Abstract
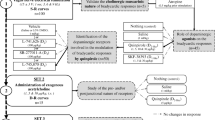
We have recently reported that quinpirole (a D2-like receptor agonist) inhibits the vasopressor sympathetic outflow in pithed rats via sympatho-inhibitory D2-like receptors. Since D2-like receptors consist of D2, D3 and D4 receptor subtypes, this study investigated whether these subtypes are involved in the above quinpirole-induced sympatho-inhibition by using antagonists of these receptor subtypes. One hundred fifty-six male Wistar rats were pithed and prepared for preganglionic spinal (T7–T9) stimulation of the vasopressor sympathetic outflow. This approach resulted in frequency-dependent vasopressor responses which were analysed before and during i.v. continuous infusions of either saline (0.02 ml/min) or quinpirole (1 μg/kg.min) in animals receiving i.v. bolus injections of vehicle [saline or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)] or the antagonists L-741,626 (D2), nafadotride or SB-277011-A (both D3) as well as L-745,870 (D4). Quinpirole inhibited the sympathetically-induced vasopressor responses. This sympatho-inhibition was (a) unaltered after 1 ml/kg saline, DMSO or 100 and 300 μg/kg L-741,626; (b) markedly blocked and abolished by, respectively, 30 and 100 μg/kg nafadotride or 100 and 300 μg/kg SB-277011-A and (c) slightly blocked after 30 and 100 μg/kg L-745,870, but 300 μg/kg L-745,870 produced no blockade whatsoever. Except for 300 μg/kg L-741,626 or 300 μg/kg L-745,870, the doses of the above compounds failed to modify per se the sympathetic vasopressor responses. The inhibition of the vasopressor sympathetic outflow induced by 1 μg/kg.min quinpirole in pithed rats is predominantly mediated by dopamine D3 and, to a lesser extent, by D4 receptor subtypes, with no evidence for the involvement of the D2 subtype.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amenta F, Barili P, Bronzetti E, Felici L, Mignini F, Ricci A (2000) Localization of dopamine receptor subtypes in systemic arteries. Clin Exp Hypertens 22:277–288
Amenta F, Bronzetti E, Cantalamessa F, El-Assouad D, Felici L, Ricci A et al (2001) Identification of dopamine plasma membrane and vesicular transporters in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 117:133–142
Asico LD, Ladines C, Fuchs S, Accili D, Carey RM, Semeraro C et al (1998) Disruption of the dopamine D3 receptor gene produces renin-dependent hypertension. J Clin Invest 102:493–498
Audinot V, Newman-Tancredi A, Gobert A, Rivet JM, Brocco M, Lejeune F et al (1998) A comparative in vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonists (+)-S 14297, nafadotride, GR 103,691 and U 99194. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:187–197
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Bechtel WD, Mierau J, Pelzer H (1986) Biochemical pharmacology of pirenzepine. Similarities with tricyclic antidepressants in antimuscarinic effects only. Arzneimittelforschung 36:793–796
Boehm S, Kubista H (2002) Fine tuning of sympathetic transmitter release via ionotropic and metabotropic presynaptic receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:43–99
Bowery BJ, Razzaque Z, Emms F, Patel S, Freedman S, Bristow L et al (1996) Antagonism of the effects of (+)-PD 128907 on midbrain dopamine neurones in rat brain slices by a selective D2 receptor antagonist L-741,626. Br J Pharmacol 119:1491–1497
Bulloch JM, McGrath JC (1988) Selective blockade by nifedipine of ‘purinergic’ rather than adrenergic nerve-mediated vasopressor responses in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol 95:1220–1228
Damase-Michel C, Montastruc JL, Gharib C, Geelen G, De Saint-Blanquat G, Tran MA (1990) Effect of quinpirole, a specific dopamine DA2 receptor agonist on the sympathoadrenal system in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:770–777
De Jong AP, Verhage M (2009) Presynaptic signal transduction pathways that modulate synaptic transmission. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19:245–254
Docherty JR (2011) Vasopressor nerve responses in the pithed rat, previously identified as alpha2-adrenoceptor mediated, may be alpha1D-adrenoceptor mediated. Eur J Pharmacol 658:182–186
Flavahan NA, Grant TL, McGrath JC (1985) Analysis of the α-adrenoceptor-mediated, and other, components in the sympathetic vasopressor responses of the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol 86:265–274
Gillespie JS, Maclaren A, Pollock D (1970) A method of stimulating different segments of the autonomic outflow from the spinal column to various organs in the pithed cat and rat. Br J Pharmacol 40:257–267
Gross ML, Koch A, Mühlbauer B, Adamczak M, Ziebart H, Drescher K et al (2006) Renoprotective effect of a dopamine D3 receptor antagonist in experimental type II diabetes. Lab Invest 86:262–274
Kleinman LI, Radford EP Jr (1964) Ventilation standards for small mammals. J Appl Physiol 19:360–362
Luippold G, Kuster E, Joos TO, Mühlbauer B (1998) Dopamine D3 receptor activation modulates renal function in anesthetized rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 358:690–693
Luippold G, Beilharz M, Wehrmann M, Unger L, Gross G, Mühlbauer B (2005) Effect of dopamine D3 receptor blockade on renal function and glomerular size in diabetic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 371:420–427
Lundby C, Møller P, Kanstrup IL, Olsen NV (2001) Heart rate response to hypoxic exercise: role of dopamine D2-receptors and effect of oxygen supplementation. Clin Sci 101:377–383
Mannelli M, Ianni L, Lazzeri C, Castellani W, Pupilli C, La Villa G et al (1999) In vivo evidence that endogenous dopamine modulates sympathetic activity in man. Hypertension 34:398–402
