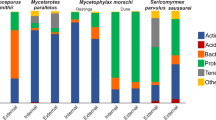
Abstract
Insects are among the most successful animals of the world in terms of species richness as well as abundance. Their biomass exceeds that of mammals by far. Among insects, ants are of particular interest not only because of their enormous ecological role in many terrestrial ecosystems, but also because they have developed an impressive behavioural repertoire. In fact, a key feature of the evolutionary success of ants is their ability to form complex societies with division of labour among individuals in a colony belonging to different castes such as workers and soldiers. In addition to these complex social interactions of ants, they have shown an extraordinary capacity to build up close associations with other organisms such as other insects, plants, fungi and bacteria. In the present review we attempt to provide an overview of the various symbiotic interactions that ants have developed with microorganisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aanen DK, Eggleton P, Rouland-Lefevre C, Guldberg-Froslev T, Rosendahl S, Boomsma JJ (2002) The evolution of fungus-growing termites and their mutualistic fungal symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14887–14892
Akman L, Yamashita A, Watanabe H, Oshima K, Shiba T, Hattori M, Aksoy S (2002) Genome sequence of the endocellular obligate symbiont of tsetse flies, Wigglesworthia glossinidia. Nat Genet 32:402–407
Baumann P, Baumann L, Lai CY, Rouhbakhsh D, Moran NA, Clark MA (1995) Genetics, physiology, and evolutionary relationships of the genus Buchnera: intracellular symbionts of aphids. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:55–94
Belda E, Moya A, Silva FJ (2005) Genome rearrangement distances and gene order phylogeny in gamma-Proteobacteria. Mol Biol Evol 22:1456–1467
Blochmann F (1892) Über das Vorkommen von bakterienähnlichen Gebilden in den Geweben und Eiern verschiedener Insekten. Zentbl Bakteriol 11:234–240
Blüthgen N, Gebauer G, Fiedler K (2003) Disentangling a rainforest food web using stable isotopes: dietary diversity in a species-rich ant community. Oecologia 137:426–435
Boursaux-Eude C, Gross R (2000) New insights into symbiotic associations between ants and bacteria. Res Microbiol 151:513–519
Brune A, Friedrich M (2000) Microecology of the termite gut: structure and function on a microscale. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:263–269
Buchner P (1965) Endosymbiosis of animals with plant microorganisms. John Wiley New York
Canback B, Tamas I, Andersson SG (2004) A phylogenomic study of endosymbiotic bacteria. Mol Biol Evol 21:1110–1122
Charlat S, Hurst GDD, Mercot H (2003) Evolutionary consequences of Wolbachia infections. Trends Genet 19:217–223
Chen X, Li S, Aksoy S (1999) Concordant evolution of a symbiont with its host insect species: molecular phylogeny of genus Glossina and its bacteriome-associated endosymbiont, Wigglesworthia glossinidia. J Mol Evol 48:49–58
Currie RC (2001) A community of ants, fungi, and bacteria: a multilateral approach to studying symbiosis. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:357–380
Currie RC, Mueller UG, Malloch D (1999a) The agricultural pathology of ant fungus gardens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7998–8002
Currie RC, Scott JA, Summerbell RC, Malloch D (1999b) Fungus-growing ants use antibiotic-producing bacteria to control garden parasites. Nature 398:701–704
Currie RC, Scott JA, Summerbell RC, Malloch D (2003a) Corrigendum. Nature 423:461
Currie RC, Wong B, Stuart AE, Schultz TR, Rehner SA, Mueller UG, Sung GH, Spatafora JW, Straus NA (2003b) Ancient tripartite coevolution in the attine ant-microbe symbiosis. Science 299:386–388
Dale C, Maudlin I (1999) Sodalis gen. nov. and Sodalis glossinidius sp. nov., a microaerophilic secondary endosymbiont of the tsetse fly Glossina morsitans morsitans. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:267–275
