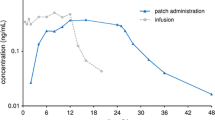
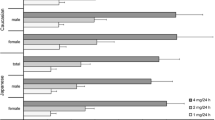
Abstract
Rotigotine (Neupro®) is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist developed for the once daily treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) using a transdermal delivery system (patch) which provides patients with the drug continuously over 24 h. To fully understand the pharmacological actions of rotigotine, the present study determined its extended receptor profile. In standard binding assays, rotigotine demonstrated the highest affinity for dopamine receptors, particularly the dopamine D3 receptor (K i = 0.71 nM) with its affinities to other dopamine receptors being (K i in nM): D4.2 (3.9), D4.7 (5.9), D5 (5.4), D2 (13.5), D4.4 (15), and D1 (83). Significant affinities were also demonstrated at α-adrenergic (α2B, K i = 27 nM) and serotonin receptors (5-HT1A K i = 30 nM). In newly developed reporter-gene assays for determination of functional activity, rotigotine behaved as a full agonist at dopamine receptors (rank order: D3 > D2L > D1 = D5 > D4.4) with potencies 2,600 and 53 times higher than dopamine at dopamine D3 and D2L receptors, respectively. At α-adrenergic sites, rotigotine acted as an antagonist on α2B receptors. At serotonergic sites, rotigotine had a weak but significant agonistic activity at 5-HT1A receptors and a minor or nonexistent activity at other serotonin receptors. Thus, in respect to PD, rotigotine can be characterized as a specific dopamine receptor agonist with a preference for the D3 receptor over D2 and D1 receptors. In addition, it exhibits interaction with D4 and D5 receptors, the role of which in relation to PD is not clear yet. Among non-dopaminergic sites, rotigotine shows relevant affinity to only 5-HT1A and α2B receptors. Further studies are necessary to investigate the contribution of the different receptor subtypes to the efficacy of rotigotine in Parkinson’s disease and possible other indications such as restless legs syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Fulaij MA, Ren Y, Beinborn M, Kopin AS (2007) Identification of amino acid determinants of dopamine 2 receptor synthetic agonist function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:298–307 doi:10.1124/jpet.106.116 384
Andersen PH (1987) Biochemical and pharmacological characterisation of [3H]GBR12935 binding in vitro to rat striatal membranes: labeling of dopamine uptake complex. J Neurochem 48:1887–1896
Bara-Jimenez W, Bibbiani F, Morris MJ, Dimitrova T, Sherzai A, Mouradian MM, Chase TN (2005) Effects of serotonin 5-HT1A agonist in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 20:932–936
Belluzzi JD, Domino EF, May JM, Bankiewicz KS, McAfee DA (1994) N-0923, a selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist, is efficacious in rat and monkey models of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 9:147–154
Bibbiani F, Oh JD, Chase TN (2001) Serotonin 5-HT1A agonist improves motor complications in rodent and primate parkinsonian models. Neurology 57:1829–1834
Blier P, Abbott FV (2001) Putative mechanisms of action of antidepressant drugs in affective and anxiety disorders and pain. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:37–43
Bonanno G, Fassio A, Severi P, Ruelle A, Raiteri MJ (1994) Fenfluramine releases serotonin from human brain nerve endings by a dual mechanism. J Neurochem 63:1163–1166
Bondiolotti GP, Galva MD, Villa F, Sciaba L, Picotti GB (1995) In vitro effects on monoamine uptake and release by the reversible monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors lazabelide and N-(2-aminoethyl)-p-chlorobenzamide: a comparison with L-deprenyl. Biochem Pharmacol 50:97–102
Bonhaus DW, Bach C, De Souza A, Salazar FHR, Matsuoka BD, Zuppan P, Chan HW, Eglen RM (1995) The pharmacology and distribution of human 5-hydroxytryptamine2B (5-HT2B) receptor gene products: comparison with 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Brit J Pharmacol 115:622–628
Bowen WD, De Costa BR, Hellewell SB, Walker M, Rice KC (1993) [3H]-(+)-pentazocine: a potent and highly selective benzomorphan-based probe for sigma1 receptors. Mo. Neuropharmacol 3:117–126
Brown GB (1986) 3H-batrachotoxinin-A benzoate binding to voltage-sensitive sodium channels: inhibition by the channel blockers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. J Neurosci 6:2064–2070
Bylund DB, Ray-Prenger C, Murphy TJ (1988) Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:600–607
Carta M, Carlsson T, Kirik D, Bjorklund A (2007) Dopamine released from 5-HT terminals is the cause of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Brain 130:1819–1833 doi:10.1093/brain/awm082
Carvey PM, McGuire SO, Ling ZD (2001) Neuroprotective effects of D3 dopamine receptor agonists. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 7:213–223
Catterall WA (1979) Neurotoxins as allosteric modifiers of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Ad Cytopharmacol 3:305–316
