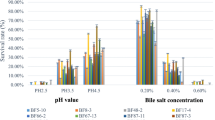
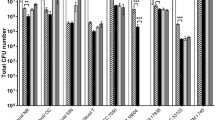
Abstract
The present work investigates some probiotic properties of four different microorganisms (Bifidobacterium animalis var. lactis BB-12, Escherichia coli EMO, Lactobacillus casei and Saccharomyces boulardii). In vitro and in vivo tests were carried out to compare cell wall hydrophobicity, production of antagonistic substances, survival capacity in the gastrointestinal tract of germ-free mice without pathological consequence, and immune modulation by stimulation of Küpffer cells, intestinal sIgA and IL-10 levels. In vitro antagonism against pathogenic bacteria and yeast was only observed for the probiotic bacteria B. animalis and L. casei. The hydrophobic property of the cell wall was higher for B. animalis and E. coli EMO, and this property could be responsible for a better ability to colonize the gastrointestinal tract of germ-free mice. Higher levels of sIgA were observed mainly for S. boulardii, followed by E. coli EMO and B. animalis, and only S. boulardii induced a significant higher level of IL-10. In conclusion, for a probiotic use, S. boulardii presented better characteristics in terms of immunomodulation, and B. animalis and L. casei for antagonistic substance production. The knowledge of the different probiotic properties could be used to choice the better microorganism depending on the therapeutic or prophylactic application.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolou E, Kirjavainen PV, Saxelin M, Rautelin H, Valtonen V, Salminen S, Ouwehand AC (2001) Good adhesion properties of probiotics: a potential risk for bacteremia? FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 31:35–39
Bellon-Fontaine MN, Rault J, van Oss CJ (1996) Microbial adhesion to solvents: a novel method to determine the electron-donor/electron acceptor or Lewis acid-base properties of microbial-cells. Colloids Surf 7:47–53
Berg RD (1995) Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Trends Microbiol 3:149–154
Brady LJ, Gallaher DD, Busta FF (2000) The role of probiotic cultures in the prevention of colon cancer. J Nutr 130:410–414
Brugier S, Patte F (1975) Antagonisme in vitro entre l’ultra-levure et différent germes bactériens. Med Paris 45:3–8
Cremonini F, Di Caro S, Nista EC, Bartolozzi F, Capelli G, Gasbarrini G, Gasbarrini A (2002) Meta-analysis: the effect of probiotic administration on antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1461–1467
Del Re B, Sgorbati B, Miglioli M, Palenzona D (2000) Adhesion, autoaggregation and hydrophobicity of 13 strains of Bifidobacterium longum. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:438–442
Duval-Iflah Y, Raibaud P, Rousseau M (1981) Antagonisms among isogenic strains of Escherichia coli in the digestive tracts of gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun 34:957–969
Ehrmann MA, Kurzak P, Bauer J, Vogel RF (2002) Characterization of lactobacilli towards their use as probiotic adjuncts in poultry. J Appl Microbiol 92:966–975
Famularo G, De Simone C, Pandey V, Sahu AR, Minisola G (2005) Probiotic lactobacilli: an innovative tool to correct the malabsorption syndrome of vegetarians? Med Hypotheses 65:1132–1135
FAO/WHO report (2002) Food and Agricultural Organization/World Health Organization Working Group. Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food, London, Ontario, Canada, April 30 and May 1
Figueiredo PP, Vieira EC, Nicoli JR, Nardi RD, Raibaud P, Duval-Iflah Y, Penna FJ (2001) Influence of oral inoculation with plasmid-free human Escherichia coli on the frequency of diarrhea during the first year of life in human newborns. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 33:70–74
Gilliland SE, Walker DK (1990) Factors to consider when selecting a culture of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a dietary adjunct to produce a hypocholesterolemic effect in humans. J Dairy Sci 73:905–911
Gomes DA, Souza AML, Lopes RV, Nunes AC, Nicoli J (2006) Comparison of antagonistic ability against enteropathogens by Gram positive and Gram negative anaerobic dominant components of the human fecal microbiota. Folia Microbiol 51:141–145
Gómez-Zavaglia A, Kociubinsky G, Pérez P, Disalvo E, De Antoni GL (2002) Effect of bile on the lipid composition and surface properties of bifidobacteria. J Appl Microbiol 93:794–799
Gregory SH, Wing EJ (2002) Neutrophil-Küpffer cell interaction: a critical component of host defenses to systemic bacterial infections. J Leukoc Biol 72:239–248
Gregory SH, Sagnimeni AJ, Wing EJ (1996) Bacteria in the bloodstream are trapped in the liver and killed by immigrating neutrophils. J Immunol 157:2514–2520
Grimbaldeston M, Nakae S, Kalesnikoff J, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2007) Mast cell-derived interleukin 10 limits skin pathology in contact dermatitis and chronic irradiation with ultraviolet B. Nat Immunol 8:1095–1104
Guyonnet D, Chassany O, Ducrotte P, Picard C, Mouret M, Mercier CH, Matuchansky C (2007) Effect of a fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium animalis DN-173 010 on the health-related quality of life and symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome in adults in primary care: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26:475–486
