Abstract
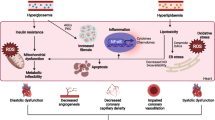
The key roles that obesity, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress play in the progression of diabetes vascular complications are well recognized; however, the relative contribution and importance of these individual factors remain uncertain. At 6, 10, or 14 weeks old, blood samples and thoracic aortae were collected from db/db mice and their non-diabetic controls. Plasma samples were analyzed for glucose, 8-isoprostane, CRP, triglycerides, LDL, and HDL as markers of glycemic status, oxidative stress, inflammation, and dyslipidemia, respectively. The responses of the aortic rings to high KCl, phenylephrine (PE), acetylcholine (ACh), and sodium nitroprusside were examined. Statistical methods were used to estimate the strength of the association between plasma variables and vascular functions. Systemic inflammation occurred in db/db mice at an earlier age than did hyperglycemia or oxidative stress. Aortae of db/db showed augmented contractions to PE which were positively correlated with weight, plasma glucose, 8-isoprostane, and CRP. Also, db/db mice showed impaired endothelium-dependent ACh vasorelaxation which was negatively correlated with weight, plasma glucose, and 8-isoprostane. Multivariate analysis and stepwise modeling show that CRP is the major determinant of the contractile responses, while weight and HDL are the major determinants of ACh-induced relaxation. Among the traditional risk factors of obesity, hyperglycemia, oxidative stress, inflammation, and dyslipidemia, our study reveals that weight and inflammation are the major determinants of vascular dysfunction in the aortae of db/db mice. Our findings partially resolve the complexity of diabetes vasculopathies and suggest targeting weight loss and inflammation for effective therapeutic approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- KCl:
-
Potassium chloride
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PE:
-
Phenylephrine
- PSS:
-
Physiological salt solution
- S.E.:
-
Standard error
- SNP:
-
Sodium nitroprusside
References
Abbott RD, Wilson PW, Kannel WB, Castelli WP (1988) High density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol screening, and myocardial infarction. The Framingham Study. Arteriosclerosis 8:207–211
Andersen K, Pedersen BK (2008) The role of inflammation in vascular insulin resistance with focus on IL-6. Horm Metab Res 40:635–639
Arcaro G, Zamboni M, Rossi L, Turcato E, Covi G, Armellini F, Bosello O, Lechi A (1999) Body fat distribution predicts the degree of endothelial dysfunction in uncomplicated obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23:936–942
Bagi Z, Koller A, Kaley G (2003) Superoxide-NO interaction decreases flow- and agonist-induced dilations of coronary arterioles in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1404–H1410
Bagi Z, Koller A, Kaley G (2004) PPARgamma activation, by reducing oxidative stress, increases NO bioavailability in coronary arterioles of mice with Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H742–H748
Belch J, MacCuish A, Campbell I, Cobbe S, Taylor R, Prescott R, Lee R, Bancroft J, MacEwan S, Shepherd J, Macfarlane P, Morris A, Jung R, Kelly C, Connacher A, Peden N, Jamieson A, Matthews D, Leese G, McKnight J, O’Brien I, Semple C, Petrie J, Gordon D, Pringle S, MacWalter R, Prevention of Progression of Arterial Disease and Diabetes Study Group, Diabetes Registry Group, Royal College of Physicians Edinburgh (2008) The prevention of progression of arterial disease and diabetes (POPADAD) trial: factorial randomised placebo controlled trial of aspirin and antioxidants in patients with diabetes and asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease. BMJ 337:a1840
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate-a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B Methodol 57:289–300
Bisoendial RJ, Hovingh GK, Levels JH, Lerch PG, Andresen I, Hayden MR, Kastelein JJ, Stroes ES (2003) Restoration of endothelial function by increasing high-density lipoprotein in subjects with isolated low high-density lipoprotein. Circulation 107:2944–2948
Ble-Castillo JL, Carmona-Diaz E, Mendez JD, Larios-Medina FJ, Medina-Santillan R, Cleva-Villanueva G, Diaz-Zagoya JC (2005) Effect of alpha-tocopherol on the metabolic control and oxidative stress in female type 2 diabetics. Biomed Pharmacother 59:290–295
Bosevski M, Borozanov V, Peovska I, Georgievska-Ismail L (2007) Endothelial dysfunction correlates with plasma fibrinogen and HDL cholesterol in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. Bratisl Lek Listy 108:297–300
