Abstract
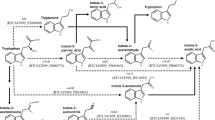
We introduced into Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae LPR1105 a new pathway for the biosynthesis of the auxin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), under the control of a stationary phase-activated promoter active both in free-living bacteria and bacteroids. The newly introduced genes are the iaaM gene from Pseudomonas savastanoi and the tms2 gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Free-living bacteria harbouring the promoter-iaaMtms2 construct release into the growth medium 14-fold more IAA than the wild-type parental strain. This IAA overproducing R. l. viciae, the RD20 strain, elicits the development of vetch root nodules containing up to 60-fold more IAA than nodules infected by the wild-type strain LPR1105. Vetch root nodules derived from RD20 are fewer in number per plant, heavier in terms of dry weight and show an enlarged and more active meristem. A significant increase in acetylene reduction activity was measured in nodules elicited in vetch by RD20.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez R, Nissen SJ, Sutter EG (1989) Relationship between indole-3-acetic acid levels in apple (Malus pumila Mill) rootstocks cultured in vitro and adventitious root formation in the presence of indole-3-butyric acid. Plant Physiol 89:439–443
Azam F, Farooq S (2003) An appraisal of methods for measuring symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legumes. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1631–1640
Badenoch-Jones J, Rolfe BG, Letham DS (1983) Phytohormones, Rhizobium mutants, and nodulation in legumes auxin metabolism in effective and ineffective pea root nodules. Plant Physiol 73(2):347–352
Bar T, Okon Y (1992) Induction of indole-3-acetic acid synthesis and possible toxicity of tryptophan in Azospirillum brasilense Sp7. Symbiosis 13:191–198
Bar T, Okon Y (1993) Tryptophan conversion to indole-3-acetic acid via indole-3-acetamide in Azospirillum brasilense Sp7. Can J Microbiol 39:81–86
Bianco C, Imperlini E, Calogero R, Senatore B, Amoresano A, Carpentieri A, Pucci P, Defez R (2006a) Indole-3-acetic acid improves Escherichia coli’s defences to stress. Arch Microbiol 185:373–382. doi:10.1007/s00203-006-0103-y
Bianco C, Imperlini E, Calogero R, Senatore B, Pucci P, Defez R (2006b) Indole-3-acetic acid regulates the central metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 152:2421–2431. doi:10.1099/mic.0.28765-0
Boot KJM, van Brussel AAN, Tak T., Spaink HP, Kijne JW (1999) Lipochitin oligosaccharides from Rhizobium leguminosarum bv viciae reduce auxin transport capacity in Vicia sativa subsp. nigra roots. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:839–844. doi:10.1094/MPMI.1999.12.10.839
Brill WJ (1977) Biology of nitrogen fixation. Sci Am 236:68–81
Burdman S, Vedder D, German M, Itzigsohn R, Kigel J, Jurkevitch E, Okon Y (1997) Legume crop yield promotion by inoculation with Azospirillum. In: Elmerich C, Kondorosi A, Newton WE (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation for the 21st Century. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Camerini S, Senatore B, Imperlini E, Bianco C, Miraglia E, Lonardo E, Defez R (2004) Improve legume yield by phytohormone release from soil bacteria. In: European Association for Grain Legume Research (eds) Legumes for the benefit of agriculture. Nutrition and the environment. AEP, Dijon, pp 127–128
Cooper JB, Long SR (1994) Morphogenetic rescue of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation mutants by trans-zeatin secretion. Plant Cell 6:215–225
Darwin C, Darwin F (1880) The power of movement in plants. John Murray, London
De Melo MP, Pithon-Curi TC, Curi R (2004) Indole-3-acetic acid increases glutamine utilization by high peroxidase activity-presenting leucocytes. Life Sci 75:1713–1725. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.03.021
Defez R (2006) Patent holder: CNR deposited on 14/06/2005, Italian Patent Office: n. RM2005A000308. PCT extension n. PCT/IT2006/000449. Method for increasing the survival of bacterial strains of the Rhizobium genus
Defez R, Spena A (1998) Deposited the 09/11/1998 at the European Patent Office, Munich, Germany, EPO application No. EP98/830674.2. PCT extension no. PCT24190. Method to control gene expression in bacteria, namely Rhizobiaceae, to improve root nodule development, nitrogen fixation and plant biomass production
Ernstsen A, Sandberg G, Crozier A, Wheeler CT (1987) Endogenous indoles and biosynthesis and metabolism of indole-3-acetic acid in cultures of Rhizobium phaseoli. Planta 171:422–428. doi:10.1007/BF00398689
Fang Y, Hirsch AM (1998) Studying early nodulin gene ENOD40 expression and induction by nodulation factor and cytokinin in alfalfa. Plant Physiol 116:53–68
