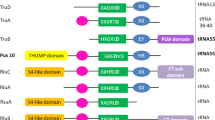
Abstract
Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPKs) are evolutionarily conserved enzymes involved in many biological processes such as metastasis, proliferation, development, differentiation, ciliary functions, vesicle transport and apoptosis in vertebrates. Biochemical mechanisms of these processes are still largely unknown. Sponges (Porifera) are simple metazoans without tissues, closest to the common ancestor of all animals. They changed little during evolution and probably provide the best insight into the metazoan ancestors’ genomic features. The purpose of this study was to address structural and functional properties of group II Nme6 gene/protein ortholog from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula, Nme6, in order to elucidate its evolutionary history. Sponge Nme6 gene and promoter were sequenced and analysed with various bioinformatical tools. Nme6 and Nme6Δ31 proteins were produced in E. coli strain BL21 and NDPK activity was measured using a coupled pyruvate kinase-lactate dehydrogenase assay. Subcellular localization in human tumour cells was examined by confocal scanning microscopy. Our results show that the sponge Nme6 compared to human Nme6 does not possess NDPK activity, does not localize in mitochondria at least in human cells although it has a putative mitochondrial signal sequence, lacks two recent introns that comprise miRNAs and have different transcriptional binding sites in the promoter region. Therefore, we conclude that the structure of Nme6 gene has changed during metazoan evolution possibly in correlation with the function of the protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal RP, Robison B, Parks RE Jr (1978) Nucleoside diphosphokinase from human erythrocytes. Meth Enzymol 51:376–386
Ambros V, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Burge CB, Carrington JC, Chen X, Dreyfuss G, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Marshall M, Matzke M, Ruvkun G, Tuschl T (2003) A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 9:277–279
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bilitou A, Watson J, Gartner A, Ohnuma S (2009) The NM23 family in development. Mol Cell Biochem 329:17–33
Boissan M, Dabernat S, Peuchant E, Schlattner U, Lascu I, Lacombe ML (2009) The mammalian Nm23/NDPK family: from metastasis control to cilia movement. Mol Cell Biochem 329:51–62
Cetkovic H, Muller WE, Gamulin V (2004) Bruton tyrosine kinase-like protein, BtkSD, is present in the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. Genomics 83:743–745
Cetkovic H, Mikoc A, Muller WE, Gamulin V (2007) Ras-like small GTPases form a large family of proteins in the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. J Mol Evol 64:332–341
Claros MG, Vincens P (1996) Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem 241:779–786
Desvignes T, Pontarotti P, Fauvel C, Bobe J (2009) Nme protein family evolutionary history, a vertebrate perspective. BMC Evol Biol 9:256
Desvignes T, Pontarotti P, Bobe J (2010) Nme gene family evolutionary history reveals pre-metazoan origins and high conservation between humans and the sea anemone. Nematostella vectensis. PLoS ONE 5:e15506
Fan Z, Beresford PJ, Oh DY, Zhang D, Lieberman J (2003) Tumor suppressor NM23-H1 is a granzyme A-activated DNase during CTL-mediated apoptosis, and the nucleosome assembly protein SET is its inhibitor. Cell 112:659–672
Gilles AM, Presecan E, Vonica A, Lascu I (1991) Nucleoside diphosphate kinase from human erythrocytes. Structural characterization of the two polypeptide chains responsible for heterogeneity of the hexameric enzyme. J Biol Chem 266:8784–8789
Grimson A, Srivastava M, Fahey B, Woodcroft BJ, Chiang HR, King N, Degnan BM, Rokhsar DS, Bartel DP (2008) Early origins and evolution of microRNAs and Piwi-interacting RNAs in animals. Nature 455:1193–1197
Harcet M, Lukic-Bilela L, Cetkovic H, Muller WEG, Gamulin V (2005) Identification and analysis of cDNAs encoding two nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPK/Nm23) from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. Croat Chem Acta 78:343–348
Harcet M, Roller M, Cetkovic H, Perina D, Wiens M, Muller WE, Vlahovicek K (2010) Demosponge EST sequencing reveals a complex genetic toolkit of the simplest metazoans. Mol Biol Evol 27:2747–2756
Hartsough MT, Morrison DK, Salerno M, Palmieri D, Ouatas T, Mair M, Patrick J, Steeg PS (2002) Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor phosphorylation of kinase suppressor of Ras via a histidine protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 277:32389–32399
Heinemeyer T, Wingender E, Reuter I, Hermjakob H, Kel AE, Kel OV, Ignatieva EV, Ananko EA, Podkolodnaya OA, Kolpakov FA, Podkolodny NL, Kolchanov NA (1998) Databases on transcriptional regulation: TRANSFAC, TRRD and COMPEL. Nucleic Acids Res 26:362–367
Hofacker IL (2003) Vienna RNA secondary structure server. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3429–3431
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAS and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:19–53
Li CW, Chen JY, Hua TE (1998) Precambrian sponges with cellular structures. Science 279:879–882
Mehus JG, Deloukas P, Lambeth DO (1999) NME6: a new member of the nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase gene family located on human chromosome 3p21.3. Hum Genet 104:454–459
