Abstract
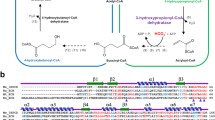
The acetyl-CoA decarbonylase/synthase (ACDS) multienzyme complex catalyzes the reversible cleavage and synthesis of acetyl-CoA in methanogens. This report of the enzyme complex in Archaeoglobus fulgidus demonstrates the existence of a functional ACDS complex in an organism that is not a methanogen. The A. fulgidus enzyme complex contained five subunits of 89, 72, 50, 49.5, and 18.5 kDa, and it catalyzed the overall synthesis of acetyl-CoA according to the following reaction:
w CO2 + 2 Fdred(Fe2+) + 2 H+ + CH3– H4SPt + CoA ⇌ acetyl-CoA + H4SPt + 2 Fdox(Fe3+) + H2O
where Fd is ferredoxin, and CH3–H4SPt and H4SPt denote N 5-methyl-tetrahydrosarcinapterin and tetrahydrosarcinapterin, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 October 1997 / Accepted: 29 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, YR., Reed, D., Millstein, J. et al. Acetyl-CoA decarbonylase/synthase complex from Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Arch Microbiol 169, 525–529 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050606
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050606