Abstract
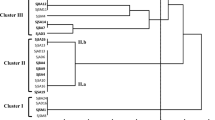
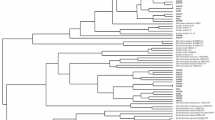
A total of 63 bacterial strains were isolated from root nodules of Kummerowia striata and K. stipulacea grown in different geographic regions of China. These bacteria could be divided into fast-growing (FG) rhizobia and slow-growing (SG) rhizobia according to their growth rate. Genetic diversity and taxonomic relationships among these rhizobia were revealed by PCR-based 16 S rDNA RFLP and sequencing, 16 S-IGS RFLP, SDS-PAGE of whole cell soluble proteins, BOX-PCR and symbiotic gene (nifH/nodC) analyses. The symbiotic FG strains were mainly isolated from temperate regions and they were identified as four genomic species in Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium meliloti based on the consensus of grouping results. The SG strains were classified as five genomic species within Bradyrhizobium and they were mainly isolated fron the subtropic and tropical regions. The phylogenetic analyses of nifH and nodC genes showed relationships similar to that of 16 S rDNA but the symbiotic genes of Bradyrhizobium strains isolated from Kummerowia were distinct from those isolated from Arachis and soybean. These results offered evidence for rhizobial biogeography and demonstrated that the Kummerowia-nodulating ability might have evolved independently in different regions in association with distinctive genomic species of rhizobia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaiotta G, Moschetti G, Aponte M, Villani F, Coppola S, Deiana P, Catzeddu P (1998) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and amplified ribosomal DNA spacer polymorphism: powerful methods to differentiate Streptococcus thermophilus strains. J Appl Microbiol 85:25–36
Beyhaut E, Tlusty B, van Berkum P, Graham PH (2006) Rhizobium giardinii is the microsymbiont of Illinois bundleflower (Desmanthus illinoensis (Michx.) Macmillan) in midwestern prairies. Can J Microbiol 52:903–907
Chen WX, Yan GH, Li JL (1988) Numerical taxonomic study of fast-growing soybean rhizobia and a proposal that Rhizobium fredii be assigned to Sinorhizobium gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:392–397
Chen WM, Laevens S, Lee TM, Coenye T, de Vos P, Mergeay M, Vandamme P (2001) Ralstonia taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa species and sputum of a cystic fibrosis patient. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1729–1735
Chen WM, James EK, Prescott AR, Kierans M, Sprent JI (2003) Nodulation of Mimosa spp. by the beta-proteobacterium Ralstonia taiwanensis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:1051–1061
Cilia V, Lafay B, Christen R (1996) Sequence heterogeneities among 16S ribosomal RNA sequences and their effect on phylogenetic analyses at the species level. Mol Biol Evol 13:451–461
De Bruijn FJ (1992) Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2180–2187
De Lajudie P, Lauren-Fulele E, Willems A, Torck U, Coopman R, Collins MD, Kersters K, Dreyfus B, Gillis M (1998) Allorhizobium undicola gen. Nov., sp. Nov., nitrogen-fixing bacteria that efficiently nodulate Neptunia natans in Senegal. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:1277–1290
De Lajudie P, Willems A, Nick G, Mohamed TS, Torck U, Filali-Maltouf A, Kersters K, Dreyfus B, Lindström K, Gillis M (1999) Agrobacterium bv. 1 strains isolated from nodules of tropical legumes. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:119–132
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Dreyfus B, Garcia JL, Gillis M (1988) Characterization of Azorhizobium caulinodans gen. Nov., sp. Nov., a stem-nodulating nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from Sesbania rostrata. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:89–98
Duzan HM, Zhou X, Souleimanov A, Smith DL (2004) Perception of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Nod factor by soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] root hairs under abiotic stress conditions. J Exp Bot. 55:2641–2646
Farrand SK, van Berkum PB, Oger P (2003) Agrobacterium is a definable genus of the family Rhizobiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1681–1687
Gao JL, Sun JG, Li Y, Wang ET, Chen WX (1994) Numerical taxonomy and deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness of tropical rhizibia isolated from Hainan. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:151–158
Gao JL, Turner SL, Kan FL, Wang ET, Tan ZY, Qiu YH, Gu J, Terefework Z, Young JPW, Lindström K, Chen WX (2004) Mesorhizobium septentrionale sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium temperatum sp. nov., isolated from Astragalus adsurgens growing in the northern regions of China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2003–2012
Han SZ, Wang ET, Chen WX (2005) Diverse bacteria isolated from root nodules of Phaseolus vulgaris and species within the genera Campylotropis and Cassia grown in China. Syst Appl Microbiol. 28:265–276
Haukka K, Lindström K, Young JPW (1996) Diversity of partial 16 S rRNA sequences among and within strains of African rhizobia isolated from Acacia and Prosopis. Syst Appl Microbiol 19:352–359
Haukka K, Lindström K, Young JPW (1998) Three phylogenetic groups of nodA and nifH genes in Sinorhizobium and Mesorhizobium isolated from leguminous trees growing in Africa and Latin America. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:419–426
