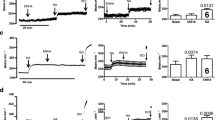
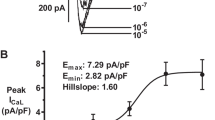
Abstract
Activation of either coexisting β1- or β2-adrenoceptors with noradrenaline or adrenaline, respectively, causes maximum increases of contractility of human atrial myocardium. Previous biochemical work with the β2-selective agonist zinterol is consistent with activation of the cascade β2-adrenoceptors→Gsα-protein→adenylyl cyclase→cAMP→protein kinase (PKA)→phosphorylation of phospholamban, troponin I, and C-protein→hastened relaxation of human atria from nonfailing hearts. However, in feline and rodent myocardium, catecholamines and zinterol usually do not hasten relaxation through activation of β2-adrenoceptors, presumably because of coupling of the receptors to Gi protein. It is unknown whether the endogenously occurring β2-adrenoceptor agonist adrenaline acts through the above cascade in human atrium and whether its mode of action could be changed in heart failure. We assessed the effects of (-)-adrenaline, mediated through β2-adrenoceptors (in the presence of CGP 20712A 300 nM to block β1-adrenoceptors), on contractility and relaxation of right atrial trabecula obtained from nonfailing and failing human hearts. Cyclic AMP levels were measured as well as phosphorylation of phospholamban, troponin I, and protein C with Western blots and the back-phosphorylation procedure. For comparison, β1-adrenoceptor-mediated effects of (-)-noradrenaline were investigated in the presence of ICI 118,551 (50 nM to block β2-adrenoceptors). The positive inotropic effects of both (-)-noradrenaline and (-)-adrenaline were accompanied by reductions in time to peak force and time to reach 50% relaxation. (-)-Adrenaline caused similar positive inotropic and lusitropic effects in atrial trabeculae from failing hearts. However, the inotropic potency, but not the lusitropic potency, of (-)-noradrenaline was reduced fourfold in atrial trabeculae from heart failure patients. Both (-)-adrenaline and (-)-noradrenaline enhanced cyclic AMP levels and produced phosphorylation of phospholamban, troponin I, and C-protein to a similar extent in atrial trabeculae from nonfailing hearts. The hastening of relaxation caused by (-)-adrenaline together with the PKA-catalyzed phosphorylation of the three proteins involved in relaxation, indicate coupling of β2-adrenoceptors to Gs protein. The phosphorylation of phospholamban at serine16 and threonine17 evoked by (-)-adrenaline through β2-adrenoceptors and by (-)-noradrenaline through β1-adrenoceptors was not different in atria from nonfailing and failing hearts. Activation of β2-adrenoceptors caused an increase in phosphorylase a activity in atrium from failing hearts further emphasizing the presence of the β2-adrenoceptor–Gsα-protein pathway in human heart. The positive inotropic and lusitropic potencies of (-)-adrenaline were conserved across Arg16Gly- and Gln27Glu-β2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms in the right atrium from patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery, chronically treated with β1-selective blockers. The persistent relaxant and biochemical effects of (-)-adrenaline through β2-adrenoceptors and of (-)-noradrenaline through β1-adrenoceptors in heart failure are inconsistent with an important role of coupling of β2-adrenoceptors with Giα-protein in human atrial myocardium.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltas LG, Karczewski P, Bartel S, Krause E-G (1997) The endogenous cardiac sarcoplasmatic reticulum Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase is activated in response to β-adrenergic stimulation and becomes Ca2+-independent in intact beating heart. FEBS Lett 409:131–136
Bartel S, Stein B, Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Neumann J, Schmitz W, Krause, EG, Karczewski P, Scholz H (1996) Protein phosphorylation in isolated trabeculae from nonfailing and failing human hearts. Mol Cell Biochem 157:171–179
Bartel S, Krause E-G, Wallukat G, Karczewski P (2003) New insights into β2-adrenoceptor signaling in the adult rat heart. Cardiovasc Res 57:694–703
