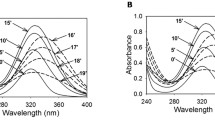
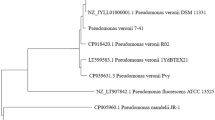
Abstract
Pseudomonas sp. strains C4, C5 and C6 degrade carbaryl (1-naphthyl N-methylcarbamate) via 1-naphthol, 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene, salicylate and gentisate. Carbon source-dependent metabolic studies suggest that enzymes responsible for carbaryl degradation are probably organized into ‘upper’ (carbaryl to salicylate), ‘middle’ (salicylate to gentisate) and ‘lower’ (gentisate to TCA cycle) pathway. Carbaryl and 1-naphthol were found to induce all carbaryl pathway enzymes, while salicylate and gentisate induce middle and lower pathway enzymes. The strains were found to harbor plasmid(s), and carbaryl degradation property was found to be stable. Genes encoding enzymes of the degradative pathway such as 1-naphthol 2-hydroxylase, salicylaldehyde dehydrogenase, salicylate 5-hydroxylase and gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase were amplified from chromosomal DNA of these strains. The gene-specific PCR products were sequenced from strain C6, and phylogenetic tree was constructed. Southern hybridization and PCR analysis using gel eluted DNA as template supported the presence of pathway genes onto the chromosome and not on the plasmid(s).



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MSM:
-
Minimal salt medium
- CH:
-
Carbaryl hydrolase
- 1NH:
-
1-Naphthol 2-hydroxylase
- 12DHNDO:
-
1,2-Dihydroxynaphthalene dioxygenase
- HBHA:
-
trans-o-Hydroxybenzylidenepyruvate hydratase–aldolase
- SALDH:
-
Salicylaldehyde dehydrogenase
- S5H:
-
Salicylate 5-hydroxylase
- GDO:
-
Gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase
- CDO:
-
Catechol dioxygenase
- C12DO:
-
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase
- C23DO:
-
Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase
- S1H:
-
Salicylate 1-hydroxylase
- ANDO:
-
Anthranilate 1,2-dioxygenase
- PPAD:
-
3-Phenylpropionate/cinnamic acid dioxygenase
- RHO:
-
Ring-hydroxylating oxygenases
- BPDO:
-
Biphenyl 2,3-dioxygenase
- PPDO:
-
Phenyl propionate dioxygenase
References
Anderson DG, McKay LL (1983) Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:549–552
Arenghi FL, Berlanda D, Galli E, Sello G, Barbieri P (2001) Organization and regulation of meta cleavage pathway genes for toluene and o-xylene derivative degradation in Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3304–3308
Basu A, Phale PS (2008) Conjugative transfer of preferential utilization of aromatic compounds from Pseudomonas putida CSV86. Biodegradation 19:83–92
Basu A, Dixit SS, Phale PS (2003) Metabolism of benzyl alcohol via catechol ortho-pathway in methylnaphthalene-degrading Pseudomonas putida CSV86. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:579–585
Bollag JM, Liu SY (1972) Fungal degradation of 1-naphthol. Can J Microbiol 18:1113–1117
Bollag JM, Liu KC (1974) Effect of methylendioxyphenyl synergists on metabolism of carbaryl by Aspergillus terreus. Experientia 30:1374–1375
Bollag JM, Czaplicki EJ, Minard RD (1975) Bacterial metabolism of 1-naphthol. J Agric Food Chem 23:85–90
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chae JC, Kim CK, Zylstra GJ (2005) Characterization of two small cryptic plasmids from Pseudomonas sp. strain S-47. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1600–1606
Chakrabarty AM (1972) Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol 112:815–823
Chang HK, Zylstra GJ (1998) Novel organization of the genes for phthalate degradation from Burkholderia cepacia DBO1. J Bacteriol 180:6529–6537
Chapalamadugu S, Chaudhry GR (1991) Hydrolysis of carbaryl by a Pseudomonas sp. and construction of a microbial consortium that completely metabolizes carbaryl. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:744–750
Chen L, Wang W, Sun W, Surette M, Duan K (2010) Characterization of a cryptic plasmid from Pseudomonas sp. and utilization of its temperature-sensitive derivatives for genetic manipulation. Plasmid 64:110–117
De MR, Nagy I, De SA, Pattanapipitpaisal P, Schoofs G, Vanderleyden J (1997) Structural analysis of the 6 kb cryptic plasmid pFAJ2600 from Rhodococcus erythropolis NI86/21 and construction of Escherichia coli-Rhodococcus shuttle vectors. Microbiology 143(Pt 10):3137–3147
Dennis JJ (2005) The evolution of IncP catabolic plasmids. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:291–298
