Abstract
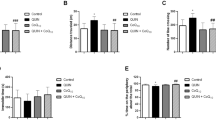
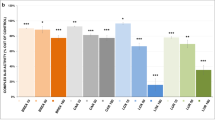
Typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs have been shown to have different clinical, biochemical, and behavioral profiles. It is well described that impairment of metabolism, especially in the mitochondria, leads to oxidative stress and neuronal death and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases in the brain. Considering that some effects of chronic use of antipsychotic drugs are still not well known and that succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and cytochrome oxidase (COX) are crucial enzymes of mitochondria, in this work, we evaluated the activities of these enzymes in rat brain after haloperidol, clozapine, olanzapine, or aripiprazole chronic administration. Adult male Wistar rats received daily injections of haloperidol (1.5 mg/kg), clozapine (25 mg/kg), olanzapine (2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg), or aripiprazole (2, 10 or 20 mg/kg) for 28 days. We verified that COX was not altered by any drug tested. Moreover, our results demonstrated that the atypical antipsychotic olanzapine inhibited SDH in the cerebellum and aripiprazole increased the enzyme in the prefrontal cortex. We also observed that haloperidol inhibited SDH in the striatum and hippocampus, whereas clozapine inhibited the enzyme only in the striatum. These results showed that antipsychotic drugs altered SDH activity but not COX. In this context, haloperidol, olanzapine, and clozapine may impair energy metabolism in some brain areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert KA, Hemmings HC, Adamo AI et al (2002) Evidence for decreased DARPP-32 in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:705–712
Andreassen OA, Ferrante RJ, Beal MF et al (1998) Oral dyskinesias and striatal lesions in rats after long-term co-treatment with haloperidol and 3-nitropropionic acid. Neuroscience 87:639–648
Angelucci F, Mathe AA, Aloe L (2004a) Neurotrophic factors and CNS disorders: findings in rodent models of depression and schizophrenia. Prog Brain Res 146:151–165
Angelucci F, Oliviero A, Pilato F et al (2004b) Transcranial magnetic stimulation and BDNF plasma levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroreport 15:717–720
Arnaiz SL, Coronel MF, Boveris A (1999) Nitric oxide, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production in brain mitochondria after haloperidol treatment. Nitric Oxide 3:235–243
Assis LC, Scaini G, Di-Pietro PB et al (2007) Effect of antipsychotics on creatine kinase activity in rat brain. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol (in press)
Balijepalli S, Kenchappa RS, Boyd MR et al (2001) Protein thiol oxidation by haloperidol results in inhibition of mitochondrial complex I in brain regions: comparison with atypical antipsychotics. Neurochem Int 38:425–435
Beal MF (1992) Does impairment of energy metabolism result in excitotoxic neuronal death in neurological illnesses? Ann Neurol 31:119–130
Beuzen JN, Taylor N, Wesnes K et al (1999) A comparison of the effects of olanzapine, haloperidol and placebo on cognitive and psychomotor functions in healthy elderly volunteers. J Psychopharmacol 13:152–158
Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Volavka J et al (2002) Neurocognitive effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in patients with chronic schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 159:1018–1028
Blass JP (2001) Brain metabolism and brain disease: is metabolic deficiency the proximate cause of Alzheimer dementia. J Neurosci Res 66:851–856
Boekema EJ, Braun HP (2007) Supramolecular structure of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphosrylation system. J Biol Chem 282:1–4
Brennan WA, Bird ED, Aprille JR (1985) Regional mitochondrial respiratory activity in Huntington’s disease brain. J Neurochem 44: 1948–1950
Buckley PF (2001) Broad therapeutic uses of atypical antipsychotic medications. Biol Psychiatry 50:912–924
Burger ME, Fachinetto R, Zeni G et al (2005) Ebselen attenuates haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and oxidative stress in rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:608–615
Cadet JL, Lohr JB (1989) Possible involvement of free radicals in neuroleptic-induced movement disorders. Evidence from treatment of tardive dyskinesia with vitamin E. Ann NY Acad Sci 570:176–185