Boehm E, Ventura-Clapier R, Mateo P, Lechene P, Veksler V (2000) Glycolysis supports calcium uptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skinned ventricular fibres of mice deficient in mitochondrial and cytosolic creatine kinase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:891–902
Bokník P, Unkel C, Kirchhefer U, Kleideiter U, Klein-Wiele O, Knapp J, Linck B, Lüss H, Müller FU, Schmitz W, Vahlensieck U, Zimmermann N, Jones LR, Neumann J (1999) Regional expression of phospholamban in the human heart. Cardiovasc Res 42:67–76
Brattelid T, Qvigstad E, Lynham JA, Molenaar P, Aass H, Geiran O, Skomedal T, Osnes J-B, Levy FO, Kaumann AJ (2004) Functional serotonin 5-HT4 receptors in porcine and human ventricular myocardium with increased 5-HT4 mRNA in heart failure. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 370:157–166
Bristow MR, Ginsburg R, Umans V, Fowler M, Minobe W, Rasmussen R, Zera P, Menlove R, Shah P, Jamieson S, Stinson EB (1986) β1- and β2-Adrenergic-receptor subpopulations in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium: coupling of both receptor subtypes to muscle contraction and selective β1-receptor down-regulation in heart failure. Circ Res 59:297–309
Bristow MR, Hershberger RE, Port JD, Minobe W, Rasmussen R (1989) β1- and β2-adrenergic receptor-mediated adenylate cyclase stimulation in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium. Mol Pharmacol 35:295–303
Brodde OE, Schüler S, Kretsch R, Brinkmann M, Borst HG, Hetzer R, Reidemeister JC, Warnecke H, Zerkowski HR (1986) Regional distribution of β-adrenoceptors in the human heart: coexistence and functional β1- and β2-adrenoceptors in both atria and ventricles in severe congestive cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 8:1235–1242
Brown LA, Harding SE (1992) The effect of pertussis toxin on β-adrenoceptor responses in isolated cardiac myocytes from noradrenaline-treated guinea-pigs and patients with cardiac failure. Br J Pharmacol 106:115–122
Bruck H, Leineweber K, Büscher R, Ulrich A, Radke J, Insel PA, Brodde O-E (2003) The Gln27Glu β2-adrenoceptor polymorphism slows the onset of desensitization of cardiac functional responses in vivo. Pharmacogenetics 13:59–66
Christ T, Engel A, Ravens U, Kaumann AJ (2006) Cilostamide potentiates more the positive inotropic effects of (-)-adrenaline through β2-adrenoceptors than the effects of (-)-noradrenaline through β1-adrenoceptors in human atrial myocardium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 374:249–253
Cohn JN, Levine TB, Olivari MT, Garberg V, Lura D, Francis GS, Simon AB, Rector T (1984) Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 311:819–823
Drago GA, Colyer J (1994) Discrimination between two sites of phosphorylation on adjacent amino acids by phosphorylation site-specific antibodies to phospholamban. J Biol Chem 269:25073–25077
El-Armouche A, Zolk O, Rau T, Eschenhagen T (2003) Iinhibitory G-proteins and their role in desensitization of the adenylyl cyclase pathway in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 60:478–487
England PJ (1976) Studies on the phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin during modification of contraction in perfused rat heart. Biochem J 160:295–304
Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Diederich M, Nose M, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Schulte am Esch J, Warnholtz A, Schafer H (1992a) Long-term β-adrenoceptor-mediated up-regulation of Giα and Goα mRNA levels and pertussis sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins in rat heart. Mol Pharmacol 42:773–783
Eschenhagen T, Mende U, Nose M, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Haverich A, Hirt S, Doring V, Kalmar P, Hoppner W, Seitz HJ (1992b) Increased messenger RNA level of the inhibitory G protein α subunit Giα-2 in human end-stage heart failure. Circ Res 70:688–696
Feldman AM, Cates AE, Veazey WB, Hershberger RE, Bristow MR, Baughman KL, Baumgartner WA, Van Dop C (1988) Increase of the 40,000-mol wt pertussis toxin substrate (G protein) in the failing human heart. J Clin Invest 82:189–197