Doddamani HP, Ninnekar HZ (2001) Biodegradation of carbaryl by a Micrococcus species. Curr Microbiol 43:69–73
Dunn NW, Gunsalus IC (1973) Transmissible plasmid coding early enzymes of naphthalene oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 114:974–979
Dunwell JM, Purvis A, Khuri S (2004) Cupins: the most functionally diverse protein superfamily? Phytochemistry 65:7–17
Elespuru R, Lijinsky W, Setlow JK (1974) Nitrosocarbaryl as a potent mutagen of environmental significance. Nature 247:386–387
Eppink MH, Schreuder HA, Van Berkel WJ (1997) Identification of a novel conserved sequence motif in flavoprotein hydroxylases with a putative dual function in FAD/NAD(P)H binding. Protein Sci 6:2454–2458
Fiore MF, Moon DH, Tsai SM, Lee H, Trevors JT (2000) Miniprep DNA isolation from unicellular and filamentous cyanobacteria. J Microbiol Methods 39:159–169
Fujii T, Takeo M, Maeda Y (1997) Plasmid-encoded genes specifying aniline oxidation from Acinetobacter sp. strain YAA. Microbiology 143(Pt 1):93–99
Gaillard M, Vallaeys T, Vorholter FJ, Minoia M, Werlen C, Sentchilo V, Puhler A, van der Meer JR (2006) The clc element of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13, a genomic island with various catabolic properties. J Bacteriol 188:1999–2013
Gotz A, Pukall R, Smit E, Tietze E, Prager R, Tschape H, van Elsas JD, Smalla K (1996) Detection and characterization of broad-host-range plasmids in environmental bacteria by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2621–2628
Grund E, Denecke B, Eichenlaub R (1992) Naphthalene degradation via salicylate and gentisate by Rhodococcus sp. strain B4. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1874–1877
Hansen JB, Olsen RH (1978) Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol 135:227–238
Hashimoto M, Fukui M, Hayano K, Hayatsu M (2002) Nucleotide sequence and genetic structure of a novel carbaryl hydrolase gene (cehA) from Rhizobium sp. strain AC100. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1220–1227
Hayatsu M, Hirano M, Nagata T (1999) Involvement of two plasmids in the degradation of carbaryl by Arthrobacter sp. strain RC100. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1015–1019
Hodkinson B, Lutzoni F (2009) A microbiotic survey of lichen-associated bacteria reveals a new lineage from the Rhizobiales. Symbiosis 49:163–180
Jouanneau Y, Micoud J, Meyer C (2007) Purification and characterization of a three-component salicylate 1-hydroxylase from Sphingomonas sp. strain CHY-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7515–7521
Kado CI, Liu ST (1981) Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol 145:1365–1373
Khan AA, Walia SK (1991) Expression, localization, and functional analysis of polychlorinated biphenyl degradation genes cbpABCD of Pseudomonas putida. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1325–1332
Kojima Y, Fujisawa H, Nakazawa A, Nakazawa T, Kanetsuna F, Taniuchi H, Nozaki M, Hayaishi O (1967) Studies on pyrocatechase. I. Purification and spectral properties. J Biol Chem 242:3270–3278
Krasowiak R, Smalla S, Sokolov S, Kosheleva I, Titok M, Thomas CM (2002) PCR primers for detection and characterization of IncP-9 plasmids. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:217–225
Larkin MJ, Day MJ (1986) The metabolism of carbaryl by three bacterial isolates, Pseudomonas sp. (NCIB 12042 & 12043) and Rhodococcus sp. (NCIB 12038) from garden soil. J Appl Bacteriol 60:233–242
Liu Y, Bollag JM (1971) Metabolism of carbaryl by a soil fungus. J Agric Food Chem 19:487–490
Mesas JM, Rodriguez MC, Alegre MT (2004) Plasmid curing of Oenococcus oeni. Plasmid 51:37–40
Minas W, Gutnick DL (1993) Isolation, characterization, and sequence analysis of cryptic plasmids from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and their use in the construction of Escherichia coli shuttle plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2807–2816
Nozaki M, Ono K, Nakazawa T, Kotani S, Hayaishi O (1968) Metapyrocatechase. II. The role of iron and sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem 243:2682–2690
Obulakondaiah M, Sreenivasulu C, Venkateswarlu K (1993) Nontarget effects of carbaryl and its hydrolysis product, 1-naphthol, towards Anabaena torulosa. Biochem Mol Biol Int 29:703–710
Rajgopal BS, Rao VR, Nagendraappa G, Sethunathan N (1984) Metabolism of carbaryl and carbofuran by soil enrichment and bacterial cultures. Can J Microbiol 30:1458–1466
