Abstract
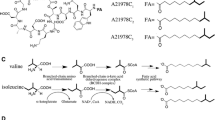
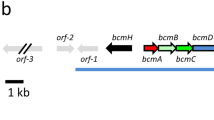
The bkdAB gene cluster, which encodes plausible E1 and E2 components of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCDH) complex, was isolated from Streptomyces virginiae in the vicinity of a regulatory island for virginiamycin production. Gene disruption of bkdA completely abolished the production of virginiamycin M (a polyketide-peptide antibiotic), while the production of virginiamycin S (a cyclodepsipeptide antibiotic) was unaffected. Complementation of the bkdA disruptant by genome-integration of intact bkdA completely restored the virginiamycin M production, indicating that the bkdAB cluster is essential for virginiamycin M biosynthesis, plausibly via the provision of isobutyryl-CoA as a primer unit. In contrast to a feature usually seen in the Streptomyces E1 component, namely, the separate encoding of the α and β subunits, S. virginiae bkdA seemed to encode the fused form of the α and β subunits, which was verified by the actual catalytic activity of the fused protein in vitro using recombinant BkdA overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Supply of an additional bkdA gene under the strong and constitutive promoter ermE* in the wild-type strain of S. virginiae resulted in enhanced production of virginiamycin M, suggesting that the supply of isobutyryl-CoA is one of the rate-limiting factors in the biosynthesis of virginiamycin M.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamas-Jacques N, Lorenzon S, Lacroix P, De Swetschin C, Crouzet J (1999) Cluster organization of the genes of Streptomyces pristinaespiralis involved in pristinamycin biosynthesis and resistance elucidated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Appl Microbiol 87:939–948
Barriere JC, Berthaud N, Beyer D, Dutka-Malen S, Paris JM, Desnottes JF (1998) Recent developments in streptogramin research. Curr Pharm Des 4:155–180
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Burns G, Brown T, Hatter K, Sokatch JR (1988) Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the transacylase components of branched chain oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida, and the pyruvate and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 176:165–169
Canu A, Leclercq R (2001) Overcoming bacterial resistance by dual target inhibition streptogramins. Curr Drug Targets 1:215–225
Cate RL, Roche TE, Davis LC (1980) Rapid intersite transfer of acetyl groups and movement of pyruvate dehydrogenase component in the kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem 255:7556–7562
Davie JR, Wynn RM, Cox RP, Chuang DT (1992) Expression and assembly of a functional E1 component (α2β2) of mammalian branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase complex in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 267:16601–16606
Debarbouille M, Gardan R, Arnaud M, Rapoport G (1999) Role of bkdR, a transcriptional activator of the sigL-dependent isoleucine and valine degradation pathway in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 181:2059–2066
De Crécy-Lagard V, Blanc V, Gil P, Naudin L, Lorenzon S, Famechohn A, Bamas-Jacques N, Crouzet J, Thiebaut D (1997a) Pristinamycin I biosynthesis in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis: molecular characterization of the first two structural peptide synthetase genes. J Bacteriol 179:705–713
De Crécy-Lagard V, Saurin W, Thibaut D, Gil P, Naudin L, Crouzet J, Blanc V (1997b) Streptogramin B biosynthesis in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis and Streptomyces virginiae: molecular characterization of the last structural peptide synthetase gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1904–2009
Delpierre GR, Eastwood FW, Graeam GE, Kingston DGI, Sarin PS, Todd L, Williams DH (1966) Antibiotics of the ostreogrycin complex. Part II. Structure of ostreogrycin A2. J Chem Soc 19:1653–1669
Fries M, Chauhan HJ, Domingo GJ, Jung HI, Perham RN (2003) Site-directed mutagenesis of a loop at the active site of E1 (α2β2) of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. A possible common sequence motif. Eur J Biochem 270:861–870
Hook DJ, Vining LC (1973) Biosynthetic precursors of etamycin, a peptidolactone antibiotic from Streptomyces griseoviridus. Can J Biochem 51:1630–1637
Ishikawa J, Hotta K (1999) FramePlot: a new implementation of the Frame analysis for predicting protein-coding regions in bacterial DNA with a high G+C content. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174:251–253