Busija DW, Miller AW, Katakam P, Simandle S, Erdos B (2004) Mechanisms of vascular dysfunction in insulin resistance. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 5:929–935
Cesari M, Penninx BW, Newman AB, Kritchevsky SB, Nicklas BJ, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Rubin SM, Ding J, Simonsick EM, Harris TB, Pahor M (2003a) Inflammatory markers and onset of cardiovascular events: results from the Health ABC study. Circulation 108:2317–2322
Cesari M, Penninx BW, Newman AB, Kritchevsky SB, Nicklas BJ, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Tracy RP, Rubin SM, Harris TB, Pahor M (2003b) Inflammatory markers and cardiovascular disease (The Health, Aging and Body Composition [Health ABC] Study). Am J Cardiol 92:522–528
Cohen RA, Tong X (2010) Vascular oxidative stress: the common link in hypertensive and diabetic vascular disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 55:308–316
Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A, Mohanty P, Garg R (2005) Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation 111:1448–1454
Darko D, Dornhorst A, Kelly FJ, Ritter JM, Chowienczyk PJ (2002) Lack of effect of oral vitamin C on blood pressure, oxidative stress and endothelial function in Type II diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond) 103:339–344
Erdei N, Bagi Z, Edes I, Kaley G, Koller A (2007) H2O2 increases production of constrictor prostaglandins in smooth muscle leading to enhanced arteriolar tone in Type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H649–H656
Feletou M, Vanhoutte PM (2006) Endothelial dysfunction: a multifaceted disorder (The Wiggers Award Lecture). Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H985–H1002
Festa A, Hanley AJ, Tracy RP, D’Agostino R Jr, Haffner SM (2003) Inflammation in the prediabetic state is related to increased insulin resistance rather than decreased insulin secretion. Circulation 108:1822–1830
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408:239–247
Ford MA, McConnell JP, Lavi S, Rihal CS, Prasad A, Sandhu GS, Hartman SJ, Lerman LO, Lerman A (2009) Coronary artery endothelial dysfunction is positively correlated with low density lipoprotein and inversely correlated with high density lipoprotein subclass particles measured by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Atherosclerosis 207:111–115
Goldberg RB (2009) Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3171–3182
Goldfine AB, Silver R, Aldhahi W, Cai D, Tatro E, Lee J, Shoelson SE (2008) Use of salsalate to target inflammation in the treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Clin Transl Sci 1:36–43
Greenland S (1983) Tests for interaction in epidemiologic studies: a review and a study of power. Stat Med 2:243–251
Guerci B, Bohme P, Kearney-Schwartz A, Zannad F, Drouin P (2001) Endothelial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Part 2: altered endothelial function and the effects of treatments in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab 27:436–447
Guo Z, Su W, Allen S, Pang H, Daugherty A, Smart E, Gong MC (2005) COX-2 up-regulation and vascular smooth muscle contractile hyperreactivity in spontaneous diabetic db/db mice. Cardiovasc Res 67:723–735
Hamilton SJ, Chew GT, Davis TM, Watts GF (2010) Niacin improves small artery vasodilatory function and compliance in statin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diab Vasc Dis Res 7:296–299
Hayashino Y, Hennekens CH, Kurth T (2009) Aspirin use and risk of type 2 diabetes in apparently healthy men. Am J Med 122:374–379
Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group (2002) MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of antioxidant vitamin supplementation in 20, 536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 360:23–33
Helmersson J, Vessby B, Larsson A, Basu S (2004) Association of type 2 diabetes with cyclooxygenase-mediated inflammation and oxidative stress in an elderly population. Circulation 109:1729–1734
Higashi Y, Matsuoka H, Umei H, Sugano R, Fujii Y, Soga J, Kihara Y, Chayama K, Imaizumi T (2010) Endothelial function in subjects with isolated low HDL cholesterol: role of nitric oxide and circulating progenitor cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E202–E209
Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Higashi M, Morikawa K, Kandabashi T, Kawamura N, Kubota T, Ichiki T, Amano M, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A (2004) Inflammatory stimuli upregulate Rho-kinase in human coronary vascular smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 37:537–546
