Abstract.
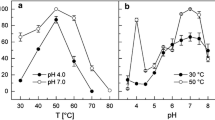
A cytoplasmic pyrophosphatase [E.C. 3.6.1.1.] was partially purified from Helicobacter pylori. The molecular mass was estimated to be 103 kDa by gel filtration. Results of SDS-PAGE suggested that the enzyme consists of six identical subunits of 19.1 kDa each. The enzyme specifically catalyzed the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate and was very sensitive to NaF, but not to sodium molybdate. The optimal pH for activity was 8.5. Mg2+ was required for maximal activity; Mn2+, Co2+, and Zn2+ poorly supported hydrolytic activity. The pyrophosphatase had an apparent K m for Mg-PPi 2– hydrolysis of 90 µM, and a V max estimated at 24.0 µmol Pi min–1 mg–1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliva, G., Romero, I., Ayala, G. et al. Characterization of the inorganic pyrophosphatase from the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Arch Microbiol 174, 104–110 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030000182
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030000182