Gilman AG (1970) A protein binding assay for adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 67:305–312
Gille E, Lemoine H, Ehle B, Kaumann AJ (1985) The affinity of (-)-propranolol for β1- and β2-adrenoceptors of human heart. Differential antagonism of the positive inotropic effects and adenylate cyclase stimulation by (-)-noradrenaline and (-)-adrenaline. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 331:60–70
Green SA, Cole G, Jacinto J, Innis M, Liggett SB (1993) A polymorphism of the human β2-adrenergic receptor within the fourth transmembrane domain alters ligand binding and functional properties of the receptor. J Biol Chem 268:23116–23121
Gupta RC, Neumann J, Watanabe AM, Sabbah NH (2002) Inhibition of type 1 protein phosphatase activity by activation of β-adrenoceptors in ventricular myocardium. Biochem Pharmacol 63:1069–1076
Hall JA, Kaumann AJ, Brown MJ (1990) Selective β1-adrenoceptor blockade enhances positive inotropic responses to endogenous catecholamines mediate through β2-adrenoceptors in human atrial myocardium. Circ Res 66:1610–1623
Hall JA, Petch MC, Brown MJ (1991) In vivo demonstration of cardiac β2-adrenoceptor sensitization by β1-antagonist treatment. Circ Res 69:959–964
Harrison GJ, van Wijhe MH, de Groot B, Dijk FJ, Gustavson LA, van Beek JHGM (2003) Glycolytic buffering affects cardiac bioenergetic signaling and contractile reserve similar to creatine kinase. Am J Physiol 285:H883–H890
Hoit BD, Suresh DP, Craft L, Walsh RA, Liggett SB (2000) β2-Adrenergic receptor polymorphisms at amino acid 16 differentially influence agonist-stimulated blood pressure and peripheral blood flow in normal individuals. Am Heart J 139:537–542
Karczewski P, Bartel S, Krause E-G (1990) Differential sensitivity to isoproterenol of troponin I and phospholamban phosphorylation in isolated rat heart. Biochem J 266:115–122
Kaumann AJ (2000) Gs-protein coupled receptors in human heart. In: Kenakin T, Angus JA (eds) The pharmacology of functional, biochemical, and recombinant receptor systems. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 73–116
Kaumann AJ, Lemoine H (1987) Beta 2-adrenoceptor-mediated positive inotropic effect of adrenaline in human ventricular myocardium. Quantitative discrepancies with binding and adenylate cyclase stimulation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 335:403–411
Kaumann AJ, Hall JA, Murray KJ, Wells FC, Brown MJ (1989) A comparison of the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline on human heart: the role of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in the stimulation of adenylate cyclase and contractile force. Eur Heart J 10(Suppl B):29–27
Kaumann AJ, Sanders L, Lynham JA, Bartel S, Kuschel M, Karczewski, Krause E-G (1996) β2-adrenoceptor activation by zinterol causes protein phosphorylation, contractile effects and relaxant effects through a cAMP pathway in human atrium. Mol Cell Biochem 163/164:113–123
Kaumann AJ, Bartel S, Molenaar P, Sanders L, Burrell K, Vetter D, Hempel P, Karzewski P, Krause E-G (1999) Activation of β2-adrenergic receptors hastens relaxation and mediates phosphorylation of phospholamban, troponin I, and C-protein in ventricular myocardium from patients with terminal heart failure. Circulation 99:65–72
Kilts JD, Gerhardt MA, Richardson MD, Sreeram G, Mackensen GB, Grocott HP, White WD, Davis RD, Newman MF, Reves JG, Schwinn DA, Kwatra MM (2000) β2-Adrenergic and several other G protein-couple receptors in human atrial membranes activate both Gs and Gi. Circ Res 87:705–709
Koss KL, Kranias EG (1996) Phospholamban: a prominent regulator of myocardial contractility. Circ Res 79:1059–1063
Kranias EG (1985) Regulation of Ca2+ transport by cyclic 3′,5′-AMP-dependent and calcium-calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta 844:193–199
Kranias EG, Garvey JL, Srivastava RD, Solaro RJ (1985) Phosphorylation and functional modifications of sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils in isolated rabbit hearts stimulated with isoprenaline. Biochem J 226:113–121