Jarvis BDW, Van Berkum P, Chen WX, Nour SM, Fernandez MP, Cleyet-Marel JC, Gillis M (1997) Transfer of Rhizobium loti, Rhizobium huakuii, Rhizobium ciceri, Rhizobium mediterraneum, and Rhizobium tianshanense to Mesorhizobium gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:895–898
Jordan DC (1982) Transfer of Rhizobium japonicum Buchanan 1980 to Bradyrhizobium gen. Nov., a genus of slow-growing, root nodule bacteria from leguminous plants. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:136–139
Jordan DC (1984) Family III. Rhizobiaceae Conn 1938, 321AL. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 234–256
Jourand P, Giraud E, Béna G, Sy A, Willems A, Gillis M, de Lajudie P, Dreyfus B (2004) Methylobacterium nodulans sp. nov., for a group of aerobic, facultatively methylotrophic, legume root-nodule-forming and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2269–2273
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA 3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laguerre G, Allard MR, Revoy F, Amarger N (1994) Rapid identification of rhizobia by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16 S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:56–63
Laguerre G, Nour SM, Macheret V, Sanjuan JJ, Drouin P, Amarger N (2001) Classification of rhizobia based on nodC and nifH gene analysis reveals a close phylogenetic relationship among Phaseolus vulgaris symbionts. Microbiology 147:981–993
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of DNA from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Mhamdi R, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Tiwari R, Aouani ME (2005) Colonization of Phaseolus vulgaris nodules by Agrobacterium-like strains. Can J Microbiol 51:105–111
Mnasri B, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Aouani ME, Mhamdi R (2007) Salt-tolerant rhizobia isolated from a Tunisian oasis that are highly effective for symbiotic N(2)-fixation with Phaseolus vulgaris constitute a novel biovar (bv. mediterranense) of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Arch Microbiol 187:79–85
Moulin L, Munive A, Dreyfus B, Boivin-Masson C (2000) Nodulation of legumes by members of the beta-subclass of Proteobacteria. Nature 411:948–950
Nick G, de Lajudie P, Eardly BD, Suomalainen S, Paulin L, Zhang XP, Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal w: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Nick G, Rasanen LA, de Lajudie P, Gillis M, Lindström K (1999) Genomic screening of rhizobia isolated from root nodules of tropical leguminous trees using DNA–DNA dot-blot hybridization and rep-PCR. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:287–299
Noel KD, Brill WJ (1980) Diversity and dynamics of indigenous Rhizobium japonicum populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:931–938
Ormeno-Orrillo E, Vinuesa P, Zuniga-Dávila D, Martínez-Romero E (2006) Molecular diversity of native bradyrhizobia isolated from Lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) in Peru. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:253–262
Parker MA (2003) Genetic markers for analysing symbiotic relationships and lateral gene transfer in Neotropical bradyrhizobia. Mol Ecol 12:2447–2455
Perret X, Staehelin C, Broughton WJ (2000) Molecular basis of symbiotic promiscuity. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:180–201
Quan ZX, Bae HS, Baek JH, Chen WF, Im WT, Lee ST (2005) Rhizobium daejeonense sp. nov. isolated from a cyanide treatment bioreactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2543–2549
Rasolomampianina R, Bailly X, Fetiarison R, Dreyfus B, de lajudie P, Avarre JC (2005) Nitrogen-fixing nodules from rose wood legume trees (Dalbergia spp.) endemic to Madagascar host seven different genera belonging to alpha- and beta-Proteobacteria. Mol Ecol 14:4135–4146
Rivas R, Willems A, Subba-Rao NS, Mateos PF, Dazzo FB, Kroppenstedt RM, Martínez-Molina E, Gillis M, Velázquez E (2003) Description of Devosia neptuniae sp. nov. that nodulates and fixes nitrogen in symbiosis with Neptunia natans, an aquatic legume from India. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:47–53
Rivas R, Willems A, Palomo JL, Garca-Benavides P (2004) Bradyrhizobium betae sp. nov., isolated from roots of Beta vulgaris affected by tumour-like deformations. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1271–1275
Sammons DW, Adams LD, Nishizawa EE (1981) Ultrasensitive silver based color staining of polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 2:135
Sarita S, Sharma PK, Priefer UB, Prell J (2005) Direct amplification of rhizobial nodC sequences from soil total DNA and comparison to nodC diversity of root nodule isolates. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:1–11
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy—the principles and practices of numerical classification. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco
Sy A, Giraud E, Jourand P, Garcia N, Willems A, de Lajudie P, Prin Y, Neyra M, Gills M, Boivin-Masson C, Dreyfus B (2001) Methylotrophic Methylobacterium bacteria nodulate and fix nitrogen in symbiosis with legumes. J Bacteriol 183:214–220
Tan ZY, Wang ET, Gao JL, Martínez-Romero E, Chen WX (1997) Phylogenetic and genetic relationships of Mesorhizobium tianshanese and related rhizobia. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:874–879
Tan ZY, Wang ET, Peng GX, Zhu ME, Martínez-Romero E, Chen WX (1999) Characterization of bacteria isolated from wild legumes in the north-western regions of China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1457–1469