Kanie N, Kamata K (2000) Contractile responses in spontaneously diabetic mice. I. Involvement of superoxide anion in enhanced contractile response of aorta to norepinephrine in C57BL/KsJ(db/db) mice. Gen Pharmacol 35:311–318
Kataja-Tuomola MK, Kontto JP, Mannisto S, Albanes D, Virtamo JR (2010) Effect of alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene supplementation on macrovascular complications and total mortality from diabetes: results of the ATBC Study. Ann Med 42:178–186
Kawasaki H (1997) Pharmacological studies on alterations in contractile reactivity in aortas isolated from experimental diabetic rats. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 72:649–665
Kelly AS, Thelen AM, Kaiser DR, Gonzalez-Campoy JM, Bank AJ (2007) Rosiglitazone improves endothelial function and inflammation but not asymmetric dimethylarginine or oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Vasc Med 12:311–318
Kontos HA (1987) Oxygen radicals from arachidonate metabolism in abnormal vascular responses. Am Rev Respir Dis 136:474–477
Lagaud GJ, Masih-Khan E, Kai S, van Breemen C, Dube GP (2001) Influence of type II diabetes on arterial tone and endothelial function in murine mesenteric resistance arteries. J Vasc Res 38:578–589
Lam TY, Seto SW, Lau YM, Au LS, Kwan YW, Ngai SM, Tsui KW (2006) Impairment of the vascular relaxation and differential expression of caveolin-1 of the aorta of diabetic +db/+db mice. Eur J Pharmacol 546:134–141
Lee JM, Robson MD, Yu LM, Shirodaria CC, Cunnington C, Kylintireas I, Digby JE, Bannister T, Handa A, Wiesmann F, Durrington PN, Channon KM, Neubauer S, Choudhury RP (2009) Effects of high-dose modified-release nicotinic acid on atherosclerosis and vascular function: a randomized, placebo-controlled, magnetic resonance imaging study. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:1787–1794
Lonn E, Bosch J, Yusuf S, Sheridan P, Pogue J, Arnold JM, Ross C, Arnold A, Sleight P, Probstfield J, Dagenais GR, HOPE and HOPE-TOO Trial Investigators (2005) Effects of long-term vitamin E supplementation on cardiovascular events and cancer: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 293:1338–1347
Lu Q, Bjorkhem I, Wretlind B, Diczfalusy U, Henriksson P, Freyschuss A (2005) Effect of ascorbic acid on microcirculation in patients with Type II diabetes: a randomized placebo-controlled cross-over study. Clin Sci (Lond) 108:507–513
Marinou K, Tousoulis D, Antonopoulos AS, Stefanadi E, Stefanadis C (2010) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: from pathophysiology to risk stratification. Int J Cardiol 138:3–8
Matsumoto T, Kakami M, Noguchi E, Kobayashi T, Kamata K (2007) Imbalance between endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors in mesenteric arteries from aged OLETF rats, a model of Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1480–H1490
Mickey RM, Greenland S (1989) The impact of confounder selection criteria on effect estimation. Am J Epidemiol 129:125–137
Miike T, Kunishiro K, Kanda M, Azukizawa S, Kurahashi K, Shirahase H (2008) Impairment of endothelium-dependent ACh-induced relaxation in aorta of diabetic db/db mice–possible dysfunction of receptor and/or receptor-G protein coupling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 377:401–410
Miller NE, Thelle DS, Forde OH, Mjos OD (1977) The Tromso heart-study. High-density lipoprotein and coronary heart-disease: a prospective case-control study. Lancet 1:965–968
Mitchell JA, Larkin S, Williams TJ (1995) Cyclooxygenase-2: regulation and relevance in inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1535–1542
Mugabo Y, Li L, Renier G (2010) The connection between C-reactive protein (CRP) and diabetic vasculopathy. Focus on preclinical findings. Curr Diabetes Rev 6:27–34
Mulvany MJ, Halpern W (1977) Contractile properties of small arterial resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Circ Res 41:19–26
Nicholls SJ, Dusting GJ, Cutri B, Bao S, Drummond GR, Rye KA, Barter PJ (2005) Reconstituted high-density lipoproteins inhibit the acute pro-oxidant and proinflammatory vascular changes induced by a periarterial collar in normocholesterolemic rabbits. Circulation 111:1543–1550
Node K, Inoue T (2009) Postprandial hyperglycemia as an etiological factor in vascular failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol 8:23
