. Additionally, fasudil markedly improved the endothelial dysfunction in the diabetic aorta (73.8 ± 8.1 vs. 47.42 ± 8.69) and corrected the dysregulated endothelial nitric oxide (eNOS) expression. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that fasudil effectively ameliorates the endothelial dysfunction in STZ-induced diabetic rats through inhibition of the Rho/ROCK pathway and thereby reducing the TNF-α-mediated NADPH oxidase activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adel H, Taye A, Khalifa MM (2014) Spironolactone improves endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 387:1187–1197
Arita R, Hata Y, Nakao S, Kita T, Miura M, Kawahara S, Zandi S, Almulki L, Tayyari F, Shimokawa H, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Ishibashi T (2009) Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil ameliorates diabetes-induced microvascular damage. Diabetes 58:215–226
Arita R, Nakao S, Kita T, Kawahara S, Asato R, Yoshida S, Enaida H, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Ishibashi T (2013) A key role for ROCK in TNF-alpha-mediated diabetic microvascular damage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2373–2383
Bar-Sagi D, Hall A (2000) Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell 103:227–238
Bedard K, Krause KH (2007) The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87:245–313
Bolz SS, Vogel L, Sollinger D, Derwand R, de Wit C, Loirand G, Pohl U (2003) Nitric oxide-induced decrease in calcium sensitivity of resistance arteries is attributable to activation of the myosin light chain phosphatase and antagonized by the RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Circulation 107:3081–3087
Busik JV, Mohr S, Grant MB (2008) Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species toxicity to endothelial cells is dependent on paracrine mediators. Diabetes 57:1952–1965
Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Simonneau C, Therond P, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Poiraudeau S, Ekindjian OG, Borderie D (2007) Implication of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in the regulation of human synoviocyte NADPH oxidase (Nox2) activity. Life Sci 81:1050–1058
Ciobanu AO, Gherghinescu CL, Dulgheru R, Magda S, Dragoi Galrinho R, Florescu M, Guberna S, Cinteza M, Vinereanu D (2013) The impact of blood pressure variability on subclinical ventricular, renal and vascular dysfunction, in patients with hypertension and diabetes. Maedica (Buchar) 8:129–136
Coskun O, Kanter M, Korkmaz A, Oter S (2005) Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat pancreas. Pharmacol Res 51:117–123
Dalaklioglu S, Tasatargil A, Kale S, Tanriover G, Dilmac S, Erin N (2013) Metastatic breast carcinoma induces vascular endothelial dysfunction in Balb-c mice: role of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and NADPH oxidase. Vasc Pharmacol 59:103–111
Dawson A, Rana BS, Pringle SD, Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Struthers AD (2004) How much echo left ventricular hypertrophy would be missed in diabetics by applying the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint Reduction electrocardiogram criteria to select patients for angiotensin receptor blockade? J Hypertens 22:1403–1408
De Backer D, Creteur J, Vincent JL (2003) Arginine vasopressin in advanced vasodilatory shock. Circulation 108:e142 author reply e142
De Miguel C, Foster JM, Carmines PK, Pollock JS (2013) Interaction between NO synthase and NADPH oxidase in control of sodium transport by the renal thick ascending limb during diabetes. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 209:148–155
Diatchuk V, Lotan O, Koshkin V, Wikstroem P, Pick E (1997) Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation by 4-(2-aminoethyl)-benzenesulfonyl fluoride and related compounds. J Biol Chem 272:13292–13301
El-Remessy AB, Tawfik HE, Matragoon S, Pillai B, Caldwell RB, Caldwell RW (2010) Peroxynitrite mediates diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction: possible role of Rho kinase activation. Exp Diabetes Res 2010:247861
El-seweidy MM, El-Swefy SE, Ameen RS, Hashem RM (2002) Effect of age receptor blocker and/or anti-inflammatory coadministration in relation to glycation, oxidative stress and cytokine production in stz diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res 45:391–398
Fried LF, Duckworth W, Zhang JH, O’Connor T, Brophy M, Emanuele N, Huang GD, McCullough PA, Palevsky PM, Seliger S, Warren SR, Peduzzi P (2009) Design of combination angiotensin receptor blocker and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor for treatment of diabetic nephropathy (VA NEPHRON-D). Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:361–368
Guan SJ, Ma ZH, Wu YL, Zhang JP, Liang F, Weiss JW, Guo QY, Wang JY, Ji ES, Chu L (2012) Long-term administration of fasudil improves cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 50:1874–1882
Harrison DG (1997) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest 100:2153–2157
Higashi M, Shimokawa H, Hattori T, Hiroki J, Mukai Y, Morikawa K, Ichiki T, Takahashi S, Takeshita A (2003) Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase suppresses angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular hypertrophy in rats in vivo: effect on endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase system. Circ Res 93:767–775
Hofni A, El-Moselhy MA, Taye A, Khalifa MM (2014) Combination therapy with spironolactone and candesartan protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 744:173–182
Hori M, Nishida K (2009) Oxidative stress and left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 81:457–464
Huang Z, Nan C, Wang H, Su Q, Xue W, Chen Y, Shan X, Duan J, Chen G, Tao W (2016) Crocetin ester improves myocardial ischemia via Rho/ROCK/NF-kappaB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 38:186–193
Hung CN, Huang HP, Wang CJ, Liu KL, Lii CK (2014) Sulforaphane inhibits TNF-alpha-induced adhesion molecule expression through the Rho A/ROCK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Med Food 17:1095–1102
