Abstract
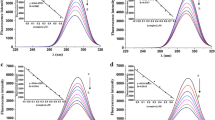
Melanin has been found to interact with a number of molecules including metal ions, antibiotics and proteins. In this study, we showed how melanin from bacteria can interact with double-stranded DNA. Investigation using capillary electrophoresis, various spectroscopic techniques and circular dichroism found that melanin interacts with DNA by intercalating between the base pairs of DNA. And this was further supported by simulating different forms of melanin docking to oligonucleotides. Transmission electron microscopy of recombinant Escherichia coli producing melanin suggested the interaction in vivo. Furthermore, we showed how the cytoplasmic localization of melanin may provide a novel function in inhibiting cellular metabolism using microcalorimetry. The implications of the interaction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes were discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubry AF (2002) Applications of affinity chromatography to the study of drug-melanin binding interactions. J Chromatogr B 768:67–74
Aurstad K, Dahle HK (1972) Fine structure of melanin-producing aeromonads. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol 80:884–890
Bowness JM, Morton RA (1953) The association of zinc and other metals with melanin and a melanin-protein complex. Biochem J 53:620–626
Chang-Ying Y, Yi L, Jun-Cheng Z, Dan Z (2008) Inhibitory effect of copper complex of indomethacin on bacteria studied by microcalorimetry. Biol Trace Elem Res 122:82–88
Cheng J, Moss SC, Eisner M (1994) X-ray characterization of melanins-II. Pigment Cell Res 7:263–273
Claus H, Decker H (2006) Bacterial tyrosinases. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:3–14
Eckhart L, Bach J, Ban J, Tschachler E (2000) Melanin binds reversibly to thermostable DNA polymerase and inhibits its activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271:726–730
Eltsov M, Zuber B (2006) Transmission electron microscopy of the bacterial nucleoid. J Struct Biol 156:246–254
Franzen AJ, Cunha MM, Miranda K, Hentschel J, Plattner H, Da Silva MB, Salgado CG, De Souza W, Rozental S (2008) Ultrastructural characterization of melanosomes of the human pathogenic fungus Fonsecaea pedrosoi. J Struct Biol 162:75–84
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK, Shaw DE, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Geng J, Yu SB, Wan X, Wang XJ, Shen P, Zhou P, Chen XD (2008) Protective action of bacterial melanin against DNA damage in full UV spectrums by a sensitive plasmid-based noncellular system. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:1151–1155
Gilchrest BA, Eller MS (1999) DNA photodamage stimulates melanogenesis and other photoprotective responses. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 4:35–40
Halgren TA (1998) Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J Comput Chem 17:490–519
Horowitz ED, Hud NV (2006) Ethidium and proflavine binding to a 2′, 5′-linked RNA duplex. J Am Chem Soc 128:15380–15381
Kaxiras E, Tsolakidis A, Zonios G, Meng S (2006) Structural model of eumelanin. Phys Rev Lett 97:218102
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer, New York
Lin WP, Lai HL, Liu YL, Chiung YM, Shiau CY, Han JM, Yang CM, Liu YT (2005) Effect of melanin produced by a recombinant Escherichia coli on antibacterial activity of antibiotics. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 38:320–326
Liu Y, Simon JD (2005) Metal–ion interactions and the structural organization of Sepia eumelanin. Pigment Cell Res 18:42–48
Mcilvaine P, Langerman N (1977) A calorimetric investigation of the growth of the luminescent bacteria Beneckea harveyi and Photobacterium leiognathi. Biophys J 17:17–25
Moussa M, Perrier-Cornet M, Gervais P (2007) Damage in Escherichia coli cells treated with a combination of high hydrostatic pressure and subzero temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6508–6518
Mukerji I, Williams AP (2002) UV resonance Raman and circular dichroism studies of a DNA duplex containing an A(3)T(3) tract: evidence for a premelting transition and three-centered H-bonds. Biochemistry 41:69–77
