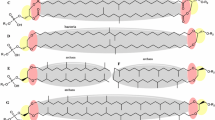
Abstract
Most fatty acid desaturases are members of a large superfamily of integral membrane, O2-dependent, iron-containing enzymes that insert double bonds into previously synthesized fatty acyl chains. The cold shock-induced, membrane-bound desaturase from Bacillus subtilis (Δ5-Des) uses existing phospholipids as substrates to introduce a cis-double bond at the fifth position of the fatty acyl chain. While essentially no three-dimensional structural information is available for these difficult-to-purify enzymes, experimental analysis of the topology of Δ5-Des has provided a model that might be extended to most acyl-lipid desaturases. In addition, studies of the cold-induced expression of Δ5-Des led to the identification of a two-component system composed of a membrane-associated kinase, DesK, and a transcriptional regulator, DesR, which stringently controls the transcription of the des gene, coding for the desaturase. A model for sensing and transduction of low-temperature signals has emerged from our results, which we discuss in the context of transcriptional regulation of membrane lipid fluidity homeostasis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar PS, Cronan JE Jr, de Mendoza D (1998) A Bacillus subtilis gene induced by cold shock encodes a membrane phospholipid desaturase. J Bacteriol 180:2194–2200
Aguilar PS, López P, de Mendoza D (1999) Transcriptional control of the low-temperature-inducible des gene, encoding the Δ5 desaturase of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 181:7028–7033
Aguilar PS, Hernandez-Arriaga AM, Cybulski LE, Erazo AC, de Mendoza D (2001) Molecular basis of thermosensing: a two-component signal transduction thermometer in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J 20:1681–1691
Albanesi D, Mansilla MC, de Mendoza D (2004) The membrane fluidity sensor DesK of Bacillus subtilis controls the signal decay of its cognate response regulator. J Bacteriol 186:2655–2663
Altabe SG, Aguilar PS, Caballero GM, de Mendoza D (2003) The Bacillus subtilis acyl lipid desaturase is a Δ5 desaturase. J Bacteriol 185:3228–3231
van Beilen JB, Penning D, Witholt B (1992) Topology of the membrane-bound alkane hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem 267:9194–9201
Bloch K (1963) The biological synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Soc Symp 24:1–16
Campbell JW, Cronan JE Jr (2001) Bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis: targets for antibacterial drug discovery. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:305–332
Cronan JE Jr, Gelmann EP (1973) An estimate of the minimum amount of unsaturated fatty acid required for growth of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 248:1188–1195
Cronan JE Jr, Rock CO (1987) Biosynthesis of membrane lipids. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. ASM, Washington DC, pp 474–497
Cronan JE Jr, Gennis RB, Maloy SR (1987) Cytoplasmic membrane. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. ASM, Washington DC, pp 31–55
Cybulski LE, Albanesi D, Mansilla MC, Altabe S, Aguilar PS, de Mendoza D (2002) Mechanism of membrane fluidity optimisation: isothermal control of the Bacillus subtilis acyl-lipid desaturase. Mol Microbiol 45:1379–1388
Cybulski LE, del Solar G, Craig PO, Espinosa M, de Mendoza D (2004) Bacillus subtilis DesR functions as a phosphorylation-activated switch to control membrane lipid fluidity. J Biol Chem 279:39340–39347
Díaz AR, Mansilla MC, Vila AJ, de Mendoza D (2002) Membrane topology of the acyl-lipid desaturase from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 277:48099–48106
English N, Palmer CNA, Alworth WL, Kang L, Hughes V, Wolf CR (1997) Fatty acid signals in Bacillus megaterium are attenuated by cytochrome P-450-mediated hydroxylation. Biochem J 327:363–368
Enoch HG, Catala A, Strittmatter P (1976) Mechanism of rat liver microsomal stearyl-CoA desaturase. Studies of the substrate specificity, enzyme-substrate interactions, and the function of lipid. J Biol Chem 251:5095–5103
Goldberg EM, Zidovetzki R (1997) Effects of dipalmitoylglycerol and fatty acids on membrane structure and protein kinase C activity. Biophys J 73:2603–2614
Grau R, de Mendoza D (1993) Regulation of the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids by growth temperature in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 8:535–542
Kaneda T (1991) Iso-fatty and anteiso-fatty acids in bacteria: biosynthesis, function, and taxonomic significance. Microbiol Rev 55:288–302
Klein W, Weber MH, Marahiel MA (1999) Cold shock response of Bacillus subtilis: isoleucine-dependent switch in the fatty acid branching pattern for membrane adaptation to low temperatures. J Bacteriol 181:5341–5349
