Abstract
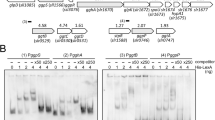
The Pho regulon is controlled by the histidine kinase-response regulator pair SphS–SphR in many cyanobacteria and up-regulation of the Pho regulon can be monitored by measuring alkaline phosphatase activity. However, the mechanism regulating signal transduction between SphS and SphR has not been described. We have created a cyanobacterial strain allowing the introduction of mutations into the transmitter domain of SphS. Mutations at Thr-167, adjacent to the H motif of SphS, introduce elevated alkaline phosphatase activity in the presence of phosphate and an enhancement of alkaline phosphatase activity, when compared to the control strain, in phosphate-limiting media. SphU acts as a negative regulator of the SphS–SphR system in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and we show that constitutive alkaline phosphatase activity in the absence of SphU requires signal transduction through SphS and SphR. However, constitutive activity in the absence of SphU is severely attenuated in the ΔSphU:SphS-T167N mutant. Our data suggest that Thr-167 contributes to the mechanism underlying regulation by SphU. We have also assembled a deletion mutant system allowing the introduction of mutations into SphR and show that Gly-225 and Trp-236, which are both conserved in SphR from cyanobacteria, are essential for activation of the Pho regulon under phosphate-limiting conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba HM, Nagaya M, Mizuno T (1993) Sensor and regulator proteins from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus species PCC7942 that belong to the bacterial signal-transduction protein families: implication in the adaptive response to phosphate limitation. Mol Microbiol 8:81–91
Allen MA (1984) Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:1–25
Ashby MK, Houmard J (2006) Cyanobacterial two-component proteins: structure, diversity, distribution, and evolution. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:472–509
Blanco AG, Sola M, Gomis-Rüth FX, Coll M (2002) Tandem DNA recognition by PhoB, a two-component signal transduction transcriptional activator. Structure 10:701–713
Cai S-J, Khorchid A, Ikura M, Inouye M (2003) Probing catalytically essential domain orientation in histidine kinase EnvZ by targeted disulfide crosslinking. J Mol Biol 328:409–418
Carmany DO, Hollingsworth K, McCleary WR (2003) Genetic and biochemical studies of phosphatase activity of PhoR. J Bacteriol 185:1112–1115
Collier JL, Grossman AR (1992) Chlorosis induced by nutrient deprivation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942: not all bleaching is the same. J Bacteriol 174:4718–4726
Dutta R, Inouye M (2000) GHKL, an emergent ATPase/kinase superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci 25:24–28
Dutta R, Qin L, Inouye M (1999) Histidine kinases: diversity of domain organization. Mol Microbiol 34:633–640
Eaton-Rye JJ (2004) The construction of gene knockouts in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. In: Carpentier R (ed) Methods in molecular biology, vol 274: photosynthesis research protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 309–324
Eaton-Rye JJ, Vermaas WFJ (1991) Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of psbB, the gene encoding CP47, employing a deletion strain of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Mol Biol 17:1165–1177
Grillo JF, Gibson J (1979) Regulation of phosphate accumulation in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus. J Bacteriol 140:508–517
Grossman AR, Schaefer MR, Chiang GG, Collier JL (1994) The responses of cyanobacteria to environmental conditions: light and nutrients. In: Bryant DA (ed) The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 641–675
Grossman AR, van Waasbergen LG, Kehoe D (2003) Environmental regulation of phycobilisome biosynthesis. In: Green BR, Parson WW (eds) Light-harvesting antennas in photosynthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 471–493
Hirani TA, Suzuki I, Hayashi H, Murata N, Eaton-Rye JJ (2001) Characterization of a two-component signal transduction system involved in the induction of alkaline phosphatase under phosphate-limiting conditions in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Mol Biol 45:133–144
Imamura S, Yoshihara S, Nakano S, Shiozaki N, Yamada A, Tanaka K, Takahashi H, Asayama M, Shirai M (2003) Purification, characterization, and gene expression of all sigma factors of RNA polymerase in a cyanobacterium. J Mol Biol 325:857–872
Kenney LJ (2002) Structure/function relationships in OmpR and other winged-helix transcription factors. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:135–141
Kondo H, Nakagawa A, Nishihira J, Nishimura Y, Mizuno T, Tanaka I (1997) Escherichia coli positive regulator OmpR has a large loop structure at the putative RNA polymerase interaction site. Nat Struct Biol 4:28–31
Kramer G, Weiss V (1999) Functional dissection of the transmitter module of the histidine kinase NtrB in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:604–609
Makino K, Shinagawa H, Amemura M, Nakata A (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the phoB gene, the positive regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol 190:37–44
Makino K, Amemura M, Kawamoto T, Kimura S, Shinagawa H, Nakata A, Suzuki M (1996) DNA binding of PhoB and its interaction with RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol 259:15–26
Moore LR, Ostrowski M, Scanlan DJ, Feren K, Sweetsir T (2005) Ecotypic variation in phosphorus-acquisition mechanisms within marine picocyanobacteria. Aquat Microb Ecol 39:257–269
Morohoshi T, Maruo T, Shirai Y, Kato J, Ikeda T, Takiguchi N, Ohtake H, Kuroda A (2002) Accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate in phoU mutants of Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4107–4110
Muda M, Rao NN, Torriani A (1992) Role of PhoU in phosphate transport and alkaline phosphatase regulation. J Bacteriol 174:8057–8064
Nagaya M, Aiba H, Mizuno T (1994) The sphR product, a two-component response regulator protein, regulates phosphate assimilation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 by binding to two sites upstream from the phoA promoter. J Bacteriol 176:2210–2215