Fedorova E, Redondo FJ, Koshiba T, Pueyo JJ, de Felipe MR, Lucas MM (2005) Aldehyde oxidase (AO) in the root nodules of Lupinus albus and Medicago truncatula: identification of AO in meristematic and infection zones. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:405–413. doi:10.1094/MPMI-18-0405
Gage DJ, Bobo T, Long SR (1996) Use of green fluorescent protein to visualize the early events of symbiosis between Rhizobium meliloti and alfaalfa (Medicago sativa). J Bacteriol 178:7159–7166
Gleason C, Chaudhuri S, Yang T, Munoz A, Poovaiah BW, Oldroyd GE (2006) Nodulation independent of rhizobia induced by a calcium-activated kinase lacking autoinhibition. Nature 441:1149–1152. doi:10.1038/nature0481
Gonzalez-Rizzo S, Crespi M, Frugier F (2006) The Medicago truncatula CRE1 cytokinin receptor regulates lateral root development and early symbiotic interaction with Sinorhizobium meliloti. Plant Cell 18:2680–2693
Hardy RWF, Burns RC, Holston RD (1973) Applications of the acetylene reduction assay for measurement of nitrogen fixation. Soil Biol Biochem 5:47–81. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2494.1976.tb01112.x
Hirsch A (1992) Developmental biology of legume nodulation. New Phytol 122:211–237
Hirsch AM, Fang Y (1994) Plant hormones and nodulation: what’s the connection? Plant Mol Biol 26:5–9. doi:10.1007/BF00039514
Hirsch AM, Bhuvaneswari TV, Torrey JG, Bisseling T (1989) Early nodulin genes are induced in alfalfa root outgrowths elicited by auxin transport inhibitors. Proc Acad Sci USA 86:1244–1248. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.4.1244
Hirsch AM, Fang Y, Asad S, Kapulnik Y (1997) The role of phytohormones in plant-microbe symbioses. Plant Soil 194:171–184. doi:10.1023/A:1004292020902
Hooykaas PJJ, Clapwicjk PM, Nuti MP, Schilperoort RA, Roersch A (1977) Transfer of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid to avirulent Agrobacteria and to Rhizobium ex-planta. J Gen Microbiol 98:477–484
Hunter WJ (1987a) Indole-3-acetic acid production by bacteroids from soybean root nodules. Physiol Plant 76:31–36. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1989.tb05448.x
Hunter WJ (1987b) Influence of 5-methyltryptophan-resistant Bradyrhizobium japonicum on soybean root nodule indole-3-acetic-acid content. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1051–1055
Jefferson R (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405. doi:10.1007/BF02667740
Jensen HL (1942) Nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants. General characters of root-nodule bacteria isolated from species of Medicago and Trifolium. Aust Proc Linn Soc 66:98–108
Kaneshiro T, Kwolek WF (1985) Stimulated nodulation of soybeans by Rhizobium japonicum mutant (B-14075) that catabolizes the conversion of tryptophan to indol-3yl-acetic acid. Plant Sci 42:141–146. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(85) 90119-0
Kittel BL, Helinski DR, Ditta GS (1989) Aromatic aminotransferase activity and indoleacetic acid production in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 171:5458–5466. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.01.047
Klee H, Montoya A, Horodyski F, Lichtenstein C, Garfinkel D, Fuller S, Flores C, Peschon J, Nester E, Gordon M (1984) Nucleotide sequence of the tms genes of the pTiA6NC octopine Ti plasmid: two gene products involved in plant tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1728–1732
Laguerre G, Depret G, Bourionand V, Duc G (2007) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae genotypes interact with pea plants in developmental responses of nodules, roots and shoots. New Phytol 176(3):680–690. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02212.x
Lambrecht M, Okon Y, Vande Broek A, Vanderleyden J (2000) Indole-3-acetic acid: a reciprocal signalling molecule in bacteria-plant interactions. Trends Microbiol 8:298–300. doi:10.1016/S0966-842X(00) 01732-7
Lohar DP, Schaff JE, Laskey JG, Kieber JJ, Bilyeu KD, Bird DM (2004) Cytokinins play opposite roles in lateral root formation, and nematode and Rhizobial symbioses. Plant J 38:203–214. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02038.x
Magrelli A, Langenkemper K, Dehio C, Schell J, Spena A (1994) Splicing of the rolA transcript of Agrobacterium rhizogenes in Arabidopsis. Science 266:1986–1988. doi:10.1126/science.7528444
Mathesius U, Schlaman HM, Spaink HP, Sautter C, Rolfe BG, Djordjevic MA (1998) Auxin transport inhibition precedes root nodule formation in white clover roots and is regulated by flavonoids and derivatives of chitin oligosaccharides. Plant J 14:23–34. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00090.x
Noel KD, Sanchez A, Fernandez L, Leemans J, Cevallos MA (1984) Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 interactions. J Bacteriol 158:148–155
Normanly J, Bartel B (1999) Redundancy as a way of life—IAA metabolism. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:207–213. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(99) 80037-5