Lindqvist Y, Huang W, Schneider G, Shanklin J (1996) Crystal structure of Δ9 stearoyl-acyl carrier protein desaturase from castor seed and its relationship to other di-iron proteins. EMBO J 15:4081–4092
Mansilla MC, Cybulski LE, Albanesi D, de Mendoza D (2004) Control of membrane lipid fluidity by molecular thermo-sensors. J Bacteriol 186:6681–6688
Marrakchi H, Choi KH, Rock CO (2002) A new mechanism for anaerobic unsaturated fatty acid formation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 277:44809–44816
Miquel M, James D Jr, Dooner H, Browse J (1993) Arabidopsis requires polyunsaturated lipids for low-temperature survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6208–6212
Murata N, Wada H (1995) Acyl-lipid desaturases and their importance in the tolerance and acclimatization to cold of cyanobacteria. Biochem J 308:1–8
Mustardy L, Los DA, Gombos Z, Murata N (1996) Immunocytochemical localization of acyl-lipid desaturases in cyanobacterial cells: evidence that both thylakoid membranes and cytoplasmic membranes are sites of lipid desaturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10524–10527
Ohlrogge J, Brownse J (1995) Lipid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:957–970
Phetsuksiri B, Jackson M, Scherman H, McNeil M, Besra GS, Baulard AR, Slayden RA, DeBarber AE, Barry CE III, Baird MS, Crick DC, Brennan PJ (2003) Unique mechanism of action of the thiourea drug isoxyl on Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem 278:53123–53130
Sakamoto T, Murata N (2002) Regulation of the desaturation of fatty acids and its role in tolerance to cold and salt stress. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:208–210
Sasata RJ, Reed DW, Loewen MC, Covello PS (2004) Domain swapping localizes the structural determinants of regioselectivity in membrane-bound fatty acid desaturases of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 279:39296–39302
Shanklin J, Cahoon EB (1998) Desaturation and related modifications of fatty acids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:611–641
Shanklin J, Whittle E, Fox BG (1994) Eight histidine residues are catalytically essential in a membrane-associated iron enzyme, stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and are conserved in alkane hydroxylase and xylene monooxygenase. Biochemistry 33:12787–12794
Strauch, MA, de Mendoza D, Hoch JA (1992) Cis-unsaturated fatty acids specifically inhibit a signal-transducing protein kinase required for initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 6:2909–2917
Stukey JE, McDonough VM, Martin CE (1990) The OLE1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes the Δ9 fatty acid desaturase and can be functionally replaced by the rat stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene. J Biol Chem 265:20144–20149
Suzuki I, Los DA, Kanesaki Y, Mikami K, Murata N (2000) The pathway for perception and transduction of low-temperature signals in Synechocystis. EMBO J 19:1327–1334
Tocher DR, Leaver MJ, Hodgson PA (1988) Recent advances in the biochemistry and molecular biology of fatty acyl desaturases. Prog Lipid Res 37:73–117
Tsutsumi T, Yamauchi E, Suzuki E, Watanabe S, Kobayashi T, Okuyama H (1995) Effect of a high alpha-linolenate and high linoleate diet on membrane-associated enzyme activities in rat brain-modulation of Na+, K+-ATPase activity at suboptimal concentrations of ATP. Biol Pharm Bull 18:664–670
Wada H, Gombos Z, Murata N (1990) Enhancement of chilling tolerance of a cyanobacterium by genetic manipulation of fatty acid desaturation. Nature 347:200–203
Wallis JG, Browse J (2002) Mutants of Arabidopsis reveal many roles for membrane lipids. Prog Lipid Res 41:254–278
Weber MHW, Klein W, Muller L, Niess UM, Marahiel M (2001) Role of the Bacillus subtilis fatty acid desaturase in membrane adaptation during cold shock. Mol Microbiol 39:1321–1329
Yung BY, Kornberg A (1988) Membrane attachment activates DnaA protein, the initiation protein of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 19:7202–7205
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (FONCYT). M.C. Mansilla and D. de Mendoza are Career Investigators from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET). D. de Mendoza is an International Research Scholar from Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansilla, M.C., de Mendoza, D. The Bacillus subtilis desaturase: a model to understand phospholipid modification and temperature sensing. Arch Microbiol 183, 229–235 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0759-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0759-8