Abstract
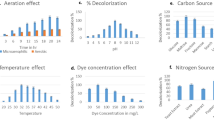
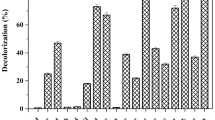
The optimization of the bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri SPM-1, obtained from textile wastewater dumping sites of Surat, Gujarat was studied for the degradation of the textile azo dye Procion Red—H3B. The strain showed significant activities of azoreductase (95%), laccase (76%) and NADH-DCIP reductase (88%) at 12, 10 and 8 h of growth, respectively, indicating the evidence for reductive cleavage of the dye. The optimization was carried on phenanthrene enrichment medium followed by exposing it to variable environmental factors and nutritional sources. The complete decolourization of dye (50 mg/L) happened within 20 h of incubation at pH 8 and temperature 32 ± 0.2 °C under microaerophilic condition. Decolourization was monitored with the shifting of absorbance peak in UV–Vis spectrophotometry and HPLC analysis. The changes in the functional groups were confirmed by the presence of new peaks in FT-IR data. GC–MS analysis helped in recognizing the degraded dye compounds thus elucidating the proposed pathway for Procion Red—H3B. The potential of bioremediation process was completed by phytotoxicity test using two plants Vigna radiata and Cicer arietinum. Our study concludes that the strain Pseudomonas stutzeri SPM-1, with its rapid decolourization efficiency holds noteworthy prospective in industrial application for textile wastewater treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams GO, Fufeyin P, Okoro SE, Ehinomen I (2015) Bioremediation, biostimulation and bioaugmention: a review. Int J Environ BioremedBiodegrad. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-3-1-5
Arora S (2014) Textile dyes: it’s impact on environment and its treatment. J BioremediatBiodegrad. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000e146
Bafana A, Chakrabarti T, Devi SS (2008) Azoreductase and dye detoxification activities of bacillus velezensis strain AB. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1212-5
Bera SP, Tank SK (2020) Screening and identification of newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. for biodegrading the textile azo dye CI Procion Red H-3B. J ApplMicrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14920
Boopathy R (2000) Factors Limiting Bioremediation Technologies. BioresTechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00144-3
Buthelezi SP, Olaniran AO, Pillay B (2012) Textile dye removal from wastewater effluents using bioflocculants produced by indigenous bacterial isolates. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214260
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by potential native plants and their microscopic observation of root growing on stabilised distillery sludge as a prospective tool for in situ phytoremediation of industrial waste. Environ SciPollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8022-1
Chung KT (2016) Azo dyes and human health: a review. J Environ Sci Health Part C . https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1236602
Dalvie DK, Kalgutkar AS, Cyrus Khojasteh-Bakht S, Scott Obach R, O’Donnell JP (2002) Biotransformation reactions of five-membered aromatic heterocyclic rings. Chem Res Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx015574b
Forss J, Lindh MV, Pinhassi J, Welander U (2017) Microbial biotreatment of actual textile wastewater in a continuous sequential rice husk biofilter and the microbial community involved. PLoS ONE 12(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170562
Grüntzig V, Nold SC, Zhou J, Tiedje JM (2001) Pseudomonas stutzeri nitrite reductase gene abundance in environmental samples measured by real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.2.760-768.2001
Jadhav SB, Phugare SS, Patil PS, Jadhav JP (2011) Biochemical degradation pathway of textile dye remazol red and subsequent toxicological evaluation by cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress studies. IntBiodeterior Biodegradation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.04.003
Juwarkar AA, Singh SK, Mudhoo A (2010) A Comprehensive overview of elements in bioremediation. Rev Environ SciBiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-010-9215-6
Kalyani DC, Patil PS, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of reactive textile dye red BLI by an isolated bacterium Pseudomonas Sp. SUK1. BioresTechnol 99(11):4635–4641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.058
Karimi L, Zohoori S, Yazdanshenas ME (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solutions under UV irradiation using nano-strontium titanate as the nanophotocatalyst. J Saudi ChemSoc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.11.010
Lalucat J, Bennasar A, Bosch R, García-Valdés E, Palleroni NJ (2006) Biology of Pseudomonas stutzeri. MicrobiolMolBiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.00047-05
Laor Y, Farmer WJ, Aochi Y, Strom PF (1998) Phenanthrene binding and sorption to dissolved and to mineral-associated humic acid. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00405-3
Manole, A., D. Herea, H. Chiriac, and V. Melnig. (2008). Laccase activity determination. Biomater Biophy Med Phys Ecol.
Matías-Camacho L, Contreras-Rodríguez A, Aguilera-Arreola MG (2020) Pseudomonas stutzeri. RevistaChilena de Infectologia. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-10182020000400443
Messner KR, Imlay JA (1999) The identification of primary sites of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation in the aerobic respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.15.10119
Misal SA, Gawai KR (2018) Azoreductase: a key player of xenobiotic metabolism. Bioresour Bioprocess . https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-018-0206-8
Pandey A, Singh P, Iyengar L (2007) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. IntBiodeterior Biodegradation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.08.006
Park SR, Harlow J, Hoff RF (2000) Bioremediation. Mil Eng. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-8903-7.ch039
Paul SA, Chavan SK, Khambe SD (2012) Studies on characterization of textile industrial wastewater in Solapur city. Int J Chem Sci 10(2):635–642
Pourramezan Z, Ghezelbash GR, Romani B, Ziaei S, Hedayatkhah A (2012) Screening and identification of newly isolated cellulose-degrading bacteria from the gut of xylophagous termite Microcerotermes diversus (Silvestri). Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712060124
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS, Govindwar SP (2011) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review. J Taiwan InstChemEng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2010.06.006
Sarkar S, Banerjee A, Chakraborty N, Soren K, Chakraborty P, Bandopadhyay R (2020) Structural-functional analyses of textile dye degrading azoreductase, laccase and peroxidase: a comparative in silico study. Electron J Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2019.12.004
Savage AJ, Tyrrel SF (2005) Compost liquor bioremediation using waste materials as biofiltration media. BioresTechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.06.016
Senan RC, Emilia Abraham T (2004) Bioremediation of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial consortium. Biodegradation. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOD.0000043000.18427.0a
Seow TW, Lim CK (2016) Removal of dye by adsorption: a review. Int J Appl Eng Res 11:2675–2679
Setten L, Soto G, Mozzicafreddo M, Fox AR, Lisi C, Cuccioloni M, Angeletti M, Pagano E, Díaz-Paleo A, Ayub ND (2013) Engineering pseudomonas protegens Pf-5 for nitrogen fixation and its application to improve plant growth under nitrogen-deficient conditions. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063666
Shah MP, Patel KA, Nair SS, Darji AM (2014) Microbial degradation and decolorization of reactive dyes by Bacillus spp. ETL-1979. Am J Microbiol Res 2(1):16–23
Singh PK, Singh RL (2017) Bio-removal of azo dyes: a review. Int J ApplSciBiotechnol 5(2):108. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijasbt.v5i2.16881
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. ApplMicrobiolBiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100686
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to all faculty members and non-teaching staff of the Department of Bioscience, Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat, Gujarat, India for providing infrastructural facilities and active moral support towards completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SPB: Designing, acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the article, reviewing it critically for significant intellectual content. SKT: Final approval of the version to be submitted for any revised version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We do not have any conflicts of interest. There is no grant or funding awarded to us during the period of study. No part of the study has been published or used anywhere else and this is an original work of the author.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bera, S.P., Tank, S.K. Bioremedial approach of Pseudomonas stutzeri SPM-1 for textile azo dye degradation. Arch Microbiol 203, 2669–2680 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02258-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02258-x