Abstract
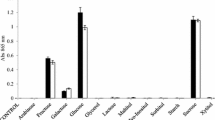
Thirteen pink-pigmented facultative methylotrophic (PPFM) strains isolated from Adyar and Cooum rivers in Chennai and forest soil samples in Tamil Nadu, India, along with Methylobacterium extorquens, M. organophilum, M. gregans, and M. komagatae were screened for phosphate solubilization in plates. P-solubilization index of the PPFMs grown on NBRIP—BPB plates for 7 days ranged from 1.1 to 2.7. The growth of PPFMs in tricalcium phosphate amended media was found directly proportional to the glucose concentration. Higher phosphate solubilization was observed in four strains MSF 32 (415 mg l−l), MDW 80 (301 mg l−l), M. komagatae (279 mg l−l), and MSF 34 (202 mg l−l), after 7 days of incubation. A drop in the media pH from 6.6 to 3.4 was associated with an increase in titratable acidity. Acid phosphatase activity was more pronounced in the culture filtrate than alkaline phosphatase activity. Adherence of phosphate to densely grown bacterial surface was observed under scanning electron microscope after 7-day-old cultures. Biochemical characterization and screening for methanol dehydrogenase gene (mxaF) confirmed the strains as methylotrophs. The mxaF gene sequence from MSF 32 clustered towards M. lusitanum sp. with 99% similarity. This study forms the first detailed report on phosphate solubilization by the PPFMs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH (1994) Phosphates and the utilization of organic phosphorus by Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae. Lett Appl Microbiol 18:294–296
Abd-Alla MH, Omar SA (2001) Survival of rhizobia/bradyrhizobia and rock-phosphate solubilizing fungus Aspergillus niger on various carriers from some agroindustrial wastes and their effects on nodulation and growth of faba bean and soyabean. J Plant Nutr 24:261–272
Achal V, Savant VV, Reddy MS (2007) Phosphate solubilization by a wild type strain and UV-induced mutants of Aspergillus tubingensis. Soil Biol Biochem 39:695–699
Altschul SF, Madden TL, SchaVer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anthony C (1986) Bacterial oxidation of methane and methanol. Adv Microb Physiol 27:113–210
Anthony C, Ghosh M, Blake CCF (1994) The structure and function of methanol dehydrogenase and related PQQ-containing quinoproteins. Biochem J 304:665–674
Antoun HA, Beauchamp CJ, Goussard N, Chabot R, Lalande R (1998) Potential of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium species as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on nonlegumes: effect on radishes (Raphanus sativus L.). Plant Soil 204:57–67
Babenko YS, Tyrygina G, Grigoryev EF, Dolgikh LM, Borisova TI (1984) Biological activity and physiology-biochemical properties of bacteria dissolving phosphates. Microbiology 53:533–539
Bacilio-Jimenez M, Aguilar-Flores S, Ventura-Zapata E, Perez-Campos E, Bouquelet S, Zenteno E (2003) Chemical characterization of root exudates from rice (Oryza sativa) and their effects on the chemotactic response of endophytic bacteria. Plant Soil 249:271–277
Balachandar D, Raja P, Nirmala K, Rithyl TR, Sundaram SP (2008) Impact of transgenic Bt-cotton on the diversity of pink-pigmented facultative methylotrophs. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(10):2087–2095
Banik S, Dey BK (1982) Available phosphate content of an alluvial soil is influenced by inoculation of some isolated phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Plant Soil 69:353–364
Barroso CB, Nahas E (2005) The status of soil phosphate fractions and the ability of fungi: dissolve hardly soluble phosphates. Appl Soil Ecol 29:73–83
Bergey DH, Krieg NE, Holt JG (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology.Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MA
Chabot R, Antoun H, Cescas MP (1993) Stimulation de la croissance du mais et de la laitue romaine par desmicroorganismes dissolvent le phosphore inorganic. Can J Microbiol 39:941–947
Chatli AS, Beri V, Sidhu BS (2008) Isolation and characterisation of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from the cold desert habitat of Salix alba Linn. in trans Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh. Indian J Microbiol 48:267–273
Chen CR, Condron LM, Davis MR, Cherlock RR (2002) Phosphorus dynamics in the rhizosphere of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don.). Soil Biol Biochem 34(4):487–499
Chistoserdova L, Wei Chen S, Lapidus A, Lidstrom ME (2003) Methylotrophy in Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 from a genomic point of view. J Bacteriol 185(10):2980–2987
Chung H, Park M, Madhaiyan M, Seshadri S, Song J, Cho H, Sa T (2005) Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the rhizosphere of crop plants of Korea. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1970–1974
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. American public health association, Baltimore, MA
De Freitas JR, Banerjee NR, Germida JJ (1997) Phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria enhance the growth and yield but not phosphorus uptake of canola (Brassica napus L.). Biol Fertil Soils 24:358–364
Ehrlich HL (1990) Geomicrobiology. Marcel Dekker, New York, Basel
Fasim F, Ahmed N, Parson R, Gadd GM (2002) Solubilization of zinc salts by a bacterium isolated from air environment of a tannery. FEMS Microbiol Lett 213:1–6