Jin L, Ying Z, Webb RC (2004) Activation of Rho/Rho kinase signaling pathway by reactive oxygen species in rat aorta. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H1495–H1500
Kaesemeyer WH, Ogonowski AA, Jin L, Caldwell RB, Caldwell RW (2000) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is a site of superoxide synthesis in endothelial cells treated with glyceryl trinitrate. Br J Pharmacol 131:1019–1023
Kikuchi Y, Yamada M, Imakiire T, Kushiyama T, Higashi K, Hyodo N, Yamamoto K, Oda T, Suzuki S, Miura S (2007) A Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 192:595–603
Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S, Liu ZG (2007) TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell 26:675–687
Kizub IV, Pavlova OO, Johnson CD, Soloviev AI, Zholos AV (2010) Rho kinase and protein kinase C involvement in vascular smooth muscle myofilament calcium sensitization in arteries from diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 159:1724–1731
Kodavanti UP, Schladweiler MC, Gilmour PS, Wallenborn JG, Mandavilli BS, Ledbetter AD, Christiani DC, Runge MS, Karoly ED, Costa DL, Peddada S, Jaskot R, Richards JH, Thomas R, Madamanchi NR, Nyska A (2008) The role of particulate matter-associated zinc in cardiac injury in rats. Environ Health Perspect 116:13–20
Laufs U, Liao JK (1998) Post-transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA stability by Rho GTPase. J Biol Chem 273:24266–24271
Li JM, Fan LM, Christie MR, Shah AM (2005) Acute tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling via NADPH oxidase in microvascular endothelial cells: role of p47phox phosphorylation and binding to TRAF4. Mol Cell Biol 25:2320–2330
Li X, Wu X, Li H, Chen H, Wang Y, Li W, Ding X, Hong X (2016) Increased Rho kinase activity predicts worse cardiovascular outcome in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. Cardiol J 23(4):456–464
Martin J, Kelly DJ, Mifsud SA, Zhang Y, Cox AJ, See F, Krum H, Wilkinson-Berka J, Gilbert RE (2005) Tranilast attenuates cardiac matrix deposition in experimental diabetes: role of transforming growth factor-beta. Cardiovasc Res 65:694–701
McKenzie JA, Ridley AJ (2007) Roles of Rho/ROCK and MLCK in TNF-alpha-induced changes in endothelial morphology and permeability. J Cell Physiol 213:221–228
Ming XF, Viswambharan H, Barandier C, Ruffieux J, Kaibuchi K, Rusconi S, Yang Z (2002) Rho GTPase/Rho kinase negatively regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation through the inhibition of protein kinase B/Akt in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 22:8467–8477
Mishra RK, Alokam R, Sriram D, Yogeeswari P (2013) Potential role of Rho kinase inhibitors in combating diabetes-related complications including diabetic neuropathy--a review. Curr Diabetes Rev 9:249–266
Mong PY, Petrulio C, Kaufman HL, Wang Q (2008) Activation of Rho kinase by TNF-alpha is required for JNK activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 180:550–558
Montaner S, Perona R, Saniger L, Lacal JC (1998) Multiple signalling pathways lead to the activation of the nuclear factor kappaB by the Rho family of GTPases. J Biol Chem 273:12779–12785
Mukherjee TK, Mukhopadhyay S, Hoidal JR (2005) The role of reactive oxygen species in TNFalpha-dependent expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1744:213–223
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Beckers CM, Achekar ID, Zeeman S, Musters RJ, van Hinsbergh VW (2007) Involvement of rho kinase in endothelial barrier maintenance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2332–2339
Peng F, Wu D, Gao B, Ingram AJ, Zhang B, Chorneyko K, McKenzie R, Krepinsky JC (2008) RhoA/Rho-kinase contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic renal disease. Diabetes 57:1683–1692
Ren XD, Kiosses WB, Schwartz MA (1999) Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J 18:578–585
Romero MJ, Platt DH, Tawfik HE, Labazi M, El-Remessy AB, Bartoli M, Caldwell RB, Caldwell RW (2008) Diabetes-induced coronary vascular dysfunction involves increased arginase activity. Circ Res 102:95–102
Schafer A, Bauersachs J (2008) Endothelial dysfunction, impaired endogenous platelet inhibition and platelet activation in diabetes and atherosclerosis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 6:52–60
Shimokawa H, Morishige K, Miyata K, Kandabashi T, Eto Y, Ikegaki I, Asano T, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A (2001) Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase induces a regression of arteriosclerotic coronary lesions in a porcine model in vivo. Cardiovasc Res 51:169–177
Takemoto M, Sun J, Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Liao JK (2002) Rho-kinase mediates hypoxia-induced downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 106:57–62
Taniyama Y, Griendling KK (2003) Reactive oxygen species in the vasculature: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Hypertension 42:1075–1081
Yao L, Chandra S, Toque HA, Bhatta A, Rojas M, Caldwell RB, Caldwell RW (2013) Prevention of diabetes-induced arginase activation and vascular dysfunction by Rho kinase (ROCK) knockout. Cardiovasc Res 97:509–519
Zhou H, Li YJ, Wang M, Zhang LH, Guo BY, Zhao ZS, Meng FL, Deng YG, Wang RY (2011) Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in myocardial fibrosis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:999–1008
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to grateful to Prof. Adel Bakeer, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, for his kind help in performing histopathological studies and interpretation of the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofni, A., Shehata Messiha, B.A. & Mangoura, S.A. Fasudil ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: a possible role of Rho kinase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 801–811 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1379-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1379-y