Abstract
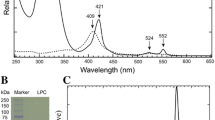
A bacterial cytochrome c peroxidase was purified from the obligate methanotroph Methylococcus capsulatus Bath in either the fully oxidized or the half reduced form depending on the purification procedure. The cytochrome was a homo-dimer with a subunit mol mass of 35.8 kDa and an isoelectric point of 4.5. At physiological temperatures, the enzyme contained one high-spin, low-potential (E m7 = –254 mV) and one low-spin, high-potential (E m7 = +432 mM ) heme. The low-potential heme center exhibited a spin-state transition from the penta-coordinated, high-spin configuration to a low-spin configuration upon cooling the enzyme to cryogenic temperatures. Using M. capsulatus Bath ferrocytochrome c 555 as the electron donor, the K M and V max for peroxide reduction were 510 ± 100 nM and 425 ± 22 mol ferrocytochrome c 555 oxidized min–1 (mole cytochrome c peroxidase)–1, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 January 1997 / Accepted: 27 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahn, J., Arciero, D., Hooper, A. et al. Cytochrome c peroxidase from Methylococcus capsulatus Bath. Arch Microbiol 168, 362–372 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050510
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050510