Abstract
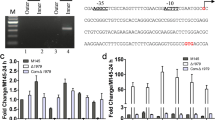
A spore pigment polyketide gene cluster, whiESa, was cloned from Streptomyces aureofaciens CCM3239 using a probe from the S. coelicolor A3(2) whiE gene cluster. Sequence analysis of a 4,657-bp DNA fragment revealed five open reading frames with the highest similarity to the S. coelicolor A3(2) whiE locus responsible for spore pigment biosynthesis, with conservation of the size and position of the genes. The whiESa gene cluster was disrupted by a homologous recombination in S. aureofaciens CCM3239, replacing the most important whiESaIII gene encoding ketosynthase with a thiostrepton resistance gene. The mutation affected spore pigmentation. In contrast to wild-type grey-pink spore pigmentation, the mutant produced white spores, although overall spore morphology was not affected. Transcriptional analysis of whiESa revealed two divergently oriented promoters, whiESap1 and whiESap2, upstream of the whiESaI and whiESaVIII genes, respectively. Both promoters were developmentally regulated in S. aureofaciens CCM3239. They were induced at the late stages of differentiation, during sporulation of aerial hyphae and were dependent upon early sporulation-specific sigma factor σRpoZ and putative transcription factor WhiB. The level of the transcript originating from the whiESap2 promoter was substantially reduced in a sigF mutant of S. aureofaciens CCM3239, indicating its dependence upon the late sporulation sigma factor σF. Comparison of the whiE promoters in three different spore pigment polyketide clusters revealed a highly conserved region upstream of the −35 promoter region that may bind a transcriptional regulator.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DO, Seidman JS, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bergh S, Uhlen M (1992) Analysis of a polyketide synthesis-encoding gene cluster of Streptomyces curacoi. Gene 117:131–136
Blanco G, Brian P, Pereda A, Mendez C, Salas JA, Chater KF (1992) Hybridization and DNA sequence analysis suggest an early evolutionary divergence of related biosynthetic gene sets encoding polyketide antibiotics and spore pigments in Streptomyces spp. Gene 130:107–116
Brown KL, Wood S, Buttner MJ (1992) Isolation and characterization of the major vegetative RNA polymerase of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2); renaturation of a sigma subunit using GroEL. Mol Microbiol 6:1133–1139
Chater KF (2000) Developmental decisions during sporulation in the aerial mycelium in Streptomyces. In: Brun YV, Shimkets LJ (eds) Prokaryotic development. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., pp 33–48
Davis NK, Chater KF (1990) Spore colour in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) involves the developmentally regulated synthesis of a compound biosynthetically related to polyketide antibiotics. Mol Microbiol 4:1679–1691
Hecker M, Schumann W, Volker U (1996) Heat-shock and general stress response in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 19:417–428
Hochschild A, Dove SL (1998) Protein–protein contacts that activate and repress prokaryotic transcription. Cell 92:597–600
Homerova D, Sevcikova B, Sprusansky O, Kormanec J (2000) Identification of DNA-binding proteins involved in regulation of expression of the Streptomyces aureofaciens sigF gene, encoding sporulation sigma factor σF. Microbiology 146:2919–2928
Hopwood DA (1997) Genetic contributions to understanding polyketide synthases. Chem Rev 97:2465–2497
Horinouchi S, Hara O, Beppu T (1983) Cloning of a pleiotropic gene that positively controls biosynthesis of A-factor, actinorhodin, and prodigiosin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 155:1238–1248
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sabaki Y, Hattori Y, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Kelemen GH, Brian P, Flardh K, Chamberlin L, Chater KF, Buttner MJ (1998) Developmental regulation of transcription of whiE, a locus specifying the polyketide spore pigment in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 180:2515–2521
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes, Norwich
Kormanec J (2001) Analyzing the developmental expression of sigma factors with S1-nuclease mapping. In: Chein CH (ed) Nuclease methods and protocols. Methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 481–494
Kormanec J, Farkasovsky M (1993) Differential expression of principal sigma factor homologues of Streptomyces aureofaciens correlates with developmental stage. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3647–3652
Kormanec J, Sevcikova B (2000) Identification and transcriptional analysis of a cold shock inducible gene, cspA, in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Gen Genet 264:251–256
Kormanec J, Sevcikova B (2002) The stress-response sigma factor σH controls the expression of ssgB, a homologue of the sporulation-specific cell division gene ssgA in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Genet Genomics 267:536–543
Kormanec J, Rezuchova B, Farkasovsky M (1993) Optimization of Streptomyces aureofaciens transformation and disruption of the hrdA gene encoding a homologue of the principal σ factor. J Gen Microbiol 139:2525–2529
Kormanec J, Potuckova L, Rezuchova B (1994) The Streptomyces aureofaciens homologue of the whiG encoding a putative sigma factor essential for sporulation. Gene 143:101–103
Kormanec J, Sevcikova B, Sprusansky O, Benada O, Kofronova O, Novakova R, Rezuchova B, Potuckova L, Homerova D (1998) The Streptomyces aureofaciens homologue of the whiB gene is essential for sporulation and its expression correlates with the developmental stage. Folia Microbiol 43:605–612
Kormanec J, Novakova R, Homerova D, Rezuchova B (2001) Streptomyces aureofaciens sporulation-specific sigma factor σrpoZ directs expression of a gene encoding protein similar to hydrolases involved in degradation of the lignin-related biphenyl compounds. Res Microbiol 152:883–888
Maxam AM, Gilbert W (1980) Sequencing end-labelled DNA with base specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol 65:449–560
Novakova R, Bistakova J, Homerova D, Rezuchova B, Kormanec J (2002) Cloning and characterization of a polyketide synthase gene cluster involved in biosynthesis of a proposed angucycline-like polyketide auricin in Streptomyces aureofaciens CCM 3239. Gene 297:197–208
Novakova R, Bistakova J, Homerova D, Rezuchova B, Feckova L, Kormanec J (2004) Cloning and characterization of a new polyketide synthase gene cluster in Streptomyces aureofaciens CCM 3239. DNA Seq (in press)
Potuckova L, Kelemen GH, Findlay KC, Lonetto MA, Buttner MJ, Kormanec J (1995) A new RNA polymerase sigma factor, σF, is required for the late stages of morphological differentiation in Streptomyces spp. Mol Microbiol 17:37–48
Rezuchova B, Barak I, Kormanec J (1997) Disruption of a sigma factor gene, sigF, affects an intermediate stage of spore pigment production in Streptomyces aureofaciens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:371–377
Wright F, Bibb MJ (1992) Codon usage in the G+C rich Streptomyces genome. Gene 113:55–65
Yu T-W, Hopwood DA (1995) Ectopic expression of the Streptomyces coelicolor whiE genes for polyketide spore pigment synthesis and their interaction with the act genes for actinorhodin biosynthesis. Microbiology 141:2779–2791
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank to Mrs Renata Knirschova for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grant 2/3010/23 from the Slovak Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novakova, R., Bistakova, J. & Kormanec, J. Characterization of the polyketide spore pigment cluster whiESa in Streptomyces aureofaciens CCM3239. Arch Microbiol 182, 388–395 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-004-0720-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-004-0720-2