Abstract
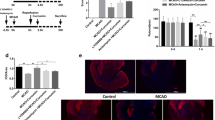
This study was carried out to investigate the exact mechanisms behind the neuroprotective effects of oleoylethanolamide (OEA) after acute cerebral ischemic injury. Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 90 min followed by reperfusion. OEA (40 mg/kg, ip) was administered with a single injection upon reperfusion. The number of apoptotic cells was detected by TUNEL staining. The expression of Bax, Bcl-2, and TLR4, as well as the activities of NF-κB, Akt, and ERK1/2 were analyzed by western blot. Our data showed that OEA treatment alleviated cell apoptosis in a mouse model of ischemic stroke, accompanied by suppression of Bax, as well as upregulation of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 level. The changes of Bax and Bcl-2 could not be observed in PPARα knockout mice models with OEA administration. Importantly, OEA inhibited MCAO-induced TLR4 expression, NF-κB activation, IκBα degradation, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Our findings demonstrated that the neuroprotective effects of OEA on cerebral ischemia may be attributed to its antiapoptotic property achieved, at least in part, through the PPARα signaling and inhibition of both TLR4/NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. These results provide new evidence indicating the neuroprotective effect of OEA on ischemic stroke.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisogno T, Martire A, Petrosino S, Popoli P, Di Marzo V (2008) Symptom-related changes of endocannabinoid and palmitoylethanolamide levels in brain areas of R6/2 mice, a transgenic model of Huntington’s disease. Neurochem Int 52:307–313
Dornbos I, Ding Y (2012) Mechanisms of neuronal damage and neuroprotection underlying ischemia/reperfusion injury after physical exercise. Curr Drug Targets 13:247–262
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Fisher M (2003) The ischemic penumbra: identification, evolution and treatment concepts. Cerebrovasc Dis 17:1–6
Galan-Rodriguez B, Suarez J, Gonzalez-Aparicio R, Bermudez-Silva F, Maldonado R, Robledo P, de Fonseca FR, Fernandez-Espejo E (2009) Oleoylethanolamide exerts partial and dose-dependent neuroprotection of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. Neuropharmacology 56:653–664
Gonzalez-Aparicio R, Blanco E, Serrano A, Pavon FJ, Parsons LH, Maldonado R, Robledo P, Fernandez-Espejo E, De Fonseca FR (2014) The systemic administration of oleoylethanolamide exerts neuroprotection of the nigrostriatal system in experimental parkinsonism. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:455–468
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Harari OA, Liao JK (2010) NF-kappaB and innate immunity in ischemic stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1207:32–40
Lan R, Xiang J, Zhang Y, Wang G-H, Bao J, Li W-W, Zhang W, Xu L-L, (2013) Cai D-F (2013) PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to neurovascular unit protection of Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 16:1–17
Lanzillotta A, Porrini V, Bellucci A, Benarese M, Branca C, Parrella E, Spano PF, Pizzi M (2015) NF-κB in innate neuroprotection and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurol 6:1–8
Martinou J-C, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92–101
Mattson M, Duan W, Pedersen W, Culmsee C (2001) Neurodegenerative disorders and ischemic brain diseases. Apoptosis 6:69–81
Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Matsushita K, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV, Alessandrini A (2001) Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:11569–11574
Pandya JD, Sullivan PG, Pettigrew LC (2011) Focal cerebral ischemia and mitochondrial dysfunction in the TNFα-transgenic rat. Brain Res 1384:151–160
Paul SL, Srikanth VK, Thrift AG (2007) The large and growing burden of stroke. Curr Drug Targets 8:786–793
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC, Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T (2007) Increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus of patients with myasthenia gravis. In vivo 21:123–132
Shih RH, Wang CY, Yang CM (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8:77
Sun Y, Alexander S, Garle M, Gibson CL, Hewitt K, Murphy SP, Kendall D, Bennett A (2007) Cannabinoid activation of PPAR [alpha]; a novel neuroprotective mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 152:734
Wang N, Zhang Y, Wu L, Wang Y, Cao Y, He L, Li X, Zhao J (2014) Puerarin protected the brain from cerebral ischemia injury via astrocyte apoptosis inhibition. Neuropharmacology 79:282–289
White BC, Sullivan JM, DeGracia DJ, O’Neil BJ, Neumar RW, Grossman LI, Rafols JA, Krause GS (2000) Brain ischemia and reperfusion: molecular mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurol Sci 179:1–33
Woodruff TM, Thundyil J, Tang S-C, Sobey CG, Taylor SM, Arumugam TV (2011) Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke. Mol Neurodegener 6:11
Yang L-c, Guo H, Zhou H, D-q S, W-j L, Zhou Y, Zhao Y, Yang W-s, Jin X (2015) Chronic oleoylethanolamide treatment improves spatial cognitive deficits through enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Biochem Pharmacol 94:270–281
Zhou Y, Yang L, Ma A, Zhang X, Li W, Yang W, Chen C, Jin X (2012) Orally administered oleoylethanolamide protects mice from focal cerebral ischemic injury by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. Neuropharmacology 63:242–249
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Nos. 81373407, 81402921, and 81603093), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian, China (Nos. 2016J01415, 2016D024, and 2015J01354), and the Science and Technology Project of Xiamen, China (No. 3502Z20144027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Hao Zhou, Wu-shuang Yang, and Ying Li contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Yang, Ws., Li, Y. et al. Oleoylethanolamide attenuates apoptosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in mice with acute ischemic stroke. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 77–84 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1309-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1309-4