Dasch GA, Weiss E, Chang KP (1984) Endosymbionts of insects. In: Krieg NR (ed) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology vol. 1, Williams & Williams, Baltimore, pp 881–883
Davidson DW, Cook SC, Snelling RR, Chua TH (2003) Explaining the abundance of ants in lowland tropical rainforest canopies. Science 300:969–972
Dedeine F, Ahrens M, Calcaterra L, Shoemaker DD (2005) Social parasitism in fire ants (Solenopsis spp.): a potential mechanism for interspecies transfer of Wolbachia. Mol Ecol 14:1543–1548
Degnan PH, Lazarus AB, Brock CD, Wernegreen JJ (2004) Host-symbiont stability and fast evolutionary rates in an ant-bacterium association: cospeciation of camponotus species and their endosymbionts, candidatus Blochmannia. Syst Biol 53:95–110
Douglas AE (1998) Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu Rev Entomol 43:17–37
Fialho RF, Stevens L (2000) Male-killing Wolbachia in a flour beetle. Proc Biol Sci 267:1469–1473
Fry AJ, Wernegreen JJ (2005) The roles of positive and negative selection in the molecular evolution of insect endosymbionts. Gene 355:1–10
Funk DJ, Helbling L, Wernegreen JJ, Moran NA (2000) Intraspecific phylogenetic congruence among multiple symbiont genomes. Proc Biol Sci 267:2517–2521
Gil R, Sabater-Munoz B, Latorre A, Silva FJ, Moya A (2002) Extreme genome reduction in Buchnera spp.: toward the minimal genome needed for symbiotic life. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4454–4458
Gil R, Silva FJ, Zientz E, Delmotte F, Gonzalez-Candelas F, Latorre A, Rausell C, Kamerbeek J, Gadau J, Hölldobler B, van Ham RC, Gross R, Moya A (2003) The genome sequence of Blochmannia floridanus: comparative analysis of reduced genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9388–9393
Gil R, Latorre A, Moya A (2004) Bacterial endosymbionts of insects: insights from comparative genomics. Env Microbiol 6:1109–1122
Goebel W, Gross R (2001) Intracellular survival strategies of mutualistic and parasitic prokaryotes. Trends Microbiol 9:267–273
van Ham RC, Kamerbeek J, Palacios C, Rausell C, Abascal F, Bastolla U, Fernandez JM, Jimenez L, Postigo M, Silva FJ, Tamames J, Viguera E, Latorre A, Valencia A, Moran F, Moya A (2003) Reductive genome evolution in Buchnera aphidicola. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:581–586
Hinkle G, Wetterer JK, Schultz TR, Sogin ML (1994) Phylogeny of the attine ant fungi based on analysis of small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Science 266:1695–1697
Hölldobler B, Wilson EO (1990) The ants. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Hurst GD, Johnson AP, Schulenburg JH, Fuyama Y (2000) Male-killing Wolbachia in Drosophila: a temperature-sensitive trait with a threshold bacterial density. Genetics 156: 699–709
Jones KG, Blackwell M (1998) Phylogenetic analysis of ambrosial species in the genus Raffaelea based on 18S rDNA sequences. Mycol Res 102:661–665
Keller L, Liautard C, Reuter M, Brown WD, Sundstrom L, Chapuisat M (2001) Sex ratio and Wolbachia infection in the ant Formica exsecta. Heredity 87:227–233
McGraw EA, O’Neill SL (2004) Wolbachia pipientis: intracellular infection and pathogenesis in Drosophila. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:67–70
Mira A, Moran NA (2002) Estimating population size and transmission bottlenecks in maternally transmitted endosymbiotic bacteria. Microb Ecol 44:137–143
Nogge G (1982) Significance of symbionts for the maintenance of an optimal nutrition state for successful reproduction in hematophagous arthropods. Parasitology 82:101–104
Ohkuna M, Kudo T (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of the intestinal bacterial community in the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:461–468
Poulsen M, Boomsma JJ (2005) Mutualistic fungi control crop diversity in fungus-growing ants. Science 307:741–744
Reuter M, Pedersen JS, Keller L (2005) Loss of Wolbachia infection during colonisation in the invasive Argentine ant Linepithema humile. Heredity 94:364–369