Nofer JR, van der Giet M, Tolle M, Wolinska I, von Wnuck LK, Baba HA, Tietge UJ, Godecke A, Ishii I, Kleuser B, Schafers M, Fobker M, Zidek W, Assmann G, Chun J, Levkau B (2004) HDL induces NO-dependent vasorelaxation via the lysophospholipid receptor S1P3. J Clin Invest 113:569–581
Okon EB, Szado T, Laher I, McManus B, van Breemen C (2003) Augmented contractile response of vascular smooth muscle in a diabetic mouse model. J Vasc Res 40:520–530
Ozcelikay AT, Tay A, Guner S, Tasyaran V, Yildizoglu-Ari N, Dincer UD, Altan VM (2000) Reversal effects of L-arginine treatment on blood pressure and vascular responsiveness of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res 41:201–209
Pannirselvam M, Verma S, Anderson TJ, Triggle CR (2002) Cellular basis of endothelial dysfunction in small mesenteric arteries from spontaneously diabetic (db/db −/−) mice: role of decreased tetrahydrobiopterin bioavailability. Br J Pharmacol 136:255–263
Pannirselvam M, Wiehler WB, Anderson T, Triggle CR (2005) Enhanced vascular reactivity of small mesenteric arteries from diabetic mice is associated with enhanced oxidative stress and cyclooxygenase products. Br J Pharmacol 144:953–960
Park Y, Capobianco S, Gao X, Falck JR, Dellsperger KC, Zhang C (2008) Role of EDHF in type 2 diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1982–H1988
Piercy V, Taylor SG (1998) A comparison of spasmogenic and relaxant responses in aortae from C57/BL/KsJ diabetic mice with those from their non-diabetic litter mates. Pharmacology 56:267–275
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, Eckel RH, American Heart Association, Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (2006) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 113:898–918
Qamirani E, Ren Y, Kuo L, Hein TW (2005) C-reactive protein inhibits endothelium-dependent NO-mediated dilation in coronary arterioles by activating p38 kinase and NAD(P)H oxidase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:995–1001
Rizvi AA (2009) Cytokine biomarkers, endothelial inflammation, and atherosclerosis in the metabolic syndrome: emerging concepts. Am J Med Sci 338:310–318
San Martin A, Du P, Dikalova A, Lassegue B, Aleman M, Gongora MC, Brown K, Joseph G, Harrison DG, Taylor WR, Jo H, Griendling KK (2007) Reactive oxygen species-selective regulation of aortic inflammatory gene expression in Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H2073–H2082
Sattar N (2004) Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction: intimate companions in the pathogenesis of vascular disease? Clin Sci (Lond) 106:443–445
Shi Y, Vanhoutte PM (2008) Oxidative stress and COX cause hyper-responsiveness in vascular smooth muscle of the femoral artery from diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 154:639–651
Shi Y, Feletou M, Ku DD, Man RY, Vanhoutte PM (2007) The calcium ionophore A23187 induces endothelium-dependent contractions in femoral arteries from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 150:624–632
Sivitz WI, Wayson SM, Bayless ML, Sinkey CA, Haynes WG (2007) Obesity impairs vascular relaxation in human subjects: hyperglycemia exaggerates adrenergic vasoconstriction arterial dysfunction in obesity and diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 21:149–157
Song Y, Cook NR, Albert CM, Van Denburgh M, Manson JE (2009) Effects of vitamins C and E and beta-carotene on the risk of type 2 diabetes in women at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 90:429–437
Sorrentino SA, Besler C, Rohrer L, Meyer M, Heinrich K, Bahlmann FH, Mueller M, Horvath T, Doerries C, Heinemann M, Flemmer S, Markowski A, Manes C, Bahr MJ, Haller H, von Eckardstein A, Drexler H, Landmesser U (2010) Endothelial-vasoprotective effects of high-density lipoprotein are impaired in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus but are improved after extended-release niacin therapy. Circulation 121:110–122
Spieker LE, Sudano I, Hurlimann D, Lerch PG, Lang MG, Binggeli C, Corti R, Ruschitzka F, Luscher TF, Noll G (2002) High-density lipoprotein restores endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic men. Circulation 105:1399–1402
Sprague AH, Khalil RA (2009) Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78:539–552
Stehouwer CD, Gall MA, Twisk JW, Knudsen E, Emeis JJ, Parving HH (2002) Increased urinary albumin excretion, endothelial dysfunction, and chronic low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes: progressive, interrelated, and independently associated with risk of death. Diabetes 51:1157–1165