Galabova D, Tuleva B, Balasheva M (1993) Phosphatase activity during growth of Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 109(1):45–48
Gallego V, Garcıa MT, Ventosa A (2005) Methylobacterium isbiliense sp. nov: isolated from the drinking water system of Sevilla, Spain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2333–2337
Gallego V, Garcia MT, Ventosa A (2006) Methylobacterium adhaesivum sp. nov: a methylotrophic bacterium isolated from drinking water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:339–342
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulose activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Goldstein AH (1986) Bacterial solubilization of mineral phosphates: historical perspectives and future prospects. Am J Altern Agricult 1:57–65
Goldstein AH, Braverman K, Osorio N (1999) Evidence for mutualism between a plant growing in a phosphate-limited desert environment and a mineral phosphate solubilizing (MPS) rhizobacterium. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:295–300
Green PN (1992) The genus Methylobacterium. In the prokaryotes. Springer, NY
Green PN (2001) Methylobacterium. In the prokaryotes. Springer, NY
Gupta R, Singal R, Shankar A, Kuhad RC, Saxena RK (1994) A modified plate assay for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. J Gen Appl Microbiol 40:255–260
Gyaneshwar P, Kumar GN, Parekh LJ, Poole PS (2002) Role of soil microorganisms in improving P nutrition of plants. Plant Soil 245:83–93
Halder AK, Mishra AK, Bhattacharya P, Chakrabarty PK (1990) Solubilization of rock phosphate by rhizobium and bradyrhizobium. J Gen Appl Microbiol 36:81–92
Halder AK, Mishra AK, Chakraborthy PK (1991) Solubilizing of inorganic phosphates by bradyrhizobium. Indian J Exp Biol 29:28–31
Hamdali H, Smirnov A, Esnault C, Ouhdouch Y, Virolle MJ (2010) Physiological studies and comparative analysis of rock phosphate solubilization abilities of Actinomycetales originating from moroccan phosphate mines and of Streptomyces lividans. Appl Soil Ecol 44(1):24–31
Harrold SA, Tabatabai MA (2006) Release of inorganic phosphorus from soils by low-molecular-weight organic acids. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 37:1233–1245
Horz HP, Yimga MT, Liesack W (2001) Detection of methanotroph diversity on roots of submerged rice plants by molecular retrieval of pmoA, mmoX, mxaF, and 16S rRNA and ribosomal DNA, including pmoA-based terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism profiling. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4177–4185
Illmer P, Schinner F (1992) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by microorganisms isolated from forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 24:389–395
Illmer H, Schinner F (1995) Solubilization of inorganic calcium phosphates solubilization mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 27:257–263
Illmer H, Barbato A, Schinner F (1995) Solubilization of hardly soluble AlPO4 with P-solubilizing microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 27:265–270
Islam MDT, Deora A, Hashidoko Y, Rahman A, Ito T, Tahara S (2007) Isolation and Identification of potential phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the rhizosphere of Oryzae sativa L. cv. BR29 of Bangladesh. Z Natureforsch 62:103–110
Johri JK, Surange S, Nautiyal CS (1999) Occurrence of salt, pH, and temperature-tolerant, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in alkaline soils. Curr Microbiol 39:89–93
Jones DL, Darrah PR (1993) Resorption of organic compounds by roots of zea mays L. and its consequences in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 153:47–59
Juma NG, Tabatabai MA (1988) Phosphatase activity in corn and soybean roots: conditions for assay and effects of metals. Plant Soil 107:39–47
Kato N, Yurimoto H, Thauer RK (2006) The physiological role of the ribulose monophosphate pathway in bacteria and archaea. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:10–21
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2006) Role of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 26:1–15
Kim KY, Jordan D, McDonald GA (1998) Effect of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae on tomato growth and soil microbial activity. Biol Fertil Soils 26:79–87
Kpomblekou A, Tabatabai MA (1994) Effect of organic acids on the release of phosphorus from phosphate rocks. Soil Sci 158:442–448
MacAlister TJ, Irvin RT, Costerton JW (1977) Cell envelope protection of alkaline phosphatase against acid denaturation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 130(1):339–346
Madhaiyan M, Poohguzhali S, Kwon SW, Sa TM (2009) Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae sp. nov: a pink-pigmented, facultative methylotroph from the phyllosphere of rice. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:22–27
Mehta S, Nautiyal CS (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 43:51–56
Murrell JC, Mc Donald IR, Bourne DG (1998) Molecular methods for the study of methanotroph ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:103–114
Nautiyal CS, Bhadauria S, Kumar P, Lal H, Mondal R, Verma D (2000) Stress induced phosphate solubilization in bacteria isolated from alkaline soils. FEMS Microbiol Lett 182:291–296
Ozkanca R, Flint KP (1996) Alkaline phosphatase activity of Escherichia coli starved in sterile lake water microcosms. J Appl Bacteriol 80:252–258