Hajishengallis G, Nikolova E, Russel MW (1992) Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite by human secretory immunoglobulin A antibodies to the cell surface protein antigen I/II: reversal by IgA 1 protease cleavage. Infect Immun 60:5057–5064
Hamilton-Miller JM (2003) The role of probiotics in the treatment and prevention of Helicobacter pylori infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents 22:360–366
Hirakata Y, Tomono K, Tateda K, Matsumoto T, Furuya N, Shimoguchi K, Kaku M, Yamaguchi K (1991) Role of bacterial association with Küpffer cells in occurrence of endogenous systemic bacteremia. Infect Immun 59:289–294
Kirjavainen PV, Salminen SJ, Isolauri E (2003) Probiotic bacteria in the management of atopic disease: underscoring the importance of viability. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 36:223–227
Martins FS, Nardi RMD, Arantes RME, Rosa CA, Neves MJ, Nicoli JR (2005) Screening of yeast as probiotic based on capacities to colonize the gastrointestinal tract and to protect against enteropathogen challenge in mice. J Gen Appl Microbiol 51:83–92
Martins FS, Rodrigues ACP, Tiago FCP, Penna FJ, Rosa CA, Arantes RME, Nardi RMD, Neves MJ, Nicoli JR (2007) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain 905 reduces the translocation of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and stimulates the immune system in gnotobiotic and conventional mice. J Med Microbiol 56:352–359
Mengheri E (2008) Health, probiotics, and inflammation. J Clin Gastroenterol 42:177–178
Miettinen M, Vuopio-Varkila J, Varkila K (1996) Production of human tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10 is induced by lactic acid bacteria. Infect Immun 64:5403–5405
Morelli L (2007) In vitro assessment of probiotic bacteria: From survival to functionality. Int Dairy J 17:1278–1283
National Research Council (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Neumann E, Oliveira MAP, Cabral CM, Moura LN, Nicoli JR, Vieira EC, Cara DC, Podoprigora GI, Vieira LQ (1998) Monoassociation with Lactobacillus acidophilus UFV-H2B20 stimulates the phagocytic system of germ free mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 31:1565–1573
Ouwehand AC, Kirjavainen PV, Grönlund MM, Isolauri E, Salminen SJ (1999) Adhesion of probiotic micro-organisms to intestinal mucus. Int Dairy J 9:623–630
Pérez P, Minaard Y, Disalvo E, De Antoni G (1998) Surface properties of bifidobacterial strains of human origin. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:21–26
Ramaré F, Nicoli JR, Dabard J, Corring T, Ladire M, Gueugneau AM, Raibaud P (1993) Trypsin-dependent production of an antibacterial substance by a human Peptostreptococcus strain in gnotobiotic rats and in vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2876–2883
Reid G, Jass J, Sebulsky MT, McCormick JK (2003) Potential uses of probiotics in clinical practice. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:658–672
Rodrigues ACP, Nardi RM, Bambirra EA, Vieira EC, Nicoli JR (1996) Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii against experimental oral infection with Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri in conventional and gnotobiotic mice. J Appl Bacteriol 81:251–256
Rodrigues AC, Cara DC, Fretez SHGG, Cunha FQ, Vieira EC, Nicoli JR, Vieira LQ (2000) Saccharomyces boulardii stimulates sIgA production and the phagocytic system of gnotobiotic mice. J Appl Microbiol 89:404–414
Sanders ME (2000) Considerations for use of probiotic bacteria to modulate human health. J Nutr 130:384–390
Shortt C (1999) The probiotic century: historical and current perspectives. Trends Food Sci Technol 10:411–417
Silva AM, Barbosa FHF, Duarte R, Vieira LQ, Nicoli JR (2002) Influence of oral treatment with Bifidobacterium Bb12 and Bb46 on Salmonella typhimurium translocation and clearance of Escherichia coli in gnotobiotic and conventional mice. Microecol Ther 29:179–184
Souza DG, Vieira AT, Soares AC, Pinho V, Nicoli JR, Vieira LQ, Teixeira MM (2004) The essential role of the intestinal microbiota in facilitating acute inflammatory responses. J Immunol 173:4137–4146
Tagg JR, Dajani AS, Wannamaker LW (1976) Bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 40:722–756
Tannock G (2005) Probiotics and prebiotics: scientific aspects, 1st edn. Caister Academic Press, Norwich
Vinderola CG, Medici M, Perdigón G (2004) Relationship between interaction sites in the gut, hydrophobicity, mucosal immunomodulating capacities and cell wall protein profiles in indigenous and exogenous bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 96:230–243
Wagner RD (2008) Effects of microbiota on GI health: gnotobiotic research. Adv Exp Med Biol 635:41–56
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants and fellowships from the Conselho Nacional do Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG). The authors are grateful to Bernardo B. de Paula for valuable technical help and Antônio M. Vaz for animal care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, F.S., Silva, A.A., Vieira, A.T. et al. Comparative study of Bifidobacterium animalis, Escherichia coli, Lactobacillus casei and Saccharomyces boulardii probiotic properties. Arch Microbiol 191, 623–630 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0491-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0491-x