Clark D, White FJ (1987) D1 dopamine receptor—the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse 1:347–388
Clarke CE, Guttman M (2002) Dopamine agonist monotherapy in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 360:1767–1769
Corvol JC, Girault JA, Herve D (2006) Role and regulation of dopamine D1 receptors in the striatum: implications for the genesis of dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 162:691–702
Cotzias GC (1971) Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinsonism. JAMA 218:1903–1908
Devedjian J-C, Esclapez F, Denis-Pouxviel C, Paris H (1994) Further characterization of human α2-adrenoceptor subtypes: [3H]RX821002 binding and definition of additional selective drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 252:43–49
Dini S, Caselli GF, Ferrari MP, Giani R, Clavenna G (1991) Heterogeneity of [3H]-mepyramine binding sites in guinea pig cerebellum and lung. Agents Actions 33(1-2):181–184
Dorje F, Wess J, Lambrecht G, Tacke R, Mutschler E, Brann MR (1991) Antagonist binding profiles of five cloned human muscarinic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:727–733
Doudet DJ, Holden JE, Jivan S, McGeer E, Wyatt RJ (2000) In vivo PET studies of the dopamine D2 receptors in rhesus monkeys with long-term MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Synapse 38:105–113
Fahn S (1999) Parkinson disease, the effect of levodopa, and the ELLDOPA trial: earlier vs later L-DOPA. Arch Neurol 56:529–535
Fan F, Paguio A, Garvin D, Wood KV (2005) Using luciferase assays to study G-protein-coupled receptor pathways and screen for GPCR modulators. Cell Notes 13:5–7
Friedman DJ, Krause DN, Duckles SP (1992) Complex prejunctional actions of the D2 dopamine agonists N-0923 and N-0924 in the rat tail artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:568–575
George SE, Bungay PJ, Naylor LH (1998) Functional analysis of the D2L dopamine receptor expressed in a cAMP-responsive luciferase reporter cell line. Biochem Pharmacol 56:25–30
Gerlach M, Double K, Arzberger T, Leblhuber F, Tatschner T, Riederer P (2003) Dopamine receptor agonists in current clinical use: comparative dopamine receptor binding profiles defined in the human striatum. J Neural Transm 110:1119–1127 doi:10.1007/s00702-003-0027-5
Giardina WJ, Williams M (2001) Adrogolide HCl (ABT-431; DAS-431), a prodrug of the dopamine D1 receptor agonist, A-86929: preclinical pharmacology and clinical data. CNS Drug Rev 7:305–316
Grandy DK, Marchionni MA, Makam H, Stofko RE, Alfano M, Frothingham L, Fischer JB, Burke-Howie KJ, Bunzow JR, Server AC, Civelli O (1989) Cloning of the cDNA and gene for a human D2 dopamine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9762–9766
Grondin R, Hadj TA, Doan VD, Ladure P, Bedard PJ (2000) Noradrenoceptor antagonism with idazoxan improves l-dopa-induced dyskinesias in MPTP monkeys. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:181–186
Hall ED, Andrus PK, Oostveen JA, Althaus JS, VonVoigtlander PF (1996) Neuroprotective effects of the dopamine D2/D3 agonist pramipexole against postischemic or methamphetamine-induced degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons. Brain Res 742:80–88
Henry B, Fox SH, Peggs D, Crossman AR, Brotchie JM (1999) The alpha2-adrenergic receptor antagonist idazoxan reduces dyskinesia and enhances anti-parkinsonian actions of l-dopa in the MPTP-lesioned primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 14:744–753
Heuring RE, Peroutka SJ (1987) Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci 7:894–903
Janowsky A, Berger P, Vocci F, Labarca R, Skolnick P, Paul SM (1986) Characterization of sodium-dependent [3H]GBR-12935 binding in brain: a radioligand for selective labelling of the dopamine transport complex. J Neurochem 46:1272–1276
Jenner P (2003) Dopamine agonists, receptor selectivity and dyskinesia induction in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 16(Suppl 1):S3–S7
Jiang N, Ou-Yang KQ, Cai SX, Hu YH, Xu ZL (2005) Identification of human dopamine D1-like receptor agonist using a cell-based functional assay. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:1181–1186
Joyce JN (2001) Dopamine D3 receptor as a therapeutic target for antipsychotic and antiparkinsonian drugs. Pharmacol Ther 90:231–259
Joyce JN, Millan MJ (2007) Dopamine D3 receptor agonists for protection and repair in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:100–105 doi:10.1016/j.coph.2006.11.004
Lane JR, Powney B, Wise A, Rees S, Milligan G (2007) Protean agonism at the dopamine D2 receptor: (S)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-propylpiperidine is an agonist for activation of Go1 but an antagonist/inverse agonist for Gi1,Gi2, and Gi3. Mol Pharmacol 71:1349–1359
Launay JM, Herve P, Peoc’h K, Tournois C, Callebert J, Nebigil CG, Etienne N, Drouet L, Humbert M, Simonneau G, Maroteaux L (2002) Function of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor in pulmonary hypertension. Nat Med 8:1129–1135