Nakata A, Amemura M, Shinagawa H (1984) Regulation of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K-12: regulation of the negative regulatory gene phoU and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol 159:979–985
Oka A, Sugisake H, Takanami M (1981) Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol 147:217–226
Okamura H, Hanaoka S, Nagadoi A, Makino K, Nishimura Y (2000) Structural comparison of the PhoB and OmpR DNA-binding/transactivation domains and the arrangement of PhoB molecules on the phosphate box. J Mol Biol 295:1225–1236
Parkinson JS, Kofoid EC (1992) Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet 26:71–112
Pratt L, Silhavy T (1994) OmpR mutants specifically defective for transcriptional activation. J Mol Biol 243:579–594
Prentki P, Krisch HM (1984) In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene 29:303–313
Ray JM, Bhaya D, Block MA, Grossman AR (1991) Isolation, transcription, and inactivation of the gene for an atypical alkaline phosphatase of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bacteriol 173:4297–4309
Richaud C, Zabulon G, Joder A, Thomas J-C (2001) Nitrogen or sulfur starvation differentially affects phycobilisome degradation and expression of the nblA gene in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 183:2989–2994
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Scanlan DJ, West NJ (2002) Molecular ecology of the marine cyanobacterial genera Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 40:1–12
Schwarz R, Forchhammer K (2005) Acclimation of unicellular cyanobacteria to macronutrient deficiency: emergence of a complex network of cellular responses. Microbiology 151:2503–2514
Shinagawa H, Makino K, Yamada M, Amemura M, Sato T, Nakata A (1994) Signal transduction in the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli: dual functions of PhoR as a protein kinase and a protein phosphatase. In: Torriani-Gorini A, Yagil E, Silver S (eds) Phosphate in microorganisms: cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 285–289
Slauch JM, Russo FD, Silhavy TJ (1991) Suppressor mutations in rpoA suggest that OmpR controls transcription by direct interaction with the α subunit of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol 173:7501–7510
Steed PM, Wanner BL (1993) Use of the rep technique for allele replacement to construct mutants with deletions of the pstSCAB-phoU operon: evidence of a new role for the PhoU protein in the phosphate regulon. J Bacteriol 175:6797–6809
Stock JB, Surette MG, Levit M, Park P (1995) Two-component signal transduction systems: structure-function relationships and mechanisms of catalysis. In: Hoch JA, Silhavy TJ (eds) Two-component signal transduction. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 25–51
Suzuki I, Kanesaki Y, Hayashi H, Hall JJ, Simon WJ, Slabas AR, Murata N (2005) The histidine kinase Hik34 is involved in thermotolerance by regulating the expression of heat shock genes in Synechocystis. Plant Physiol 138:1409–1421
Suzuki S, Ferjani A, Suzuki I, Murata N (2004) The SphS–SphR two component system is the exclusive sensor for the induction of gene expression in response to phosphate limitation in Synechocystis. J Biol Chem 279:13234–13240
Tanaka T, Saha SK, Tomomori C, Ishima R, Liu D, Tong KI, Park H, Dutta R, Qin L, Swindells MB, Yamazaki T, Ono AM, Kainosho M, Inouye M, Ikura M (1998) NMR structure of the histidine kinase domain of the E. coli osmosensor EnvZ. Nature 396:88–92
Taylor BL, Zhulin I (1999) PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:479–506
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tomomori C, Tanaka T, Dutta R, Park H, Saha SK, Zhu Y, Ishima R, Liu D, Tong KI, Kurokawa H, Qian H, Inouye M, Ikura M (1999) Solution structure of the homodimeric core domain of Escherichia coli histidine kinase EnvZ. Nat Struct Biol 6:729–734
Tuominen I, Tyystjärvi E, Tyystjärvi I (2003) Expression of primary sigma factor (PSF) and PSF-like sigma factors in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 185:1116–1119
Vermaas WFJ (1998) Gene modifications and mutation mapping to study the function of photosystem II. Methods Enzymol 298:293–311
Wanner BL (1987) Phosphate regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology, vol 2. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 1326–1333
Wanner BL (1996) Phosphorus assimilation and control of the phosphate regulon. In: Neidhardt FC, Curtiss R III, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low KB, Magassanik B, Reznikoff WS, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd edn, vol 1. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 1357–1381
Watson GMF, Scanlan DJ, Mann NH (1996) Characterization of the genes encoding a phosphate-regulated two component sensory system in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH7803. FEMS Microbiol Lett 142:105–109
Williams JGK (1988) Construction of specific mutations in the photosystem II photosynthetic reaction center by genetic engineering methods in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Methods Enzymol 167:766–778
Yamada M, Makino K, Amemura M, Shinagawa H, Nakata A (1989) Regulation of the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli: analysis of mutant phoB and phoR genes causing different phenotypes. J Bacteriol 171:5601–5606
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program (W.J., A.I.) and an Otago University Research Grant to J.J.E.-R. We thank Abby Cuttriss for constructing the pΔSphR-specR and pTZ:SphR-camR plasmids and Shahram Zandvakili for constructing pslr0741.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Mary Allen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juntarajumnong, W., Hirani, T.A., Simpson, J.M. et al. Phosphate sensing in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: SphU and the SphS–SphR two-component regulatory system. Arch Microbiol 188, 389–402 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0259-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0259-0