Nosanchuk JD, Casadevall A (2003) The contribution of melanin to microbial pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 5:203–223
Olsthoorn CS, Bostelaar LJ, De Rooij JF, Van Boom JH, Altona C (1981) Circular dichroism study of stacking properties of oligodeoxyadenylates and polydeoxyadenylate. A three-state conformational model. Eur J Biochem 115:309–321
Plonka PM, Grabacka M (2006) Melanin synthesis in microorganisms—biotechnological and medical aspects. Acta Biochim Pol 53:429–443
Price K, Linge C (1999) The presence of melanin in genomic DNA isolated from pigmented cell lines interferes with successful polymerase chain reaction: a solution. Melanoma Res 9:5–9
Riley PA (1997) Melanin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29:1235–1239
Ruming Z, Yi L, Zhixiong X, Ping S, Songsheng Q (2000) A microcalorimetric method for studying the biological effects of La(3+) on Escherichia coli. J Biochem Biophys Methods 46:1–9
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold spring harbor laboratory press, New York
Stark KB, Gallas JM, Zajac GW, Eisner M, Golab JT (2003) Spectroscopic study and simulation from recent structural models for eumelanin: I. Monomer, dimers. J Phys Chem B 107:3061–3067
Tseng HC, Lin CK, Hsu BJ, Leu WM, Lee YH, Chiou SJ, Hu NT, Chen CW (1990) The melanin operon of Streptomyces antibioticus: expression and use as a marker in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 86:123–128
Van Dam L, Levitt MH (2000) BII nucleotides in the B and C forms of natural-sequence polymeric DNA: a new model for the C form of DNA. J Mol Biol 304:541–561
Wan X, Liu HM, Liao Y, Su Y, Geng J, Yang MY, Chen XD, Shen P (2007) Isolation of a novel strain of Aeromonas media producing high levels of DOPA-melanin and assessment of the photoprotective role of the melanin in bioinsecticide applications. J Appl Microbiol 103:2533–2541
Wan X, Chai B, Liao Y, Su Y, Ye T, Shen P, Chen X (2009) Molecular and biochemical characterization of a distinct tyrosinase involved in melanin production from Aeromonas media. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:261–269
Wang Y, Aisen P, Casadevall A (1995) Cryptococcus neoformans melanin and virulence: mechanism of action. Infect Immun 63:3131–3136
Wang G, Aazaz A, Peng Z, Shen P (2000) Cloning and overexpression of a tyrosinase gene mel from Pseudomonas maltophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett 185:23–27
Wolff K (1973) Melanocyte–keratinocyte interactions in vivo: the fate of melanosomes. Yale J Biol Med 46:384–396
Yu SB, Geng J, Zhou P, Feng AR, Chen XD, Hu JM (2007) Analysis of plasmid DNA damage induced by melanin with capillary electrophoresis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 43:816–821
Zhang F, Zhang QQ, Wang WG, Zhu CJ, Wang XL (2007) The application and comparison of several chemometric methods of excitation-emission matrix spectra in studying the interactions of metal complexes with DNA. Anal Chim Acta 599:199–208
Zhou P, Yu S, Liu Z, Hu J, Deng Y (2005) Electrophoretic separation of DNA using a new matrix in uncoated capillaries. J Chromatogr A 1083:173–178
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Xiangdong Gao and Prof. Erfei Bi (University of Pennsylvania) for their help in writing the manuscript. They would also like to thank Prof. Yi Liu and Dr. Barry Wong (Wuhan University, PR China) for their helpful comments on the manuscript. This study was supported by National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (NSFC Grants No. 20875073)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Jing Geng and Peng Yuan made equal contribution to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, J., Yuan, P., Shao, C. et al. Bacterial melanin interacts with double-stranded DNA with high affinity and may inhibit cell metabolism in vivo. Arch Microbiol 192, 321–329 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0560-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0560-1