Carlson CD, Cavazzoni PA, Berg PH et al (2003) An integrated analysis of acute treatment-emergent extrapyramidal syndrome in patients with schizophrenia during olanzapine clinical trials: comparisons with placebo, haloperidol, risperidone, or clozapine. J Clin Psychiatry 64:898–906
Casademont J, Rodriguez-Santiago B, Miro O et al (2005) Mitochondrial respiratory chain in brain homogenates: activities in different brain areas in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Clin Exp Res 1:1–7
Corrêa C, Amboni G, Assis LC et al (2007) Effects of lithium and valproate on hippocampus citrate synthase activity in an animal model of mania. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:887–891
Desmond JE, Fiez JA (1998) Neuroimaging studies of the cerebellum: language, learning, and memory. Trends Cogn Sci 2:355–362
Deutch AY, Moghaddam B, Innis RB et al (1991) Mechanisms of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs: Implications for novel therapeutic strategies for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 4:121–156
Dixon LB, Lehman AF, Levine J (1995) Conventional antipsychotic medications for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 21:567–577
Duman RS (2002a) Pathophysiology of depression: the concept of synaptic plasticity. Eur Psychiatry 17(Suppl 3):306–310
Duman RS (2002b) Synaptic plasticity and mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 7(Suppl 1):S29–S34
Ellis CE, Murphy EJ, Mitchell DC et al (2005) Mitochondrial lipid abnormality and electron transport chain impairment in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Mol Cell Biol 22:10190–10201
Fatemi SH, Laurence JA, Araghi-Niknam M et al (2004) Glial fibrillary acidic protein is reduced in cerebellum of subjects with major depression, but not schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 69:317–323
Fischer JC, Ruitenbeek W, Berden JA et al (1985) Differential investigation of the capacity of succinate oxidation in human skeletal muscle. Clin Chim Acta 153:23–26
France-Lanord V, Brugg B, Michel PP et al (1997) Mitochondrial free radical signal in ceramide-dependent apoptosis: a putative mechanism for neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 4:1612–1621
Halliwell B (1996) Free radicals, proteins and DNA: oxidative damage versus redox regulation. Biochem Soc Trans 24:1023–1027
Heales SJ, Bolaños JP, Stewart VC et al (1999) Nitric oxide, mitochondria and neurological disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1410:215–228
Jordan S, Koprivica V, Chen R et al (2002) The antipsychotic aripiprazole is a potent, partial agonist at the human 5-HT1A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 441:137–140
Kapur S, Remington G (2001) Atypical antipsychotics: new directions and new challenges in the treatment of schizophrenia. Annu Rev Med 52:503–517
Kato T, Kato N (2000) Mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2:180–190
Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi RA et al (2006) Parkinson’s disease brain mitochondrial complex I has oxidatively damaged subunits and is functionally impaired and misassembled. J Neurosci 19:5256–5264
Konradi C, Eaton M, MacDonald ML et al (2004) Molecular evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:300–308
Lohr JB, Cadet JL, Lohr MA et al (1988) Vitamin E in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia: the possible involvement of free radical mechanisms. Schizophr Bull 14:291–296
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–267
Machado-Vieira R, Lara DR, Portela LV et al (2002) Elevated serum S100B protein in drug-free bipolar patients during first manic episode: a pilot study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 12:269–272
Mahadik SP, Mukherjee S (1996) Free radical pathology and antioxidant defense in schizophrenia: a review. Schizophr Res 19:1–17
Mahadik SP, Laev H, Korenovsky A et al (1988) Haloperidol alters rat CNS cholinergic system: enzymatic and morphological analyses. Biol Psychiatry 24:199–217
Maurer I, Möller HJ (1997) Inhibition of complex I by neuroleptics in normal human brain cortex parallels the extrapyramidal toxicity of neuroleptics. Mol Cell Biochem 174:255–259
Parikh V, Khan MM, Mahadik SP (2003) Differential effects of antipsychotics on expression of antioxidant enzymes and membrane lipid peroxidation in rat brain. J Psychiatr Res 37:43–51
Parikh V, Terry AV, Khan MM (2004) Modulation of nerve growth factor and choline acetyltransferase expression in rat hippocampus after chronic exposure to haloperidol, risperidone, and olanzapine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:365–374
