Abstract
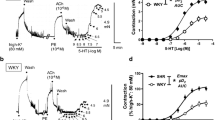
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) is a vasoconstricting lysosphingolipid, and the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway plays an important role in SPC-induced contraction. Since RhoA/Rho-kinase-mediated signaling is involved in the generation and/or maintenance of hypertension, we compared the effect of SPC on the contractility of endothelium-denuded small mesenteric arteries in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY). Fura-2 Ca2+ signals, contractile responses, and phosphorylation of 20-kDa myosin light chains (MLC20) were measured. Ten μM SPC induced a gradual and sustained vasoconstriction, which was greater in arteries of the SHR (82.5±4.3%, n=9) than in those of the WKY (26.7±4.5%, n=10). In Ca2+-free media, SPC gradually increased vascular tone in the SHR, but caused little vasoconstriction in the WKY. In the SHR and WKY, SPC evoked a greater vasoconstriction than did high K+depolarization at a given Ca2+ ratio, and the Ca2+ ratio–tension curve induced by SPC was significantly shifted to the left compared with that induced by high K+ depolarization. However, the magnitude of shift to the left was greater in the SHR than in the WKY. The Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 significantly inhibited SPC-induced contractions, but neither the protein kinase C inhibitor calphostin-C nor PD98059, which inhibits activation of some mitogen-activated protein kinases, had any effect on the SHR or the WKY. SPC significantly increased the phosphorylation of MLC20 in both the SHR and the WKY, and Y-27632 inhibited the SPC-induced increase in MLC20 phosphorylation in the SHR. Our results suggest that SPC induces greater vascular tone in the SHR than in the WKY. Furthermore, our results indicate that activation of the Rho-kinase pathway plays an important role in the SPC-induced Ca2+ sensitization in the SHR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alewijinse AE, Peters SLM, Michel MC (2004) Cardiovascular effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate and other sphingomyelin metabolites. Br J Pharmacol 143:666–684
Altmann C, Steenpaβ V, Czyborra P, Hein P, Michel MC (2003) Comparison of signaling mechanisms involved in rat mesenteric microvessel contraction by noradrenaline and sphingosylphosphorylcholine. Br J Pharmacol 138:261–271
Asano M, Nomura Y (2003) Comparison of inhibitory effects of Y-27632, a rho kinase inhibitor, in strips of small and large mesenteric arteries from spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rats. Hypertens Res 26:97–106
Bischoff A, Czyborra P, Fetscher C, Meyer Zu Heringdore D, Jakobs KH, Michel MC (2000) Sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine constrict renal and mesenteric microvessels in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 130:1871–1877
Bischoff A, Finger J, Michel MC (2001) Nifedipine inhibits sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced renovascular contraction in vitro and in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 364:179–182
Chin T-Y, Chueh S-H (1998) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase via a Ca2+-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol 275:C1255–C1263
Coussin F, Scott RH, Wise A, Nixon GF (2002) Comparison of sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced intracellular signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscles: differential role in vasoconstriction. Circ Res 91:151–157
Hannun YA, Luberto C, Argraves KM (2001) Enzymes of sphingolipid metabolism: from modular to integrative signaling. Biochemistry 40:4893–4903
Jang GJ, Ahn DS, Cho YE, Morgan KG, Lee YH (2005) C2-ceramide induces vasodilation in phenylephrine-induced pre-contracted rat thoracic aorta: role of RhoA/Rho-kinase and intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 372:242–250
Jensen PE (1996) Calphostin C-sensitive enhancements of force by lysophosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerols in mesenteric arteries from the rat. Br J Pharmacol 119:15–22
Kimura K, Ito M, Amano M, Chihara K, Fukata Y, Nakafuku M, Yamamori B, Feng J, Nakano T, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kaibuchi K (1996) Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Science 273:245–248
Kolesnick R (2001) The therapeutic potential of modulating the ceramide/sphingomyelin pathway. J Clin Invest 110:3–8
Masumoto A, Hirooka Y, Shimokawa H, Hironaga K, Setoguchi S, Takeshita A (2001) Possible involvement of Rho-kinase in the pathogenesis of hypertension in humans. Hypertension 38:1307–1310
Mukai Y, Shimokawa H, Matoba T, Kandabashi T, Satoh S, Hiroki J, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A (2001) Involvement of Rho-kinase in hypertensive vascular disease: a novel therapeutic target in hypertension. FASEB J 15:1062–1064
Nakao F, Kobayashi S, Mogani K, Mizukami Y, Shirao S, Miwa S, Todoroki-Ikeda N, Ito M, Matsuzaki M (2002) Involvement of Src family protein tyrosine kinases in Ca2+ sensitization of coronary artery contraction mediated by a sphingosylphosphorylcholine-Rho-kinase pathway. Circ Res 91:953–960
Satoh S, Kreutz R, Wilm C, Ganten D, Pfitzer G (1994) Augmented agonist-induced Ca2+-sensitization of coronary artery contraction in genetically hypertensive rats. Evidence for altered signal transduction in the coronary smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 94:1397–1403
Savoia C, Tabet F, Yao G, Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM (2005) Negative regulation of RhoA/Rho kinase by angiotensin II type 2 receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells: role in angiotensin II-induced vasodilation in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 23:1037–1045
Shirao S, Kashiwagi S, Sato M, Miwa, Nakao F, Kurokawa T, Todoroki-Ikeda N, Mogami K, Mizukami Y, Kuriyama S, Haze K, Suzuki M, Kobayashi S (2002) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine is a novel messenger for rho-kinase-mediated Ca2+ sensitization in the bovine cerebral artery. Unimportant role for protein kinase C. Circ Res 91:112–119
Spiegel S, Milstien S (1995) Sphingolipid metabolites: members of a new class of lipid second messengers. J Membr Biol 146:225–237
Thomas GD, Snetkov VA, Patel R, Leach RM, Aaronson PI, Ward JPT (2005) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced vasoconstriction of pulmonary artery: activation of non-store-operated Ca2+ entry. Cardiovasc Res 68:56–64
Todoroki-Ikeda N, Mizukami Y, Mogami K, Kusuda T, Yamamoto K, Miyake K, Sato M, Suzuki S, Yamagata H, Hokazono Y, Kobayashi S (2000) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine induces Ca2+ sensitization of vascular smooth muscle contraction: possible involvement of Rho-kinase. FEBS Lett 482:85–90
Touyz RM, Mabrouk EI, He G, Wu XH, Schiffrin EL (1999) Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition attenuates angiotensin II-mediated signaling and contraction in spontaneously hypertensive rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 84:505–515
Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S (1997) Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 389:990–994
Wettschureck N, Offermanns S (2002) Rho/rho-kinase mediated signaling in physiology and pathophysiology. J Mol Med 80:629–638
Yeon DS, Kim JS, Ahn DS, Kwon SC, Kang BS, Morgan KG, Lee YH (2002) Role of protein kinase C- or RhoA-induced Ca2+-sensitization in stretch-induced myogenic tone. Cardiovasc Res 53:431–438
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a Grant (#HMP 02-PJ1-PG3-21401-0009) of the 2002 Good Health R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, SK., Ahn, D.S., Cho, YE. et al. Augmented sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced Ca2+-sensitization of mesenteric artery contraction in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 373, 30–36 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0036-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0036-7