Kawachi R, Wangchaisoonthorn U, Nihira T, Yamada Y (2000a) Identification by gene deletion analysis of a regulator, VmsR, that controls virginiamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces virginiae. J Bacteriol 182:6259–6263
Kawachi R, Akashi T, Kamitani Y, Sy A, Wangchaisoonthorn U, Nihira T, Yamada Y (2000b) Identification of an AfsA homologue (BarX) from Streptomyces virginiae as a pleiotropic regulator controlling autoregulator biosynthesis, virginiamycin biosynthesis and virginiamycin M1 resistance. Mol Microbiol 36:302–313
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kitani S, Bibb MJ, Nihira T, Yamada Y (2000) Conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces lavendulae FRI-5. J Microbiol Biotechnol 10:535–538
MacNeil DJ, Occi JL, Gewain KM, MacNeil T, Gibbons PH, Ruby CL, Danis SJ (1992) Complex organization of the Streptomyces avermetilis genes encoding the avermectin polyketide synthase. Gene 115:119–125
Manzella J (2001) Quinupristin-dalfopristin: a new antibiotic for severe gram-positive infections. Am Fam Physician 64:1863–1866
Matsuno K, Yamada Y, Lee CK, Nihira T (2004) Identification by gene deletion analysis of barB as a negative regulator controlling an early process of virginiamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces virginiae. Arch Microbiol 181:52–59
Moellering RC, Linden PK, Reinhardt J, Blumberg EA, Bompart F, Talbot GH (1999) The efficacy and safety of quinupristim/dalfopristin for the treatment of infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Synercid emergency-use study groups. J Antimicrob Chemother 44:251–261
Namwat W, Lee CK, Kinoshita H, Yamada Y, Nihira T (2001) Identification of the varR gene as a transcriptional regulator of virginiamycin S resistance in Streptomyces virginiae. J Bacteriol 183:2025–2031
Namwat W, Kamioka Y, Kinoshita H, Yamada Y, Nihira T (2002) Characterization of virginiamycin S biosynthetic genes from Streptomyces virginiae. Gene 286:283–290
Nakano H, Takehara E, Nihira T, Yamada Y (1998) Gene replacement analysis of the Streptomyces virginiae barA gene encoding the butyrolactone autoregulator receptor reveals that BarA acts as a repressor in virginiamycin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 180:3317–3322
Otsuka M, Ichinose K, Fujii I, Ebizuka Y (2004) Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of an iterative type I polyketide synthase gene cluster for biosynthesis of the antitumor chlorinated polyenone neocarzilin in “Streptomyces carzinostaticus”. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:3468–3476
Paget MSB, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ (1999) Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σE is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181:204–211
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Skinner DD, Morgenstern MR, Fedechko RW, Denoya CD (1995) Cloning and sequencing of a cluster of genes encoding branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase from Streptomyces avermitilis and the production of a functional E1 [αß] component in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:183–190
Sprusansky O, Stirrett K, Skinner D, Denoya C, Westpheling J (2005) The bkdR gene of Streptomyces coelicolor is required for morphogenesis and antibiotic production and encodes a transcriptional regulator of a branched-chain amino acid dehydrogenase complex. J Bacteriol 187:664–671
Yanagimoto M (1983) Novel actions of inducer in staphylomycin production by streptomyces virginiae. J Ferment Technol 61:443–448
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a scholarship from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan (to N.P.), and by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (no. 18780244) from MEXT, a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (no. 15380063) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Bio Design program of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan, and Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology from the JST-NRCT joint program of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) of Japan and the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT).
We thank S.K. Lee for his helpful assistance in constructing plasmids in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulsawat, N., Kitani, S., Kinoshita, H. et al. Identification of the bkdAB gene cluster, a plausible source of the starter-unit for virginiamycin M production in Streptomyces virginiae . Arch Microbiol 187, 459–466 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0212-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0212-2