Loschmann PA, Smith LA, Lange KW, Jahnig P, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1992) Motor activity following the administration of selective D-1 and D-2 dopaminergic drugs to MPTP-treated common marmosets. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 109:49–56
Mackenzie RG, Vanleeuven D, Pugsley TA, Shih Y-H, Demattos S, Tang L, Todd R, O’malley KL (1994) Characterization of the human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in transfected cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol 266:79–85
Madhavan L, Freed WJ, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG (2003) 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor activation protects against N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced apoptotic cell death in striatal and mesencephalic cultures. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:913–923
Mailman RB, Nichols DE (1998) Dopamine D1 receptor agonists as antiparkinson drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:255–256
Mailman R, Huang X, Nichols DE (2001) Parkinson’s disease and D1 dopamine receptors. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2:1582–1591
Manson AJ, Iakovidou E, Lees AJ (2000) Idazoxan is ineffective for levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 15:336–337
Maratos EC, Jackson MJ, Pearce RK, Cannizzaro C, Jenner P (2003) Both short- and long-acting D-1/D-2 dopamine agonists induce less dyskinesia than l-DOPA in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Exp Neurol 179:90–102
Martin PL, Kelly M, Cusack NJ (1993) (−)-2-(N-propyl-N-2-thienylethylamino)-5-hydroxytetralin (N-0923), a selective D2 dopamine receptor agonist demonstrates the presence of D2 dopamine receptors in the mouse vas deferens but not in the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1342–1348
Mauler F, Horvath E (2005) Neuroprotective efficacy of repinotan HCl, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, in animal models of stroke and traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:451–459
Metman LV, Gillespie M, Farmer C, Bibbiani F, Konitsiotis S, Morris M, Shill H, Bara-Jimenez W, Mouradian MM, Chase TN (2001) Continuous transdermal dopaminergic stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 24:163–169
Michel AD, Loury DN, Whiting RL (1989) Identification of a single α1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the α1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Brit J Pharmacol 98:883–889
Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:791–804
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Mulheron JG, Casanas SJ, Arthur JM, Garnovskaya MN, Gettys TW, Raymond JR (1994) Human 5-HT1A receptor expressed in insect cells activates endogenous G0-like G protein. J Biol Chem 269:12954–12962
Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Chaput C, Verriele L, Millan MJ (1997) [35S]Guanosine-5¢-O-(3-thio)triphosphate binding as a measure of efficacy at human recombinant dopamine D4.4 receptors: actions of antiparkinsonian and antipsychotic agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:181–191
Nicholson SL, Brotchie JM (2002) 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, serotonin) and Parkinson’s disease—opportunities for novel therapeutics to reduce the problems of levodopa therapy. Eur J Neurol 9(Suppl 3):1–6
Olanow CW, Obeso JA (2000) Preventing levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Ann Neurol 47:S167–S176
Pacholczyk T, Blakely RD, Amara SG (1991) Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature 350:350–354
Parkinson Study Group (2003) A controlled trial of rotigotine monotherapy in early Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 60:1721–1728
Perovic S, Muller WEG (1995) Pharmacological profile of hypericum extract: effect on serotonin uptake by postsynaptic receptors. Arzneim-Forsch Drug Res 45:1145–1148
Piercey MF (1998) Pharmacology of pramipexole, a dopamine D3-preferring agonist useful in treating Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 21:141–151
Poewe W, Leussi F (2005) Clinical studies with transdermal rotigotine in early Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 65:S11–S14
Rascol O, Blin O, Thalamas C, Descombes S, Soubrouillard C, Azulay P, Fabre N, Viallet F, Lafnitzegger K, Wright S, Carter JH, Nutt JG (1999) ABT-431, a D1 receptor agonist prodrug, has efficacy in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 45:736–741
Rascol O, Arnulf I, Peyro-Saint PH, Brefel-Courbon C, Vidailhet M, Thalamas C, Bonnet AM, Descombes S, Bejjani B, Fabre N, Montastruc JL, Agid Y (2001a) Idazoxan, an alpha-2 antagonist, and l-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16:708–713
Rascol O, Nutt JG, Blin O, Goetz CG, Trugman JM, Soubrouillard C, Carter JH, Currie LJ, Fabre N, Thalamas C, Giardina WW, Wright S (2001b) Induction by dopamine D1 receptor agonist ABT-431 of dyskinesia similar to levodopa in patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 58:249–254