Rigaud T, Pennings PS, Juchault P (2001) Wolbachia bacteria effects after experimental interspecific transfers in terrestrial isopods. J Invertebr Pathol 77:251–257
Sameshima S, Hasegawa E, Kitade O, Minaka N, Matsumoto T (1999) Phylogenetic comparison of endosymbionts with their host ants based on molecular evidence. Zool Sci 16:993–1000
Sauer C, Stackebrandt E, Gadau J, Hölldobler B, Gross R (2000) Systematic relationships and cospeciation of bacterial endosymbionts and their carpenter ant host species: proposal of the new taxon Candidatus Blochmannia gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 5:1877–1886
Sauer C, Dudaczek D, Hölldobler B, Gross R (2002) Tissue localization of the endosymbiotic bacterium " Candidatus Blochmannia floridanus" in adults and larvae of the carpenter ant Camponotus floridanus. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4187–4193
Schröder D, Deppisch H, Obermayer M, Krohne G, Stackebrandt E, Holldobler B, Goebel W, Gross R (1996) Intracellular endosymbiotic bacteria of Camponotus species (carpenter ants): systematics, evolution and ultrastructural characterization. Mol Microbiol 21:479–489
Shigenobu S, Watanabe H, Hattori M, Sakaki Y, Ishikawa H (2000) Genome sequence of the endocellular bacterial symbiont of aphids Buchnera sp. APS. Nature 407:81–86
Shoemaker DD, Ross KG, Keller L, Vargo EL, Werren JH (2000) Wolbachia infections in native and introduced populations of fire ants (Solenopsis spp.). Insect Mol Biol 9:661–673
Stoll S (2005) Die Bakterien der spezifischen Darmflora in den Ameisengattungen Camponotus und Tetraponera. Diploma Thesis, University of Würzburg
Stouthamer R, Breeuwer JAJ, Hurst GDD (1999) Wolbachia pipientis: microbial manipulator of arthropod reproduction. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:71–102
Tamas I, Klasson L, Canback B, Naslund AK, Eriksson AS, Wernegreen JJ, Sandstrom JP, Moran NA, Andersson SG (2002) 50 million years of genomic stasis in endosymbiotic bacteria. Science 296:2376–2379
Van Borm S, Wenseleers T, Billen J, Boomsma JJ (2002a) Cloning and sequencing of wsp encoding gene fragments reveals a diversity of co-infecting Wolbachia strains in Acromyrmex leafcutter ants. Mol Phylogenet Evol 26:102–109
Van Borm S, Buschinger A, Boomsma JJ, Billen J (2002b) Tetraponera ants have gut symbionts related to nitrogen-fixing rood-nodule bacteria. Proc R Soc Lond B 269:2023–2027
Wenseleers T, Billen J (2000) No evidence for Wolbachia-induced parthenogenesis in the social Hymenoptera. J Evol Biol 13:277–280
Wenseleers T, Ito F, Van Borm S, Huybrechts R, Volckaert F, Billen J (1998) Widespread occurrence of the microorganism Wolbachia in ants. Proc R Soc Lond B 265:1447–1452
Wenseleers T, Sundström L, Billen J (2002) Deleterious Wolbachia in the ant Formica truncorum. Proc Biol Sci 269:623–629
Wernegreen JJ (2002) Genome evolution in bacterial endosymbionts of insects. Nat Rev Genet 3:850–861
Wolschin F, Hölldobler B, Gross R, Zientz E (2004) Replication of the endosymbiotic bacterium Blochmannia floridanus is correlated with the developmental and reproductive stages of its ant host. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4096–4102
Zientz E, Silva FJ, Gross R (2001) Genome interdependence in insect-bacterium symbioses. Genome Biol 2:REVIEWS1032
Zientz E, Dandekar T, Gross R (2004) Metabolic interdepence of obligate intracellular bacteria and their insect hosts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:745–770
Acknowledgements
We thank Dagmar Beier for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the DFG priority programme SFB567(C/2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zientz, E., Feldhaar, H., Stoll, S. et al. Insights into the microbial world associated with ants. Arch Microbiol 184, 199–206 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0041-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-005-0041-0