Kuschel M, Zhou Y-Y, Spurgeon HA, Bartel S, Karczewski P, Zhang S-J, Krause E-G, Lakatta EG, Xiao R-P (1999) β2-Adrenergic cAMP signaling is uncoupled from phosphorylation of cytoplasmic proteins in canine heart. Circulation 99:2458–2465
Lemoine H, Kaumann AJ (1991) Regional differences of β1- and β2-adrenoceptor-mediated functions in feline heart. A β2-adrenoceptor-mediated positive inotropic effect possibly unrelated to cyclic AMP. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 344:56–69
Levy FO, Zhu X, Kaumann AJ, Birnbaumer L (1993) Efficacy of beta1-adrenergic receptors is lower than that of beta2-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10798–17802
Li J, Wang J, Russell FD, Molenaar P (2005) Activation of calcineurin in human failing heart ventricle by endothelin-1, angiotensin II and urotensin II. Br J Pharmacol 145:432–440
Liggett SB, Wagoner LE, Craft LL, Hornung RW, Hoit BD, McIntosh TC (1998) The Ile164 β2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism adversely affects the outcome of congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest 102:1534–1539
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Martinez FD, Graves PE, Baldini M, Solomon S, Erickson R (1997) Association between genetic polymorphisms of the β2-adrenoceptor and response to albuterol in children with and without a history of wheezing. J Clin Invest 100:3184–3188
Mattiazzi A, Mundiña-Weilenmann C, Guoxiang C, Vittone L, Kranias E (2005) Role of phospholamban phosphorylation on Thr17 in cardiac physiological and pathological conditions. Cardiovasc Res 68:366–375
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Mittmann K, Jaquet K, Heilmeyer LMG Jr (1990) A common motif of two adjacent phosphoserines in bovine, rabbit and human cardiac troponin I. FEBS 273:41–45
Molenaar P, Sarsero D, Arch JRS, Kelly J, Henson SM, Kaumann AJ (1997) Effects of (-)-RO363 at human atrial β-adrenoceptor subtypes, the human cloned β3-adrenoceptor and rodent intestinal β3-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 120:165–176
Molenaar P, Bartel S, Cochrane A, Vetter D, Jalali H, Pohlner P, Burrell K, Karczewski P, Krause E-G, Kaumann A (2000) Both β2- and β1-adrenergic receptors mediate hastened relaxation and phosphorylation of phospholamban and troponin I in ventricular myocardium of Fallot infants, consistent with selective coupling of β2-adrenergic receptor to Gs-protein. Circulation 102:1814–1821
Molenaar P, Rabnott G, Yang I, Fong KM, Savarimuthu SM, Li L, West MJ, Russell FD (2002) Conservation of the cardiostimulant effects of (-)-norepinephrine across ser49gly and gly389arg beta1-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms in human right atrium in vitro. J Am Coll Cardiol 40:1275–1282
Molenaar P, Christ T, Ravens U, Kaumann A (2006) Carvedilol blocks β2- more than β1-adrenoceptors in human heart. Cardiovasc Res 69:128–139
Morano I (1999) Tuning the human heart molecular motors by myosin light chains. J Mol Med 77:544–555
Motomura S, Deighton NM, Zerkowski H-R, Doetsch N, Michel MC, Brodde O-E (1990) Chronic β1-adrenoceptor antagonist treatment sensitizes β2-adrenoceptors, but desensitizes M2-muscarinic receptors in the human right atrium. Br J Pharmacol 101:363–369
Müller FU, Boheler KR, Eschenhagen T, Schmitz W, Scholz H (1993) Isoprenaline stimulates gene transcription of the inhibitory G protein α-subunit Giα-2 in rat heart. Circ Res 72:696–700
Mundiña-Weilenmann C, Vitone L, Ortale M, de Cingolani GC, Mattiazzi A (1996) Immunodetection of phosphorylation sites gives new insights into the mechanisms underlying phospholamban phosphorylation in the intact heart. J Biol Chem 271:33561–33567
Namm DH, Mayer SE, Maltbie M (1968) The role of potassium and calcium on the effect of epinephrine on cardiac cyclic adenosine 3′,5′,-monophosphate, phosphorylase kinase and phosphorylase. Mol Pharmacol 4:522–530
Neumann J, Schmitz W, Scholz H, von Meyerinck L, Doring V, Kalmar P (1988) Increase in myocardial Gi-proteins in heart failure. Lancet 2:936–937