Terefework, Kaijalainen S, Lindström K (2001) AFLP fingerprint as a tool to study the genetic diversity of Rhizobium galegae isolated from Galega orientalis and Galega offcinalis. J Biotechnol 91:169–180
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougim F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tool. Nucleic Acid Res 24:4867–4882
Tian CF, Wang ET, Han TX, Sui XH, Chen WX (2007) Genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with Vicia faba in three ecological regions of China. Arch Microbiol. May 4 (Epub ahead of print)
Valverde A, Velazquez E, Fernandez-Santos F, Vizcaino N, Rivas R, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Igual JM, Willems A (2005) Phyllobacterium trifolii sp. nov., nodulating Trifolium and Lupinus in Spanish soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1985–1989
Vandamme P, Goris J, Chen WM, De Vos P, Willems A (2002) Burkholderia tuberum sp. nov. and Burkholderia phymatum sp. nov., nodulate the roots of tropical legumes. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:507–512
Vauterin L, Vauterin P (1992) Computer-aided objective comparison of electrophoresis patterns for grouping and identification of microorganisms. Eur Microbiol 1:25–40
Versalovic J, Schneider M, de Bruijn FJ, Lupski JR (1994) Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Methods Mol Cell Biol 5:25–40
Vinuesa P, Silva C, Werner D, Martínez-Romero E (2005a) Population genetics and phylogenetic inference in bacterial molecular systematics: the roles of migration and recombination in Bradyrhizobium species cohesion and delineation. Mol Phylogenet Evol 34:29–54
Vinuesa P, Silva C, Lorite MJ, Izaguirre-Mayoral ML, Bedmar EJ, Martínez-Romero E (2005b) Molecular systematics of rhizobia based on maximum likelihood and Bayesian phylogenies inferred from rrs, atpD, recA and nifH sequences, and their use in the classification of Sesbania microsymbionts from Venezuelan wetlands. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:702–716
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root-nodule bacteria. Blackwell, Oxford
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ramanan N (1997) The actinomycete Thermobispora bispora contains two distinct types of transcriptionally active 16 S rRNA genes. J Bacteriol 179:3270–3276
Wang HK, Xia Y, Yang ZY, Natschke SL, lee KH (1998) Recent advances in the discovery and development of flavonoids and their analogues as antitumor and anti-HIV agents. Adv Exp Med Biol 439:191–225
Wang LL, Liu J, Wang ET,Chen WX (2006) Endophytic occupation of root nodules and roots of Melilotus dentatus by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Microb Ecol 52:436–443
Wei GH, Wang ET, Tan ZY, Zhu ME, Chen WX (2002) Rhizobium indigoferae sp. nov. and Sinorhizobium kummerowiae sp. nov., respectively isolated from Indigofera spp. and Kummerowia stipulacea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2231–2239
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Willems A, Coopman R, Gillis M (2001a) Phylogenetic and DNA–DNA hybridization analyses of Bradyrhizobium species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:111–117
Willems A, Coopman R, Gillis M (2001b) Comparison of sequence analysis of 16S–23S rDNA spacer regions, AFLP analysis and DNA–DNA hybridizations in Bradyrhizobium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:623–632
Yang SS, Bellogin RA, Buendia A, Camacho M, Chen M, Cubo T, Daza A, Diaz CL, Espuny MR, Gutierrez R, Harteveld M, Li XH, Lyra MC, Madinabeitia N, Medina C, Miao L, Ollero FJ, Olsthoorn MM, Rodriguez DN, Santamaria C, Schlaman HR, Spaink HP, Temprano F, Thomas-Oates JE, Van Brussel AA, Vinardell JM, Xie F, Yang J, Zhang HY, Zhen J, Zhou J, Ruiz-Sainz JE (2001) Effect of pH and soybean cultivars on the quantitative analyses of soybean rhizobia populations. J Biotechnol 91:243–255
Yoo HH, Kim T, Ahn S, Park JH (2005) Evaluation of the Estrogenic activity of Leguminosae plants. Biol Pharm Bull 28:538–540
Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martínez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2001) A revision of Rhizobium Frank 1889, with an emended description of the genus, and the inclusion of all species of Agrobacterium Conn 1942 and Allorhizobium undicola de Lajudie et al. 1998 as new combinations: Rhizobium radiobacter, R. rhizogenes, R. rubi, R. undicola and R. vitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:89–103
Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martínez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2003) Classification and nomenclature of Agrobacterium and Rhizobium—a reply to Farrand et al. (2003). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1689–1695
Acknowledgments
We thank our local collaborators in each province for their great help in the collection and isolation of the rhizobial strains. Dr. Wen Feng Chen, Dr. Xin Hua Sui and Dr. Feng Qin Wang gave us valuable suggestions and technical support. This study was financially supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973) (project no. 2006CB100206) and National Program for Basic S & T Platform Construction (project no. 2005DKA 21201-10). ETW was financially supported by the grants of SIP 20060213 and 20070538 authorized by IPN, Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ursula Priefer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D.X., Man, C.X., Wang, E.T. et al. Diverse rhizobia that nodulate two species of Kummerowia in China. Arch Microbiol 188, 495–507 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0271-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0271-4