Rickard RW, Dorough HW (1984) In vivo formation of nitrosocarbamates in the stomach of rats and guinea pigs. J Toxicol Environ Health 14:279–290
Sah S, Phale PS (2011) 1-Naphthol 2-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas sp. strain C6: purification, characterization and chemical modification studies. Biodegradation 22:517–526
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shamsuzzaman KM, Barnsley EA (1974) The regulation of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 60:582–589
Shea TB, Berry ES (1983) Toxicity and intracellular localization of carbaryl and 1-naphthol in cell cultures derived from goldfish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 30:99–104
Sikka HC, Miyazaki S, Lynch RS (1975) Degradation of carbaryl and 1-naphthol by marine microorganisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 13:666–672
Smulders CJ, Bueters TJ, Van Kleef RG, Vijverberg HP (2003) Selective effects of carbamate pesticides on rat neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and rat brain acetylcholinesterase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 193:139–146
Stingley RL, Brezna B, Khan AA, Cerniglia CE (2004) Novel organization of genes in a phthalate degradation operon of Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1. Microbiology 150:3749–3761
Suarez M, Ferrer E, Garrido-Pertierra A, Martin M (1995) Purification and characterization of the 3-hydroxybenzoate 6-hydroxylase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 126:283–290
Sud RK, Sud AK, Gupta KG (1972) Degradation of sevin (1-naphthyl-N-methyl carbamate) by Achromobacter sp. Arch Microbiol 87:353–358
Suemori A, Kurani R, Tomizuka N (1993) Purification and properties of 3 types of monohydroxybenzoate oxygenase from Rhodococcus erythropolis S1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1487–1491
Swetha VP, Phale PS (2005) Metabolism of carbaryl via 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene by soil isolates Pseudomonas sp. strains C4, C5, and C6. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5951–5956
Swetha VP, Basu A, Phale PS (2007) Purification and characterization of 1-naphthol 2-hydroxylase from carbaryl-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strain C4. J Bacteriol 189:2660–2666
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thuring RW, Sanders JP, Borst P (1975) A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem 66:213–220
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2003) Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:503–549
Vivian A (1994) Plasmid expansion? Microbiology 140(Pt 2):213–214
Walker N, Janes NF, Spokes JR, Van Berkum P (1975) Degradation of 1-naphthol by a soil pseudomonad. J Appl Bacteriol 39:281–286
Wheatcroft R, Williams PA (1981) Rapid methods for the study of both stable and unstable plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol 124:433–437
Wilson GD, d’Arcy DM, Cohen GM (1985) Selective toxicity of 1-naphthol to human colorectal tumour tissue. Br J Cancer 51:853–863
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Liu YH (2003) Purification and characterization of a novel carbaryl hydrolase from Aspergillus niger PY168. FEMS Microbiol Lett 228:39–44
Zhao DL, Yu ZC, Li PY, Wu ZY, Chen XL, Shi M, Yu Y, Chen B, Zhou BC, Zhang YZ (2011) Characterization of a cryptic plasmid pSM429 and its application for heterologous expression in psychrophilic Pseudoalteromonas. Microb Cell Fact 10:30
Zhou NY, Al-Dulayymi J, Baird MS, Williams PA (2002) Salicylate 5-hydroxylase from Ralstonia sp. strain U2: a monooxygenase with close relationships to and shared electron transport proteins with naphthalene dioxygenase. J Bacteriol 184:1547–1555
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the research fellowship to RS and VDT from CSIR, Govt. of India and the research grant to PP from DBT, Govt. of India. Thanks to Dr. Smalla K, Institute for biochemistry and plant virology, Braunschweig, Germany, for providing standard plasmids for the incompatibility group classification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Trivedi, V.D. & Phale, P.S. Metabolic regulation and chromosomal localization of carbaryl degradation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strains C4, C5 and C6. Arch Microbiol 195, 521–535 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-013-0903-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-013-0903-9