Sumi M, Sata M, Miura S, Rye KA, Toya N, Kanaoka Y, Yanaga K, Ohki T, Saku K, Nagai R (2007) Reconstituted high-density lipoprotein stimulates differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells and enhances ischemia-induced angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:813–818
Tang EH, Leung FP, Huang Y, Feletou M, So KF, Man RY, Vanhoutte PM (2007) Calcium and reactive oxygen species increase in endothelial cells in response to releasers of endothelium-derived contracting factor. Br J Pharmacol 151:15–23
Tiwari S, Zhang Y, Heller J, Abernethy DR, Soldatov NM (2006) Atherosclerosis-related molecular alteration of the human CaV1.2 calcium channel alpha1C subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17024–17029
Tso C, Martinic G, Fan WH, Rogers C, Rye KA, Barter PJ (2006) High-density lipoproteins enhance progenitor-mediated endothelium repair in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1144–1149
Tsuchiya K, Akaza I, Yoshimoto T, Hirata Y (2009) Pioglitazone improves endothelial function with increased adiponectin and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in type 2 diabetes. Endocr J 56:691–698
van der Harst P, Asselbergs FW, Buikema H, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ, van Gilst WH (2006) Effects of C-reactive protein and cholesterol on responsiveness in vitro of the internal thoracic artery to angiotensin II in patients having coronary artery bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol 98:751–753
Van Linthout S, Spillmann F, Lorenz M, Meloni M, Jacobs F, Egorova M, Stangl V, De Geest B, Schultheiss HP, Tschope C (2009) Vascular-protective effects of high-density lipoprotein include the downregulation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Hypertension 53:682–687
Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Plantinga Y, Taddei S, Salvetti A (2007) C-reactive protein and hypertension: is there a causal relationship? Curr Pharm Des 13:1693–1698
Ward NC, Wu JH, Clarke MW, Puddey IB, Burke V, Croft KD, Hodgson JM (2007) The effect of vitamin E on blood pressure in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Hypertens 25:227–234
Wilkinson MF, Earle ML, Triggle CR, Barnes S (1996) Interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and LPS enhance calcium channel current in isolated vascular smooth muscle cells of rat tail artery. FASEB J 10:785–791
Wong WT, Tian XY, Xu A, Ng CF, Lee HK, Chen ZY, Au CL, Yao X, Huang Y (2010) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-dependent oxidative stress mediates endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:757–768
Woodman RJ, Chew GT, Watts GF (2005) Mechanisms, significance and treatment of vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus on lipid-regulating therapy. Drugs 65:31–74
Wycherley TP, Brinkworth GD, Noakes M, Buckley JD, Clifton PM (2008) Effect of caloric restriction with and without exercise training on oxidative stress and endothelial function in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 10:1062–1073
Xie Z, Su W, Guo Z, Pang H, Post SR, Gong MC (2006) Up-regulation of CPI-17 phosphorylation in diabetic vasculature and high glucose cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 69:491–501
Yuhanna IS, Zhu Y, Cox BE, Hahner LD, Osborne-Lawrence S, Lu P, Marcel YL, Anderson RG, Mendelsohn ME, Hobbs HH, Shaul PW (2001) High-density lipoprotein binding to scavenger receptor-BI activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat Med 7:853–857
Zhang C, Park Y, Picchi A, Potter BJ (2008) Maturation-induces endothelial dysfunction via vascular inflammation in diabetic mice. Basic Res Cardiol 103:407–416
Zhong JC, Yu XY, Huang Y, Yung LM, Lau CW, Lin SG (2007) Apelin modulates aortic vascular tone via endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation pathway in diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Res 74:388–395
Zimmerman MA, Flores SC (2009) Autoimmune-mediated oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction: implications of accelerated vascular injury in type I diabetes. J Surg Res 155:173–178
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by funds from the Canadian Heart and Stroke Foundation. Nada Sallam was gratefully funded by a scholarship from the Ministry of Higher Education, Egypt.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sallam, N., Fisher, A., Golbidi, S. et al. Weight and inflammation are the major determinants of vascular dysfunction in the aortae of db/db mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 383, 483–492 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0614-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0614-1