Rascol O, Ferreira JJ, Payoux P, Brefel-Courbon C, Montastruc JL (2002) Management of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Rev Neurol (Paris) 158:117–124
Rees S, Den Dass I, Foord S, Goodson S, Bull D, Kilpatrick G, Lee M (1994) Cloning and characterization of the human 5-HT5A serotonin receptor. FEBS Lett 355:242–246
Rinne JO, Laihinen A, Rinne UK, Nagren K, Bergman J, Ruotsalainen U (1993) PET study on striatal dopamine D2 receptor changes during the progression of early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 8:134–138
Scheller D, Chan P, Li Q, Wu T, Zhang R, Guan L, Ravenscroft P, Guigoni C, Crossman AR, Hill M, Bezard E (2007) Rotigotine treatment partially protects from MPTP toxicity in a progressive macaque model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 203:415–422
Setola V, Hufeisen SJ, Grande-Allen KJ, Vesely I, Glennon RA, Blough B, Rothman RB, Roth BL (2003) 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “Ecstasy”) induces fenfluramine-like proliferative actions on human cardiac valvular interstitial cells in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 63:1223–1229
Shen Y, Monsma FJ, Metcalf MA, Jose PA, Hamblin MW, Sibley DR (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of a 5-hydroxytryptamine7 serotonin receptor subtype. J Biol Chem 268:18200–18204
Sit SY (2000) Dopamine agonists in the treatment of Parkinson s disease past, present and future. Curr Pharm Des 6:1211–1248
Srinivasan J, Schmidt WJ (2004) Treatment with alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist, 2-methoxy idazoxan, protects 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinsonian symptoms in rats: neurochemical and behavioral evidence. Behav Brain Res 154:353–363
Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O’dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HMM, Niznik HB (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature 350:614–619
Swart PJ, de Zeeuw RA (1992) Extensive gastrointestinal metabolic conversion limits the oral bioavailability of the dopamine D2 agonist N-0923 in freely moving rats. Pharmazie 47:613–615
Tan EK, Yeo AP, Tan V, Pavanni R, Wong MC (2005) Prescribing pattern in Parkinson’s disease: are cost and efficacy overriding factors? Int J Clin Pract 59:511–514
Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (1997) Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 340:249–258
Taylor JR, Lawrence MS, Redmond DE Jr, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1991) Dihydrexidine, a full dopamine D1 agonist, reduces MPTP-induced parkinsonism in monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 199:389–391
Van der Weide J, De Vries JB, Tepper PG, Horn AS (1987) In vitro binding of the very potent and selective D-2 dopamine agonist, [3H]N-0437 to calf caudate membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 134:211–219
Van der Weide J, De Vries JB, Tepper PG, Krause DN, Dubocovich ML, Horn AS (1988) N-0437: a selective D-2 dopamine receptor agonist in in vitro and in vivo models. Eur J Pharmacol 147:249–258
Vanhauwe JF, Fraeyman N, Francken BJ, Luyten WH, Leysen JE (1999) Comparison of the ligand binding and signaling properties of human dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:908–916
Van Tol HHM, Wu CM, Guan H-G, Ohara K, Bunzow JR, Civelli O, Kennedy J, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Jovanovic V (1992) Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature 358:149–152
Watts RL, Wendt J, Nausieda PL, Boroojerdi B, Poole KH, Sommerville KW (2004) Efficacy of the rotigotine transdermal patch in patients with early-stage, idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Results of a multicenter, multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. 2004. 8th Congress of European Federation of Neurological Societies
Williams M, Wright S, Lloyd GK (1997) Improved therapies for Parkinson’s disease: life beyond dopamine D2/D3 receptor agonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 18:307–310
Yamagushi T, Ohyama M, Suzuki M, Ozawa Y, Hatanaka K, Hidaka K, Yamamoto M (1998) Neurochemical and behavorial characterization of potential antidepressant properties of indeloxazine hydrochloride. Neuropharmacol 37:1169–1176
Zanettini R, Antonini A, Gatto G, Gentile R, Tesei S, Pezzoli G (2007) Valvular heart disease and the use of dopamine agonists for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 356:39–46
Zhou Q-Y, Grandy DK, Thambi L, Kushner JA, Van Tol HHM, Cone R, Pribnow D, Salon J, Bunzow JR, Civelli O (1990) Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature 347:76–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheller, D., Ullmer, C., Berkels, R. et al. The in vitro receptor profile of rotigotine: a new agent for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 379, 73–86 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0341-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0341-4