Abstract
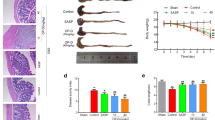
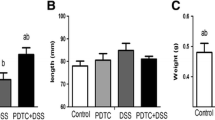
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), a nuclear enzyme activated by strand breaks in DNA, plays an important role in the colon injury associated with experimental colitis. The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of 5-aminoisoquinolinone (5-AIQ), a novel and potent inhibitor of PARP activity, in the development of experimental colitis. To address this question, we used an experimental model of colitis, induced by dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS). Compared with DNBS-treated mice, mice treated with 5-AIQ (3 mg/kg i.p.) or 3-aminobenzamide (3-AB; 10 mg/kg i.p. twice a day) and subjected to DNBS-induced colitis experienced a significantly lower rate in the extent and severity of the histological signs of colon injury. DNBS-treated mice experienced diarrhea and weight loss. Four days after administration of DNBS, the mucosa of the colon exhibited large areas of necrosis. Neutrophil infiltration (determined by histology as well as an increase in myeloperoxidase [MPO] activity in the mucosa) was associated with an up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Immunohistochemistry for PAR showed an intense staining in the inflamed colon. On the contrary, the treatment of DNBS-treated mice with 5-AIQ or with 3-AB significantly reduced the degree of hemorrhagic diarrhea and weight loss caused by administration of DNBS. 5-AIQ also caused a substantial reduction in the degree of colon injury, in the rise in MPO activity (mucosa), in the increase in staining (immunohistochemistry) for PAR, as well as in the up-regulation of ICAM-1 caused by DNBS in the colon. Thus, 5-AIQ treatment reduces the degree of colitis caused by DNBS. We propose that 5-AIQ treatment may be useful in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiko S, Grisham MB (1995) Spontaneous intestinal inflammation and nitric oxide metabolism in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. Gastroenterology 109:142–150
Appleyard CB, Wallace JL (1995) Reactivation of hapten-induced colitis and its prevention by anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Physiol 269:G119–G125
Banasik M, Komura H, Shimoyama M (1992) Specific inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose)synthetase and mono (ADP-ribose) transferase. J Biol Chem 267:1569–1575
Berger NA (1985) Poly(ADP-ribose) in the cellular response to DNA damage. Radiat Res 101:4–15
Boughton-Smith NK, Evans SM, Hawkey CJ (1993) Nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Lancet 341:338–340
Chatterjee PK, Zacharowski K, Cuzzocrea S, Otto M, Thiemermann C (2000) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase reduce renal ischemia–reperfusion injury in the anesthetized rat in vivo. FASEB J 14:641–651
Chiarugi A (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: killer or conspirator? The ‘suicide hypothesis’ revisited. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:22–129
Clark WM, Lauten JD, Lessov N (1995) Time course of ICAM-1 expression and leukocyte subset infiltration in rat forebrain ischemia. Mol Chem Neuropathol 26:213–230
Cosi C (2002) New inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and their potential therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Patents 12:1047–1071
Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B, Costantino G, Szabó A, Salzman AL, Caputi AP, Szabó C (1997) Beneficial effects of 3-aminobenzamide, an inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase in a rat model of splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion. Br J Pharmacol 121:1065–1074
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E (2000) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG126 reduces the development of acute and chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol 157:145–158
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E (2001) Calpain inhibitor I reduces colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in the rat. Gut 48:478–488
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E (2002) Effects of 5-aminoisoquinolinone, a water-soluble, potent inhibitor of the activity of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, in a rodent model of lung injury. Biochem Pharmacol 63:293–304
Davenpeck KL, Gauthier TW, Albertine KH (1994) Role of P-selectin in microvascular leukocyte–endothelial interaction in splanchnic ischemia–reperfusion. Am J Physiol 267:H622–H630
Desreumaux P, Brandt E, Gambiez L (1997) Distinct cytokine patterns in early and chronic ileal lesions of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 113:118–126
Eliasson MJ, Sampei K, Mandir AS, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Bao J, Pieper A, Wang ZQ, Dawson TM, Snyder SH, Dawson VL (1997) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase gene disruption renders mice resistant to cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 3:1089–1095
Farhood A, McGuire GM, Manning AM (1995) Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression and its role in neutrophil-induced ischemia–reperfusion injury in rat liver. J Leukoc Biol 57:368–374
Fiocchi C (1998) Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 115:182–205
Furie MB, Tancinco MC, Smith CW (1991) Monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte integrins CD11a/CD18 and CD11b/CD18 or intercellular adhesion molecule-1 inhibit chemoattractant-stimulated neutrophil transendothelial migration in vitro. Blood 78:2089–2097
Horie Y, Wolf R, Iyasaka M (1996) Leukocyte adhesion and hepatic microvascular responses to intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Gastroenterology 111:666–673
Ikai K, Ueda K (1983) Immunohistochemical demonstration of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) synthetase in bovine tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 31:261–264
Ikeda I, Kasajima T, Ishiyama S (1997) Distribution of inducible nitric oxide synthase in ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 92:1339–1341
Jijon HB, Churchill T, Malfair D (2000) Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase attenuates inflammation in a model of chronic colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G641–G651
Kitahora T, Suzuki K, Asakura H (1988) Active oxygen species generated by monocytes and polymorphonuclear cells in Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 33:951–955