Manrique-Maldonado G, Gonzalez-Hernandez A, Marichal-Cancino BA, Villamil-Hernandez MT, Del Mercado OA, Centurion D et al (2011) The dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of the sympathetic vasopressor outflow in pithed rats: pharmacological correlation with the D(2)-like type. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109:506–512
Mercuro G, Horn PT, Kohli JD, Orelind ER, Cherchi A (1990a) Catecholamine injections in canine paravertebral ganglia produce hypotension by neurogenic vasodilatation. Cardiologia 35:899–903
Mercuro G, Horn PT, Orelind ER, Kohli JD (1990b) Inhibitory effects of catecholamines in the paravertebral sympathetic ganglia of the anesthetized dog. Eur J Pharmacol 185:61–68
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Newman-Tancredi A, Lejeune F, Cussac D, Rivet JM et al (2000) S33084, a novel, potent, selective, and competitive antagonist at dopamine D(3)-receptors: I. Receptorial, electrophysiological and neurochemical profile compared with GR218,231 and L741,626. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:1048–1062
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Mühlbauer B, Kuster E, Luippold G (2000) Dopamine D(3) receptors in the rat kidney: role in physiology and pathophysiology. Acta Physiol Scand 168:219–223
Neve KA, Seamans JK, Trantham-Davidson H (2004) Dopamine receptor signaling. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 24:165–204
Patel S, Freedman S, Chapman KL, Emms F, Fletcher AE, Knowles M et al (1997) Biological profile of L-745,870, a selective antagonist with high affinity for the dopamine D4 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:636–647
Reavill C, Taylor SG, Wood MD, Ashmeade T, Austin NE, Avenell KY et al (2000) Pharmacological actions of a novel, high-affinity, and selective human dopamine D(3) receptor antagonist, SB-277011-A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1154–1165
Satoh Y, Kohli JD, Goldberg LI (1989) Effects of alpha adrenoceptor and dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists on ganglionic transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:253–257
Seeman P, Van Tol HH (1994) Dopamine receptor pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:264–270
Shipley RE, Tilden JH (1947) A pithed rat preparation suitable for assaying pressor substances. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 64:453–455
Staudacher T, Pech B, Tappe M, Gross G, Mühlbauer B, Luippold G (2007) Arterial blood pressure and renal sodium excretion in dopamine D3 receptor knockout mice. Hypertens Res 30:93–101
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biomedical approach, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, Tokyo
Vaughan CJ, Aherne AM, Lane E, Power O, Carey RM, O’Connell DP (2000) Identification and regional distribution of the dopamine D(1A) receptor in the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:599–609
Villalón CM, Contreras J, Ramirez-San Juan E, Castillo C, Perusquia M, Lopez-Munoz FJ et al (1995a) 5-Hydroxytryptamine inhibits pressor responses to preganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation in pithed rats. Life Sci 57:803–812
Villalón CM, Contreras J, Ramirez-San Juan E, Castillo C, Perusquia M, Terron JA (1995b) Characterization of prejunctional 5-HT receptors mediating inhibition of sympathetic vasopressor responses in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol 116:3330–3336
Villalón CM, Centurion D, Rabelo G, de Vries P, Saxena PR, Sanchez-Lopez A (1998) The 5-HT1-like receptors mediating inhibition of sympathetic vasopressor outflow in the pithed rat: operational correlation with the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D subtypes. Br J Pharmacol 124:1001–1011
Villalón CM, Altamirano-Espinoza A, Ruiz-Salinas II, Manrique-Maldonado G, Marichal-Cancino BA, González-Hernández A et al (2011) The role of dopamine D2, but not D3 or D4, receptor subtypes in quinpirole-induced inhibition of the cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow in pithed rats. Proceedings of the 2011 BPS Winter Meeting. http://www.pA2online.org/abstracts/Vol 9 Issue3 abst 001P.pdf
Wang X, Villar VA, Armando I, Eisner GM, Felder RA, Jose PA (2008) Dopamine, kidney, and hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2131–2146
Wilffert B, Smith G, de Jonge A, Thoolen M, Timmermans P, Van Zwieten P (1984) Inhibitory dopamine receptors on the sympathetic neurons innervating the cardiovascular system of the pithed rat. Characterization and role in relation to presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 326:91–98
Willems JL, Buylaert WA, Lefebvre RA, Bogaert MG (1985) Neuronal dopamine receptors on autonomic ganglia and sympathetic nerves and dopamine receptors in the gastrointestinal system. Pharmacol Rev 37:165–216
Zeng C, Zhang M, Asico LD, Eisner GM, Jose PA (2007) The dopaminergic system in hypertension. Clin Sci 112:583–597
Zeng C, Armando I, Luo Y, Eisner GM, Felder RA, Jose PA (2008) Dysregulation of dopamine-dependent mechanisms as a determinant of hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:551–569
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Mauricio Villasana for his skilful technical assistance. The present study was financially supported by the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, project no. 60789; México DF).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Salinas, I., González-Hernández, A., Manrique-Maldonado, G. et al. Predominant role of the dopamine D3 receptor subtype for mediating the quinpirole-induced inhibition of the vasopressor sympathetic outflow in pithed rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 393–403 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0841-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0841-8