Pal SS (1998) Interaction of an acid tolerant strain of phosphate solubilizing bacteria with a few acid tolerant crops. Plant Soil 198:169–177
Patt TE, Cole GC, Hanson RS (1976) Methylobacterium: a new genus of facultatively methylotrophic bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:226–229
Perez E, Sulbaran M, Ball MM, Yarzabal LA (2007) Isolation and characterization of mineral phosphate solubilizing bacteria naturally colonizing a limonitic crust in the south-eastern Venezuelan region. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2905–2914
Pinenborg JWM, Lie TA, Zehnder AJB (1990) Simplified measurement of soil pH using an agar-contact technique. Plant Soil 126:155–160
Premono Edi M, Moawad MA, Vlek PLG (1996) Effect of phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas putida on the growth of maize and its survival in the rhizosphere. Indones J Crop Sci 11:13–23
Richardson AE, Hadodas PA (1997) Soil isolates of Pseudomonas sp. that utilize inositol phosphates. Can J Microbiol 43:509–516
Rodrıguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339
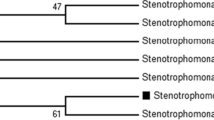
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sawyer J, Creswell J (2000) Integrated crop management. In phosphorus basics. Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
Scheffer F, Schachtschabel P (1988) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde. Enke, Stuttgart
Seshadri S (1995) Phosphate solubilizing fungi from Thanjavur delta, South India. PhD thesis, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, India
Seshadri S, Lakshminarasimhan C (2003) Population dynamics of P-solubilizers in the rhizosphere of major weed species from a tropical delta soil. First Int Meet Microb Phosphate Solub., Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences 102:281–284
Seshadri S, Muthukumarasamy R, Lakshminarasimhan C, Ingacimuthu S (2000) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by Azospirillum halopraeferens. Curr Sci 79(5):565–567
Seshadri S, Ignacimuthu S, Lakshminarsimhan C (2002) Variation in heterotrophic and phosphate solubilizing bacteria from Chennai, southeast coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci 31:69–72
Seshadri S, Ignacimuthu S, Lakshminarasimhan C (2004) Effect of nitrogen and carbon sources on the inorganic phosphate solubilization by different Aspergilus niger strains. Chem Eng Commun 191:1043–1052
Sundara B, Natarajan V, Hari K (2002) Influence of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on the changes in soil available phosphorus and sugarcane and sugar yields. Field Crops Res 77:43–49
Sy A, Giraud E, Jourand P, Garcıa N, Willems A, de Lajudie P, Prin Y, Neyra M, Gillis M, Boivin-Masson C, Dreyfus B (2001) Methylotrophic Methylobacterium bacteria nodulate and fix nitrogen in symbiosis with legumes. J Bacteriol 183:214–220
Tarafdar JC, Bareja M, Panwar J (2003) Efficiency of some phosphatase producing soil fungi. Indian J Microbiol 43:27–32
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Van Wezel GP, Mahr K, Konig M, Traag BA, Pimentel-Schmitt EF, Willimek A, Titgemeyer F (2005) GlcP constitutes the major glucose uptake system of streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 55:624–636
Vassileva M, Vassilev N, Azcon R (1998) Rock phosphate solubilization by Aspergillus niger on olive cake-based medium and its further application in a soil plant system. World J Microbiol Biotech 14:281–284
Vazquez P, Holguin G, Puente ME, Lopez-Cortes A, Bashan Y (2000) Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms associated with the rhizosphere of mangroves in a semiarid coastal lagoon. Biol Fertil Soils 30:460–468
Vessey JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586
Wang X, Sahr F, Xue T, Sun B (2007) Methylobacterium salsuginis sp. nov: isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(8):1699–1703
Watanabe FS, Olsen SR (1965) Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorous in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 29:677–678
Whitelaw MA, Harden TJ, Helyar KR (1999) Phosphate solubilization in solution culture by the soil fungus Penicillium radicum. Soil Biol Biochem 31:655–665
Yi Y, Huang W, Ge Y (2008) Exopolysaccharide: a novel important factor in the microbial dissolution of tricalcium phosphate. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1059–1065
Zhao XR, Lin QM, Li BG (2002) The solubilization of four insoluble phosphates by some microorganisms. Acta Microbiol Sin 42:236–241 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Life Sciences Research Board, DRDO, India, and Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for financial support, Dr. Mary E. Lidstorm, University of Washington, Seattle, for providing the bacterial strain, and Shri AMM Murugappa Chettiar Research Center for providing necessary facilities. The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Gerry Brennan and Ms. Sharon Elizhabeth, Queens University, Belfast, UK, for their help in scanning electron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ursula Priefer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayashree, S., Vadivukkarasi, P., Anand, K. et al. Evaluation of pink-pigmented facultative methylotrophic bacteria for phosphate solubilization. Arch Microbiol 193, 543–552 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-011-0691-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-011-0691-z