Kukielka GL, Youker KA, Hawkins HK (1994) Regulation of ICAM-1 and IL-6 in myocardial ischemia: effect of reperfusion. Ann NY Acad Sci 723:258–270
Lora L, Mazzon E, Billington D (1997) Effects of cyclosporin A on paracellular and transcellular transport of horseradish peroxidase in perfused rat livers. Dig Dis Sci 42:514–521
Lundberg JO, Hellstrom PM, Lundberg JM (1994) Greatly increased luminal nitric oxide in ulcerative colitis. Lancet 344:1673–1674
Luscinskas FW, Ding H, Lichtman AH (1995) P-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 mediate rolling and arrest, respectively, of CD4+ T lymphocytes on tumor necrosis factor alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. J Exp Med 181:1179–1186
Mabley JG, Jagtap P, Perretti M (2001) Anti-inflammatory effects of a novel, potent inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Inflamm Res 50:561–569
Mazzon E, Dugo L, Li JH (2002) GPI 6150, a PARP inhibitor, reduces the colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 64:327–337
McDonald MC, Mota-Filipe H, Wright JA, Abdelrahman M, Threadgill MD, Thompson AS, Thiemermann C (2000) Effects of 5-aminoisoquinolinone, a water-soluble, potent inhibitor of the activity of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase on the organ injury and dysfunction caused by haemorrhagic shock. Br J Pharmacol 130:843–850
Middleton SJ, Shorthouse M, Hunter JD (1993) Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet 341:465–466
Miller MJ, Thompson JH, Zhang XJ (1995) Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and peroxynitrite formation in guinea pig ileitis. Gastroenterology 109:1475–1483
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS (1989) Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology 96:795–803
Mota-Filipe H, Sepodes B, McDonald MC (2002) The novel PARP inhibitor 5-aminoisoquinolinone reduces the liver injury caused by ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. Med Sci Monit 8:BR444–BR453
Mourelle M, Vilaseca J, Guarner F (1996) Toxic dilatation of colon in a rat model of colitis is linked to an inducible form of nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol 33:G425–G430
Mullane KM, Kraemer R, Smith B (1985) Myeloperoxidase activity as a quantitative assessment of neutrophil infiltration into ischemic myocardium. J Pharmacol Methods 14:157–167
Mulligan MS, Polley MJ, Bayer RJ (1992) Neutrophil-dependent acute lung injury. Requirement for P-selectin (GMP-140). J Clin Invest 90:1600–1607
Nathan C (1996) Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J 6:3051–3064
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ribbons KA, Zhang XJ, Thompson JH (1995) Potential role of nitric oxide in a model of chronic colitis in rhesus macaques. Gastroenterology 108:705–711
Shiratora Y, Aoki S, Takada H (1989) Oxygen-derived free radical generating capacity of polymorphonuclear cells in patients with ulcerative colitis. Digestion 44:163–171
Shreeniwas R, Koga S, Karakurum M (1992) Hypoxia-mediated induction of endothelial cell interleukin-1 alpha. An autocrine mechanism promoting expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules on the vessel surface. J Clin Invest 90:2333–2339
Sturiale S, Barbara G, Qiu B (1999) Neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) terminates colitis by degrading substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11653–11658
Suto MJ, Turner WR, Arundel-Suto CM (1991) Dihydroisoquinolinones: the design and synthesis of a new series of potent inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Anticancer Drug Des 6:107–117
Szabó C, Dawson VL (1998) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase in inflammation and ischaemia–reperfusion. Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:287–298
Szabó C, Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B (1997) Endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of endotoxic shock. Importance of the activation of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase by peroxynitrite. J Clin Invest 100:723–735
Szabó G, Bährle S, Stumpf N (2002) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition reduces reperfusion injury after heart transplantation. Circ Res 90:100–106
Takazoe M, Tanaka T, Kondo K (2002) The present status and recent development of the treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases: desirable effect of extracorporeal immunomodulation. Ther Apher 6:305–311
Thiemermann C (2002) Development of novel, water-soluble inhibitors of poly (adenosine 5′-diphosphate ribose) synthetase activity for use in shock and ischemia–reperfusion injury. Crit Care Med 30:1163–1165
Wallace JL, Keenan CM, Gale D (1992) Exacerbation of experimental colitis by non-steroidal antinflammatory drugs is not related to elevated leukotriene B4 synthesis. Gastroenterology 102:18–27
Wayman NS, McDonald MC, Thompson AC (2001) 5-Aminoisoquinolinone, a potent inhibitor of poly (adenosine 5′diphosphate ribose) polymerase, reduces myocardial infarct size. Eur J Pharmacol 430:93–100
Wenkert E, Johnston DBR, Dave KG (1964) Derivatives of hemimellitic acid. A synthesis of erythrocentaurin. J Org Chem 29:2534–2542
Zingarelli B, Squadrito F, Graziani P (1993) Effects of zileuton, a new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, in experimentally induced colitis in rats. Agents Actions 39:150–156
Zingarelli B, Salzman AL, Szabó C (1998) Genetic disruption of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibits the expression of P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res 83:85–94
Zingarelli B, Szabó C, Salzman AL (1999) Blockade of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibits neutrophil recruitment, oxidant generation, and mucosal injury in murine colitis. Gastroenterology 116:335–345
Zingarelli B, O’Connor M, Hake PW (2003) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase modulate signal transduction pathways in colitis. Eur J Pharmacol 469:183–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuzzocrea, S., Mazzon, E., Di Paola, R. et al. 5-Aminoisoquinolinone reduces colon injury by experimental colitis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 370, 464–473 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-1002-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-1002-x