Abstract
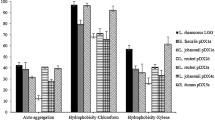
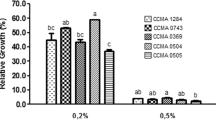
The ability of Paenibacillus polymyxa to inhibit the growth of Escherichia coli generic ATCC 25922 (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922) and to adhere to monolayers of the enterocyte-like human cell line Caco-2 was evaluated. P. polymyxa JB-0501 (P. polymyxa JB-0501), found in a livestock feed probiotic supplement, was compared to P. polymyxa reference strain ATCC 43685 and ATCC 7070 (P. polymyxa ATCC) in terms of carbohydrate utilization and resistance to lysozyme, acid, bile salts, and hydrogen peroxide. JB-0501 grew at pH 4.5 and at H2O2 concentrations less than 7.3 μg/ml and presented a higher affinity to hexadecane and decane. Bile salts at 0.2 % inhibited the growth of all three strains. P. polymyxa JB-0501 and P. polymyxa ATCC 43865 adhered to Caco-2 cell monolayers. The percentage of cells that adhered ranged from about 0.35 to 6.5 % and was partially proportional to the number applied. Contact time (from 15 min to 1 h) had little impact on adhesion. P. polymyxa JB-0501 inhibited the growth of E. coli ATCC 25922, as proven by the diffusion tests in agar. Taken together, these results suggested that P. polymyxa JB-0501 has the potential probiotic properties to justify its consideration as a livestock feed supplement.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A, Granumb PE, Rönner U (1998) The adhesion of Bacillus cereus spores to epithelial cells might be an additional virulence mechanism. Int J Food Microbiol 39:93–99
Angioi A, Zanetyi S, Sann A, Delogu G, Fadda G (1995) Adhesiveness of Bacillus subtilis strains to epithelial cells cultured in vitro. Microb Ecol Health Dis 8:71–77
Ash C, Priest FG, Collins MD (1993) Molecular identification of rRNA group 3 bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test. Proposal for the creation of a new genus Paenibacillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 64:253–260
Cepeljnik T, Lah B, Narat M, Marinsek-Logar R (2007) Adaptation of adhesion test using Caco-2 cells for anaerobic bacterium Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans, a probiotic candidate. Folia Microbiol 52:367–373
Charteris WP, Kelly PM, Morelli L, Collins JK (1998) Development and application of an in vitro methodology to determine the transit tolerance of potentially probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species in the upper human gastrointestinal tract. J Appl Microbiol 84:759–768
Choi SK, Park SY, Kim R, Kim SB, Lee CH, Kim JF, Park SH (2009) Identification of polymyxin synthetase gene cluster of Paenibacillus polymyxa and heterologous expression of the gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 191:3350–3358
Dave RI, Shah NP (1997) Viability of yoghurt and probiotic bacteria in yoghurts made from commercial starter cultures. Int Dairy J 7:31–416
Doyle RJ, Rosenberg M (1995) Measurement of microbial adhesion to hydrophobic substrata. Methods Enzymol 253:542–550
Doyle RJ, Nedjat-Haiem F, Singh JS (1984) Hydrophobic characteristics of Bacillus spores. Cur Microbiol 10:329–333
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. J Appl Bacteriol 66:365–378
Fuller R (1992) History and development of probiotics. In: Fuller R (ed) Probiotics. The scientific basis. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 1–9
Gagnon M, Kheadr E, Le Blay G, Fliss I (2004) In vitro inhibition of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by bifidobacterial strains of human origin. Int J Food Microb 92:69–78
Gibson GR, Wang X (1994) Regulatory effects of bifidobacteria on the growth of other colonic bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 77:412–442
Gilliland SE, Staley TE, Bush LJ (1984) Importance of bile tolerance of Lactobacillus acidophilus used as a dietary adjunct. J Dairy Sci 67:3045–3051
Koshikawa T, Yamazaki M, Yoshimi M, Ogawa S, Yamada A, Watabe K, Tori A (1989) Surface hydrophobicity of spores of Bacillus spp. J Gen Microbiol 135:2717–2722
Kristoffersen SM, Ravnum S, Tourasse NJ, Økstad OA, Kolstø AB, Davies W (2007) Low concentrations of bile salts induce stress responses and reduce motility in Bacillus cereus ATCC 14570. J Appl Bacteriol 189:5302–5313
Landman DC, Georgescu DA, Martin Quale J (2008) Polymyxins revisited. Clinical Microbiol Rev 21:449–465
Lankaputhra EV, Shah NP (1995) Survival of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. in the presence of acid and bile salts. Cult Dairy Prod J 30:2–7
Naghmouchi K, Paterson L, Forster B, McAllister T, Ohene-Adjei S, Drider D, Teather R, Baah J (2011) Paenibacillus polymyxa JB05-01-1 and its perspectives for food conservation and medical applications. Arch Microbiol 3:169–177
Naghmouchi K, Hammami R, Fliss I, Teather R, Baah J, Drider D (2012) Colistin A and colistin B among inhibitory substances of Paenibacillus polymyxa JB05-01-1. Arch Microbiol 194:363–370
Scheldeman P, Goossens K, Rodriguez-Diaz M, Pil A, Goris J, Herman L, De Vos P, Logan NA, Heyndrickx M (2004) Paenibacillus lactis sp. nov., isolated from raw and heat-treated milk. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:885–891
Selim S, Negrel J, Govaerts C, Gianinazzi S, van Tuinen D (2005) Isolation and partial characterization of antagonistic peptides produced by Paenibacillus sp. strain B2 isolated from the sorghum mycorrhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6501–6507
Suskovic J, Brkic B, Matosic S, Maric V (1997) Lactobacillus acidophilus M92 as potential probiotic strain. Milchwissenschaft 52:430–435
Wolf CE, Gibbons WR (1996) Improved method for quantification of the bacteriocin nisin. J Appl Bacteriol 80:453–457
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Best Environmental Technologies Inc., Edmonton, AB, Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghmouchi, K., Baah, J., Cudennec, B. et al. Required characteristics of Paenibacillus polymyxa JB-0501 as potential probiotic. Arch Microbiol 195, 537–543 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-013-0905-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-013-0905-7