Reiffert SU, Jaquet K, Heilmeyer LMG, Herberg FW (1998) Stepwise subunit interaction changes by mono- and bisphosphorylation of cardiac troponin I. Biochemistry 37:13516–13525
Sanders L, Lynham JA, Bond B, del Monte F, Harding SE, Kaumann AJ (1995) Sensitization of human atrial 5-HT4 receptors by chronic beta-blocker treatment. Circulation 92:2526–2539
Sanders K, Lynham JA, Kaumann AJ (1996) Chronic beta1-adrenoceptor blockade sensitizes H1 and H2 receptor systems in human atrium: role of cyclic nucleotides. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 353:61–670
Sarsero D, Russell FD, Lynham JA, Rabnott G, Yang I, Fong KM, Li L, Kaumann AJ, Molenaar P (2003) (-)-CGP 12177 increases contractile force and hastens relaxation of human myocardial preparations through a propranolol-resistant state of the β1-adrenoceptor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 367:10–21
Schwinger RHG, Münch G, Bölck B, Karczewski P, Krause E-G, Erdmann E (1999) Reduced Ca2+-sensitivity of SERCA 2a in failing human myocardium due to a reduced serin-16 phospholamban phosphorylation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:479–491
Sigmund M, Jakob H, Becker H, Hanrath P, Schumacher C, Eschenhagen T, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Steinfath M (1996) Effects of metoprolol on myocardial beta-adrenoceptors and Gi alpha-proteins in patients with congestive heart failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 51:127–132
Small KM, McGraw DW, Liggett SB (2003) Pharmacology and physiology of human adrenergic receptor polymorphisms. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:381–411
Tada M, Inui M, Yamada M, Kadoma M-A, Kuzuya T, Abe H, Kakiuchi S (1983) Effects of phospholamban phosphorylation catalyzed by adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases on calcium transport ATPase of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Cell Cardiol 15:335–346
Turki J, Lorenz JN, Green SA, Donnelly ET, Jacinto M, Liggett SB (1996) Myocardial signaling defects and impaired cardiac function of a human β2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism expressed in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10483–10488
Wang T, Plumpton C, Brown MJ (1999) Selective β1-adrenoceptor blockade enhances the activity of the stimulatory G-protein in human atrial myocardium. Br J Pharmacol 128:135–141
Weisberg A, Winegrad S (1996) Alteration of myosin cross bridges by phosphorylation of myosin-binding protein C in cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8999–9003
Xiao R-P, Hohl C, Altschuld R, Jones L, Livingston B, Ziman B, Tantini B, Lakatta EG (1994) β2-Adrenergic receptor-stimulated increase in cAMP in rat heart cells is not coupled to changes in Ca2+ dynamics, contractility, or phospholamban phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 269:19151–19156
Xiao R-P, Ji X, Lakatta EG (1995) Functional coupling of the β2-adrenoceptor to a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in cardiac myocytes. Mol Pharmacol 47:322–329
Xiao R-P, Avdonin P, Zhou Y-Y, Cheng H, Akhter SA, Eschenhagen T, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ, Lakatta EG (1999) Coupling of β2-adrenoceptor to Gi proteins and its physiological relevance in murine cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 84:43–52
Zheng M, Zhu W, Han Q, Xiao RP (2005) Emerging concepts and therapeutic implications of β-adrenergic receptor subtype signaling. Pharmacol Ther 108:257–268
Acknowledgements
PM thanks the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia for support. AJK is grateful to the British Heart Foundation for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molenaar, P., Savarimuthu, S.M., Sarsero, D. et al. (-)-Adrenaline elicits positive inotropic, lusitropic, and biochemical effects through β2-adrenoceptors in human atrial myocardium from nonfailing and failing hearts, consistent with Gs coupling but not with Gi coupling. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 375, 11–28 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0138-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0138-x