Peet M, Laugharne J, Rangarajan N (1993) Tardive dyskinesia, lipid peroxidation, and sustained amelioration with vitamin E treatment. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 8:151–153
Polydoro M, Schröder N, Lima MN et al (2004) Haloperidol- and clozapine-induced oxidative stress in the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:751–756
Prabakaran S, Swatton JE, Ryan MM et al (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in schizophrenia: evidence for compromised brain metabolism and oxidative stress. Mol Psychiatry 9:684–697
Prince JA, Yassin MS, Oreland L (1997) Neuroleptic-induced mitochondrial enzyme alterations in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:261–267
Prince JA, Yassin MS, Oreland L (1998) A histochemical demonstration of altered cytochrome oxidase activity in the rat brain by neuroleptics. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 8:1–6
Reinke A, Martins MR, Lima MS et al (2004) Haloperidol and clozapine, but not olanzapine, induces oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 372:157–160
Rizzardini M, Lupi M, Mangolini A et al (2006) Neurodegeneration induced by complex I inhibition in a cellular model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Res Bull 4:465–474
Rothermundt M, Missler U, Arolt V et al (2001) Increased S100B blood levels in unmedicated and treated schizophrenic patients are correlated with negative symptomatology. Mol Psychiatry 6:445–449
Rothermundt M, Ponath G, Arolt V (2004) S100B in schizophrenic psychosis. Int Rev Neurobiol 59:445–470
Rustin P, Chretien D, Bourgeron T et al (1994) Biochemical and molecular investigations in respiratory chain deficiencies. Clin Chim Acta 228:35–51
Sagara Y (1998) Induction of reactive oxygen species in neurons by haloperidol. J Neurochem 71:1002–1012
Schroeter ML, Abdul-Khaliq H, Diefenbacher A et al (2002) S100B is increased in mood disorders and may be reduced by antidepressive treatment. Neuroreport 13:1675–1678
Schroeter ML, Abdul-Khaliq H, Fruhauf S et al (2003) Serum S100B is increased during early treatment with antipsychotics and in deficit schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 62:231–236
Schurr A (2002) Energy metabolism, stress hormones and neural recovery from cerebral ischemia/hypoxia. Neurochem Int 41:1–8
Shang T, Kotamraju S, Kalivendi SV et al (2004) 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons is mediated by transferrin receptor iron-dependent depletion of tetrahydrobiopterin and neuronal nitric-oxide synthase-derived superoxide. J Biol Chem 18:19099–19112
Sharma T, Mockler D (1998) The cognitive efficacy of atypical antipsychotics in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18:12–19
Sullivan PG, Dragicevic NB, Deng JH et al (2004) Proteasome inhibition alters neural mitochondrial homeostasis and mitochondria turnover. J Biol Chem 20:20699–20707
Terry AV, Hill WD, Parikh V et al (2002) Differential effects of chronic haloperidol and olanzapine exposure on brain cholinergic markers and spatial learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 164:360–368
Terry AV, Hill WD, Parikh V et al (2003) Differential effects of haloperidol, risperidone and clozapine exposure on cholinergic markers and spatial learning performance in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:300–309
Tollefson GD, Beasley CM Jr, Tamura RN et al (1997) Blind, controlled, long-term study of the comparative incidence of treatment-emergent tardive dyskinesia with olanzapine or haloperidol. Am J Psychiatry 154:1248–1254
Velligan DI, Newcomer J, Pultz J et al (2002) Does cognitive function improve with quetiapine in comparison to haloperidol. Schizophr Res 53:239–248
Vilner BJ, Costa BR, Bowen WD (1995) Cytotoxic effects of sigma ligants: sigma receptor mediated alteration in cellular morphology and viability. J Neurosci 15:117–134
Weis S, Llenos IC (2004) GFAP-immunopositive astrocytes in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 67:293–295
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from Eli Lilly do Brazil, Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense (UNESC) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Streck, E.L., Rezin, G.T., Barbosa, L.M. et al. Effect of antipsychotics on succinate dehydrogenase and cytochrome oxidase activities in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 376, 127–133 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0178-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0178-2