Milanesi L, Muselli M, Arrigo P (1996) Hamming-Clustering method for signals prediction in 5′ and 3′ regions of eukaryotic genes. Comput Appl Biosci 12:399–404
Milon L, Meyer P, Chiadmi M, Munier A, Johansson M, Karlsson A, Lascu I, Capeau J, Janin J, Lacombe ML (2000) The human nm23-H4 gene product is a mitochondrial nucleoside diphosphate kinase. J Biol Chem 275:14264–14272
Muller WE, Bohm M, Grebenjuk VA, Skorokhod A, Muller IM,Gamulin V (2002) Conservation of the positions of metazoan introns from sponges to humans. Gene 295:299–309
Munier A, Feral C, Milon L, Pinon VP, Gyapay G, Capeau J, Guellaen G, Lacombe ML (1998) A new human nm23 homologue (nm23–H5) specifically expressed in testis germinal cells. FEBS Lett 434:289–94
Munier A, Serres C, Kann ML, Boissan M, Lesaffre C, Capeau J, Fouquet JP, Lacombe ML (2003) Nm23/NDP kinases in human male germ cells: role in spermiogenesis and sperm motility? Exp Cell Res 289:295–306
Perina D, Cetkovic H, Harcet M, Premzl M, Lukic-Bilela L, Muller WE, Gamulin V (2006) The complete set of ribosomal proteins from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. Gene 366:275–284
Perina D, Herak Bosnar M, Bago R, Mikoc A, Harcet M, Dezeljin M, Cetkovic H (2011) Sponge non-metastatic group I Nme gene/protein—structure and function is conserved from sponges to humans. BMC Evol Biol 11:87
Philippe H, Derelle R, Lopez P, Pick K, Borchiellini C, Boury-Esnault N, Vacelet J, Renard E, Houliston E, Quéinnec E, Da Silva C, Wincker P, Le Guyader H, Leys S, Jackson DJ, Schreiber F, Erpenbeck D, Morgenstern B, Wörheide G, Manuel M (2009) Phylogenomics revives traditional views on deep animal relationships. Curr Biol CB 19:706–712
Postel EH (2003) Multiple biochemical activities of NM23/NDP kinase in gene regulation. J Bioenerg Biomembr 35:31–40
Postel EH, Ferrone CA (1994) Nucleoside diphosphate kinase enzyme activity of NM23-H2/PuF is not required for its DNA binding and in vitro transcriptional functions. J Biol Chem 269:8627–8630
Raible F, Tessmar-Raible K, Osoegawa K, Wincker P, Jubin C, Balavoine G, Ferrier D, Benes V, de Jong P, Weissenbach J, Bork P, Arendt D (2005) Vertebrate-type intron-rich genes in the marine annelid Platynereis dumerilii. Science 310:1325–1326
Seack J, Perovic S, Gamulin V, Schroder HC, Beutelmann P, Muller IM, Muller WE (2001) Identification of highly conserved genes: SNZ and SNO in the marine sponge Suberites domuncula: their gene structure and promoter activity in mammalian cells(1). Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:21–34
Seifert M, Welter C, Mehraein Y, Seitz G (2005) Expression of the nm23 homologues nm23-H4, nm23-H6, and nm23-H7 in human gastric and colon cancer. J Pathol 205:623–632
Srivastava M, Simakov O, Chapman J, Fahey B, Gauthier ME, Mitros T, Richards GS, Conaco C, Dacre M, Hellsten U, Larroux C, Putnam NH, Stanke M, Adamska M, Darling A, Degnan SM, Oakley TH, Plachetzki DC, Zhai Y, Adamski M, Calcino A, Cummins SF, Goodstein DM, Harris C, Jackson DJ, Leys SP, Shu S, Woodcroft BJ, Vervoort M, Kosik KS, Manning G, Degnan BM, Rokhsar DS (2010) The Amphimedon queenslandica genome and the evolution of animal complexity. Nature 466:720–726
Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Kopper L, Thorgeirsson UP, Talmadge JE, Liotta LA, Sobel ME (1988) Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst 80:200–204
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tsuiki H, Nitta M, Furuya A, Hanai N, Fujiwara T, Inagaki M, Kochi M, Ushio Y, Saya H, Nakamura H (1999) A novel human nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase, Nm23-H6, localizes in mitochondria and affects cytokinesis. J Cell Biochem 76:254–269
Zimmerman AL, Wu S (2010) MicroRNAs, cancer and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett 300:10–19
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Croatian MSES grants 098-0982913-2478 (H. Ćetković) and 098-09824642513 (M. Herak Bosnar).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Drago Perina and Maja Herak Bosnar contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online resource 1
Sequences alignment of N-terminal predicted mitochondrial localization signal of Nme6 orthologs from human, rat, chicken, frog, fish, cnidarian, placozoan and sponge. PEM probability of export to mitochondria, CS cleavage site, np not predictable. Boxes indicate cleavage site (JPEG 223 kb)
Online resource 2
Kinase activity of Nme6Sd and Nme6SdΔ31 was determined by measuring the oxidation of NADH in a coupled pyruvate kinase-lactate dehydrogenase enzyme assay system. Reactions were initiated by the addition of 50 ng of enzyme in 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.4), 75 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM phosphoenolpyruvate, 0.1 mg/mL NADH, 1 mM ATP, 0.2 mM dTDP, 2 U/mL of pyruvate kinase, 2 U/mL of lactate dehydrogenase and 1 mg/mL BSA. Activity was monitored measuring the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm for 10 min. Top line represents the control reaction (without protein). Nme1 exhibits NDPK activity. In contrast, Nme6Sd and Nme6SdΔ31 exhibit no detectible NDPK activity. All reactions were done in triplicate (JPEG 257 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perina, D., Bosnar, M.H., Mikoč, A. et al. Characterization of Nme6-like gene/protein from marine sponge Suberites domuncula . Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 384, 451–460 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0635-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0635-9