Ona O, Smets I, Gysegom P, Bernaerts K, Van Impe J, Prinsen E, Vanderleyden J (2003) The effect of pH on indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) biosynthesis of Azospirillum brasilense Sp7. Symbiosis 35:199–208
Pandolfini T, Storlazzi A, Calabria E, Defez R, Spena A (2000) The spliceosomal intron of the rolA gene of Agrobacterium rhizogenes is a prokaryotic promoter. Mol Microbiol 35:1326–1334. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01810.x
Pandolfini T, Rotino GL, Camerini S, Defez R, Spena A (2002) Optimisation of transgene action at the post-transcriptional level: high quality parthenocarpic fruits in industrial tomatoes. BMC Biotechnology 2:1. Online at http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6750/2/1/ doi:10.1186/1472-6750-2-1
Pii Y, Crimi M, Cremonese G, Spena A, Pandolfini T (2007) Auxin and nitric oxide control indeterminate nodule formation. BMC Plant Biol 7:21. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-7-21
Prinsen E, Costacurta A, Michiels K, Vanderleyden J, Van Onckelen H (1993) Azospirillum brasilense indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis: evidence for a non-tryptophan dependent pathway. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 6:609–615. doi:10.1094/MPMI-6-609
Remans R, Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J (2006) Auxin signaling in plant defense. Science 313:171. doi:10.1126/science.313.5784.171a
Sekine M, Watanabe K, Shono K (1989) Molecular cloning of a gene for indol-3-acetamide hydrolase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol 171:1718–1724
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072
Stougaard J (2000) Regulators and regulation of legume root nodule development. Plant Physiol 124:531–540
Szeto WW, Nixon BT, Ronson CW, Ausubel FM (1987) Identification and characterization of the Rhizobium meliloti ntrC gene: R. meliloti has separate regulatory pathways for activation of nitrogen fixation genes in free-living and symbiotic cells. J Bacteriol 169:1423–1432
Taller BJ, Sturtevant DB (1991) Cytokinin production by rhizobia. In: Hennecke H, Verma DPS (eds) Advances in molecular genetics of plant-microbe interactions, vol 1. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 215–221
Theunis M, Kobayashi H, Broughton WJ, Prinsen E (2004) Flavonoids, NodD1, NodD2, and nod-box NB15 modulate expression of the y4wEFG locus that is required for indole-3-acetic acid synthesis in Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:1153–1161
Thimann KV (1936) On the physiology of the formation of nodules on legume roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 22:511–514
Tirichine L, Imaizumi-Anraku H, Yoshida S, Murakami Y, Madsen LH, Miwa H, Nakagawa T, Sandal N, Albrektsen AS, Kawaguchi M, Downie A, Sato S, Tabata S, Kouchi H, Parniske M, Kawasaki S, Stougaard J (2006) Deregulation of a Ca21/calmodulin-dependent kinase leads to spontaneous nodule development. Nature 441:1153–1156. doi:10.1038/nature04862
Truchet G, Barker DG, Camut S, de Billy F, Vasse J, Huguet T (1989) Alfalfa nodulation in the absence of Rhizobium. Mol Gen Genet 219:65–68. doi:10.1007/BF00261158
Vande Broek A, Gysegom P, Ona O, Hendrickx N, Prinsen E, Van Impe J, Vanderleyden J (2005) Transcriptional analysis of the Azospirillum brasilense indole-3-pyruvate decarboxylase gene and identification of a cis-acting sequence involved in auxin responsive expression. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:311–323. doi:10.1094/MPMI-18-0311
Vanderleyden J (2006) 7th European Nitrogen Fixation Conference Aarhus, Denmark
Varma Penmetsa RJA, Frugoli L, Smith S, Long SR, Cook DR (2003) Dual genetic pathways controlling nodule number in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 131:998–1008. doi:10.1104/pp.015677
Vasse J, de Billy F, Camut S, Truchet G (1990) Correlation between ultrastructural differentiation of bacteroids and nitrogen fixation in alfalfa nodules. J Bacteriol 172:4295–4306
Went FW (1935) Auxin, the plant growth hormone. Bot Rev 1:162–182
Yamada T, Curtis JP, Brooks B, Kosuge T (1985) Nucleotide sequences of the Pseudomonas savastanoi indoleacetic acid genes show homology with Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6522–6526
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the European Union INCO-DEV SONGLINES grant, project ICA4-CT-2001-10059 and by Italian MIUR, project FIRB RBNE0118BHE. We thank C. Sole (in memory) for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ursula Priefer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camerini, S., Senatore, B., Lonardo, E. et al. Introduction of a novel pathway for IAA biosynthesis to rhizobia alters vetch root nodule development. Arch Microbiol 190, 67–77 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0365-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-008-0365-7